Abstract
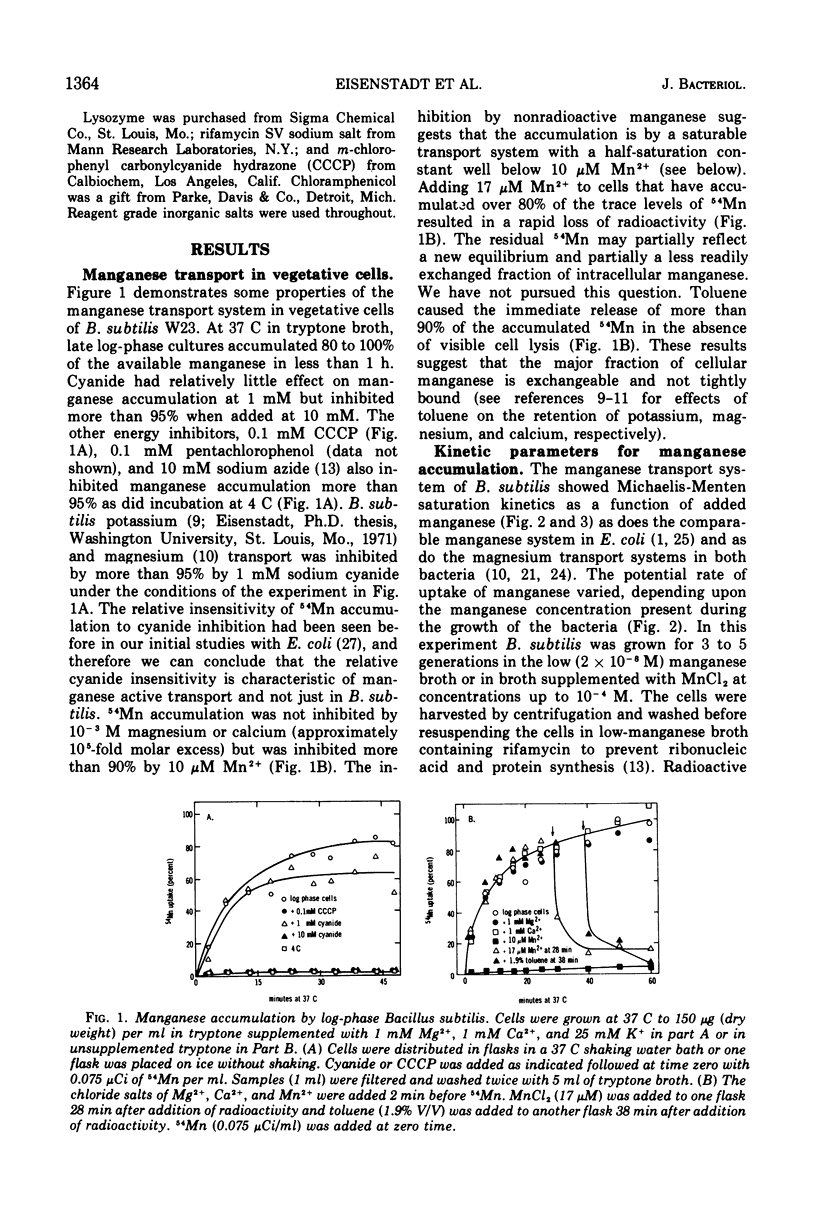
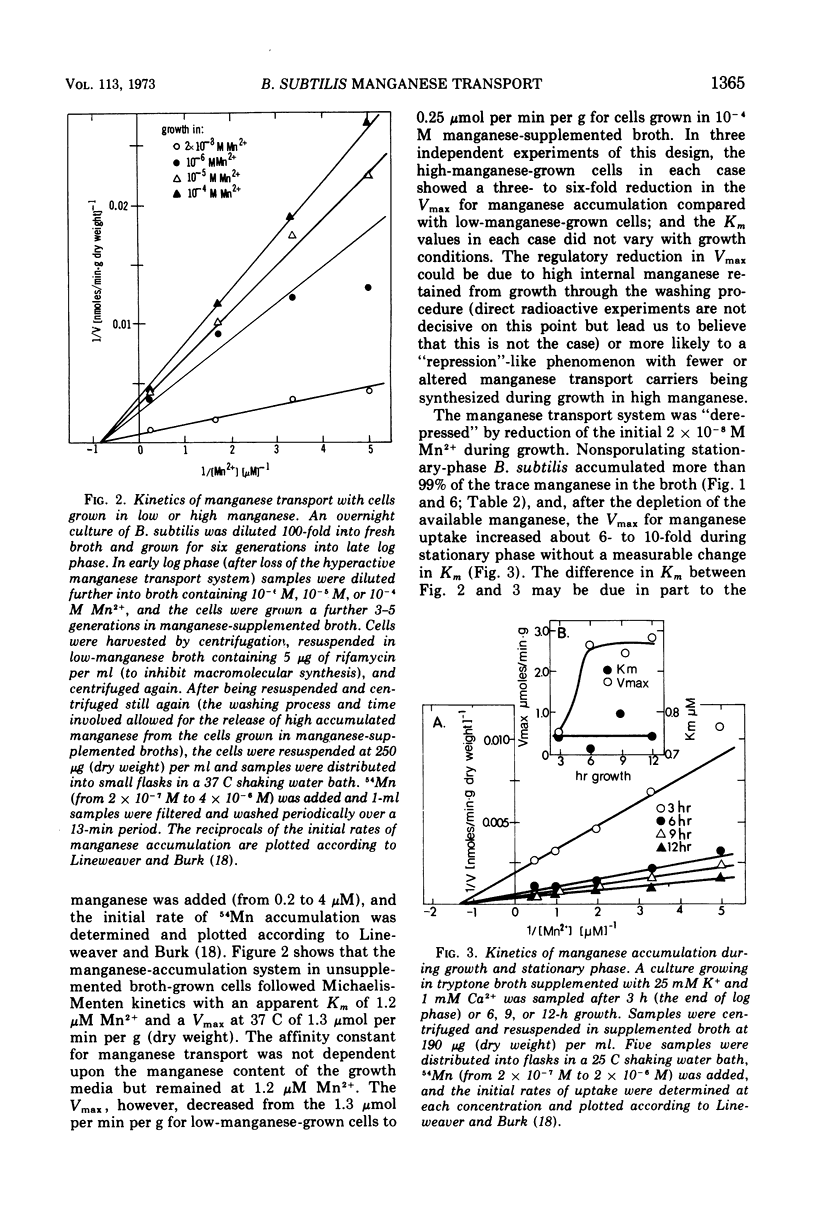
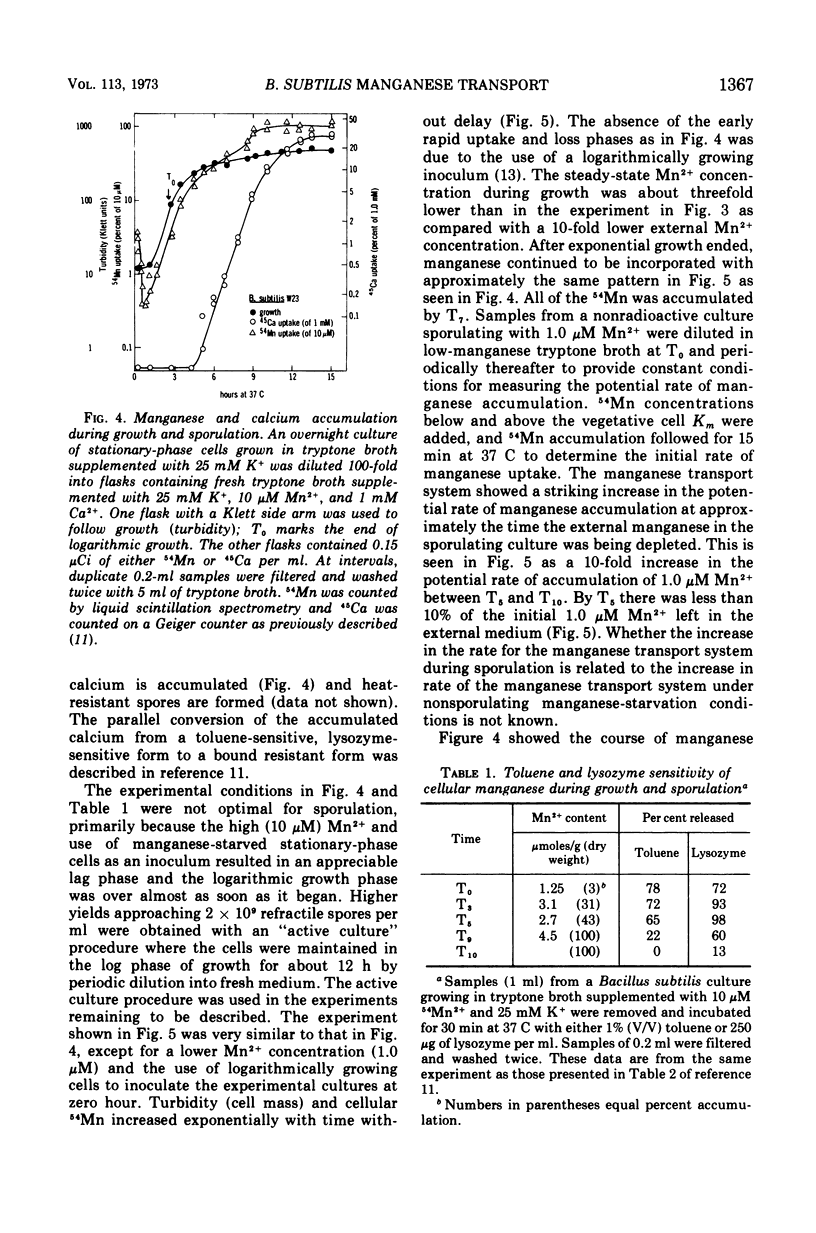
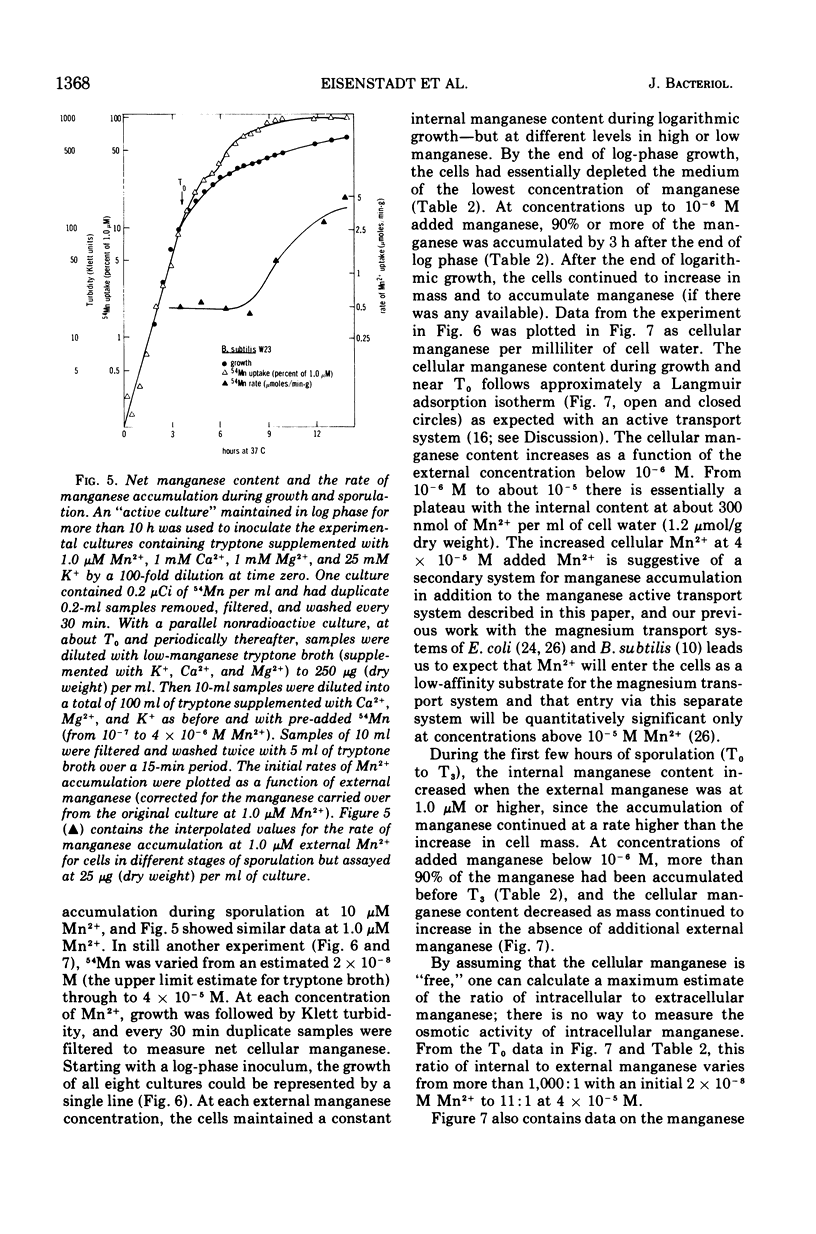
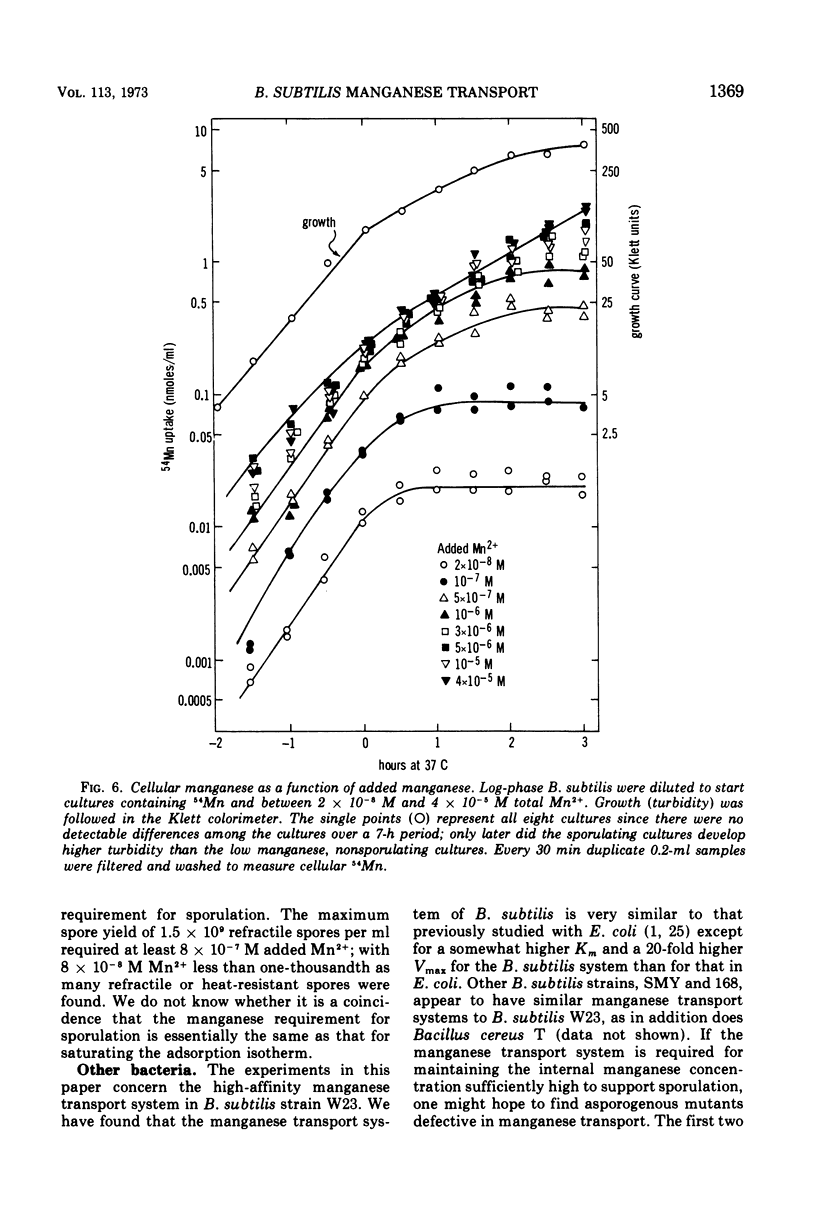
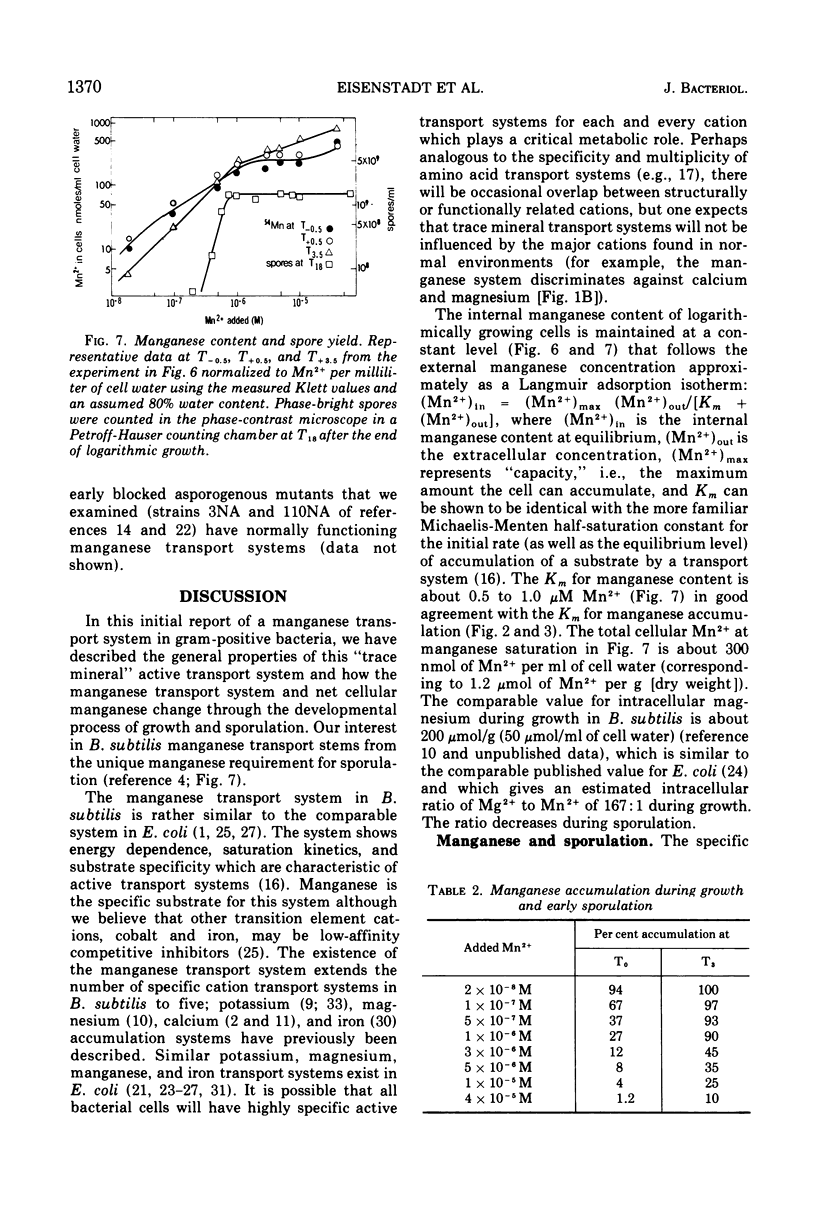
Manganese is accumulated in Bacillus subtilis by a highly specific active transport system. This trace element “pump” is insensitive to added magnesium or calcium and preferentially accumulates manganese in the presence of cobalt, iron, and copper. Manganese uptake in B. subtilis is inhibited by cyanide, azide, pentachlorophenol, and m-chlorophenyl carbonylcyanide hydrazone. The uptake of manganese follows Michaelis-Menten kinetics, and the net accumulation of manganese is regulated by increasing the Vmax after exposure to manganese-starvation conditions and by decreasing the Vmax for manganese uptake during growth in excess manganese. The Km remains constant during these regulatory changes in Vmax. Manganese accumulated during growth is exchangeable for exogenous manganese and can be released from the cells by toluene (which causes leakage but not lysis) or by lysis with lysozyme. Two stages can be distinguished with regard to intracellular manganese during the process of growth and sporulation. During logarithmic growth, B. subtilis maintains a relatively constant internal manganese content, which is a function of the external manganese concentration following approximately a Langmuir adsorption isotherm. At the end of log phase, net accumulation of manganese slows. A second phase of net manganese accumulation begins at about the same time during sporulation as the accumulation of calcium begins. The manganese accumulated during growth and early sporulation is exchangeable and therefore relatively “free”; intracellular manganese is converted later during sporulation into a bound form that cannot be released by toluene or lysozyme.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhattacharyya P. Active Transport of Manganese in Isolated Membranes of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1307–1311. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1307-1311.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAMBERLIN M., BERG P. Deoxyribo ucleic acid-directed synthesis of ribonucleic acid by an enzyme from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Jan 15;48:81–94. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHARNEY J., FISHER W. P., HEGARTY C. P. Managanese as an essential element for sporulation in the genus Bacillus. J Bacteriol. 1951 Aug;62(2):145–148. doi: 10.1128/jb.62.2.145-148.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuel T. F. Bacillus subtilis glutamine synthetase. Specific catalytic changes associated with limited sulfhydryl modification. J Biol Chem. 1971 Feb 10;246(3):599–605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuel T. F., Stadtman E. R. Some kinetic properties of Bacillus subtilis glutamine synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1970 Oct 25;245(20):5206–5213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstadt E. Potassium content during growth and sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):264–267. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.264-267.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher S., Buxbaum L., Toth K., Eisenstadt E., Silver S. Regulation of manganese accumulation and exchange in Bacillus subtilis W23. J Bacteriol. 1973 Mar;113(3):1373–1380. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.3.1373-1380.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUYBERS K. Cationic reversion of induced phage development in Bacillus megatherium. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1953 Jan;84(1):242–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUBIN M., ENNIS H. L. ON THE ROLE OF INTRACELLULAR POTASSIUM IN PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Apr 27;80:614–631. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(64)90306-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUBIN M. INTRACELLULAR POTASSIUM AND CONTROL OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. Fed Proc. 1964 Sep-Oct;23:994–1001. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin E. C. The genetics of bacterial transport systems. Annu Rev Genet. 1970;4:225–262. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.04.120170.001301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel J. F., Piechaud M., Schaeffer P. Constituvité vis-a-vis du nitrate de la nitrate-réductase chez les mutants asporogènes précoces de bacillus subtilis. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1970 Dec;119(6):711–718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. L., Kennedy E. P. Transport of magnesium by a repressible and a nonrepressible system in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 May;69(5):1091–1093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.5.1091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHULTZ S. G., SOLOMON A. K. Cation transport in Escherichia coli. I. Intracellular Na and K concentrations and net cation movement. J Gen Physiol. 1961 Nov;45:355–369. doi: 10.1085/jgp.45.2.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver S., Clark D. Magnesium transport in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1971 Feb 10;246(3):569–576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver S., Johnseine P., King K. Manganese Active Transport in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1299–1306. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1299-1306.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver S., Johnseine P., Whitney E., Clark D. Manganese-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli: physiological and genetic studies. J Bacteriol. 1972 Apr;110(1):186–195. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.1.186-195.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver S., Kralovic M. L. Manganese accumulation by Escherichia coli: evidence for a specific transport system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Mar 10;34(5):640–645. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90786-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuominen F. W., Bernlohr R. W. Pyruvate kinase of the spore-forming bacterium, Bacillus licheniformis. II. Kinetic properties. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1746–1755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh B. L., Warren R. A. The iron-uptake system of Bacillus subtilis. Can J Microbiol. 1971 Feb;17(2):175–177. doi: 10.1139/m71-030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. C., Newton A. Iron transport in Escherichia coli: roles of energy-dependent uptake and 2,3-dihydroxybenzoylserine. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):1142–1150. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.1142-1150.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willis D. B., Ennis H. L. Ribonucleic acid and protein synthesis in a mutant of Bacillus subtilis defective in potassium retention. J Bacteriol. 1968 Dec;96(6):2035–2042. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.6.2035-2042.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


