Abstract
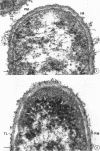
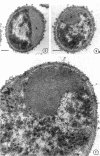
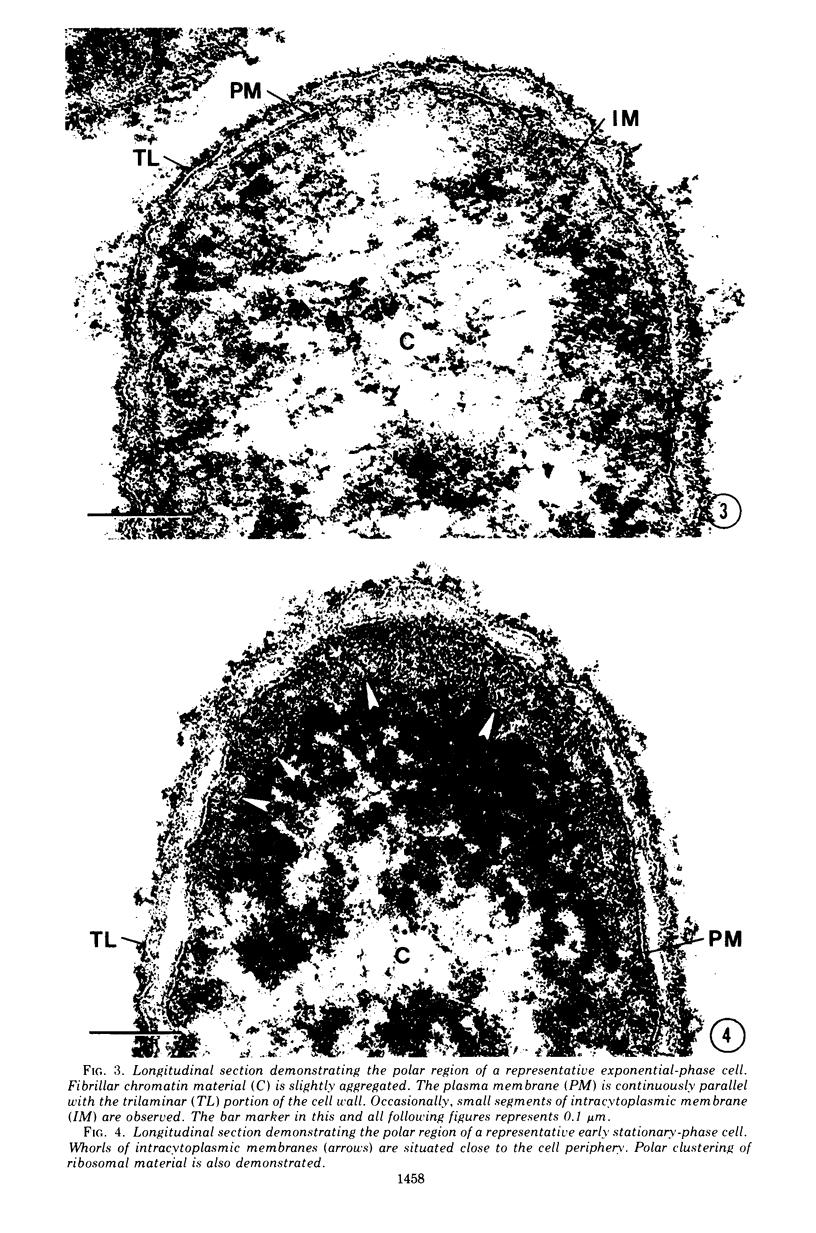
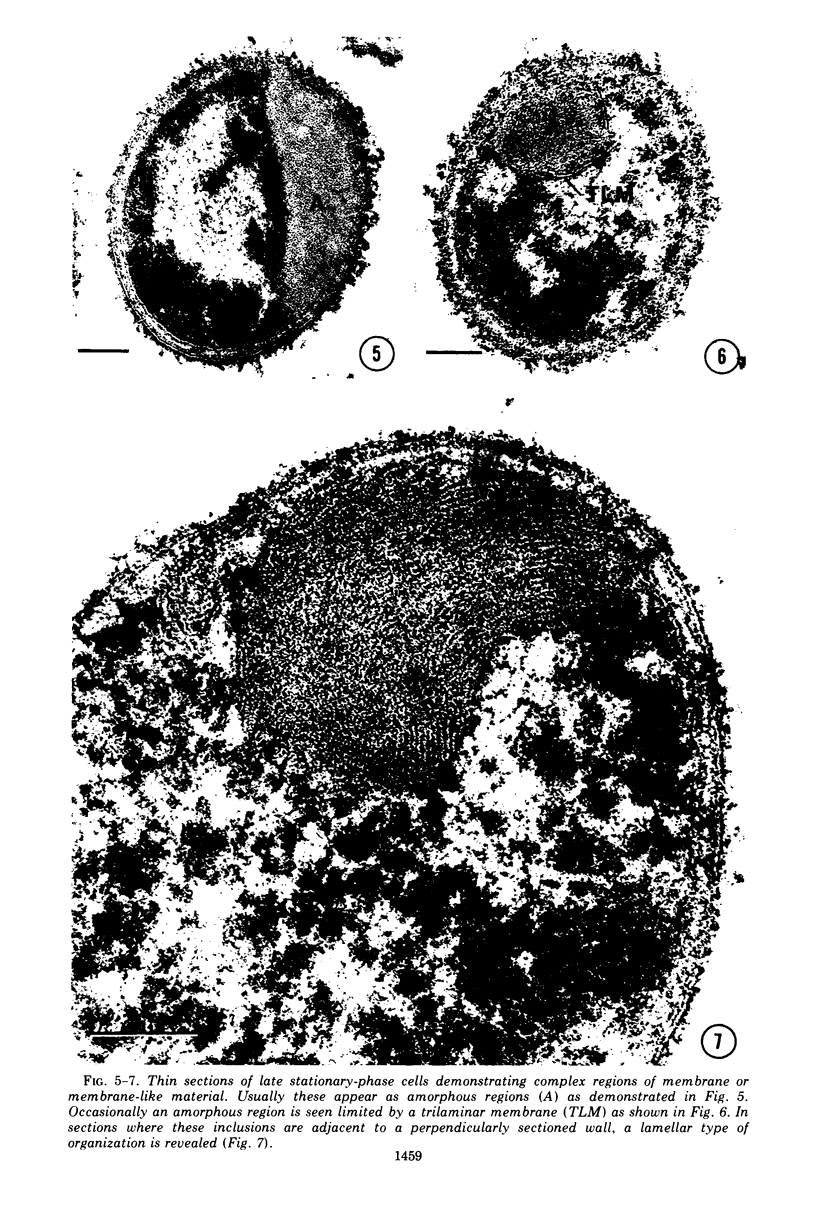
Cytological differences were observed between stationary- and exponentialphase cells of Acetobacter suboxydans grown in a defined medium. Unstained cells observed with the light microscope just after entering the stationary phase differed from exponentially growing cells in that the former exhibited localized increases in density, particularly in the polar regions. Electron microscopy of thin sections revealed that early stationary-phase cells possessed predominantly polar complexes of intracytoplasmic membranes accompanied by polar increases in ribosomal material. When cultures were allowed to continue far into the stationary phase, cells contained extensive aggregations of membrane-like material as the predominant fine-structural feature. In contrast, thin sections of exponentially growing cells exhibited only occasional indications of intracytoplasmic membranes. Intracytoplasmic membranes heretofore have been observed only rarely in the heterotrophic Pseudomonadales.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CLAUS G. W., ROTH L. E. FINE STRUCTURE OF THE GRAM-NEGATIVE BACTERIUM ACETOBACTER SUBOXYDANS. J Cell Biol. 1964 Feb;20:217–233. doi: 10.1083/jcb.20.2.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrick L., Jr, Berk R. S. Membranous inclusions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1971 Apr;106(1):250–256. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.1.250-256.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen-Bazire G., Kunisawa R., Poindexter J. S. The internal membranes of Caulobacter crescentus. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Feb;42(2):301–308. doi: 10.1099/00221287-42-2-301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies S. L., Whittenbury R. Fine structure of methane and other hydrocarbon-utilizing bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 May;61(2):227–232. doi: 10.1099/00221287-61-2-227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Boer W. E., Hazeu W. Observations on the fine structure of a methane-oxidizing bacterium. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1972;38(1):33–47. doi: 10.1007/BF02328075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLT S. C., MARR A. G. LOCATION OF CHLOROPHYLL IN RHODOSPIRILLUM RUBRUM. J Bacteriol. 1965 May;89:1402–1412. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.5.1402-1412.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt S. C., Trüper H. G., Takács B. J. Fine structure of Ectothiorhodospira mobilis strain 8113 thylakoids: chemical fixation and freeze-etching studies. Arch Mikrobiol. 1968;62(2):111–128. doi: 10.1007/BF00410398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLENBERGER E., RYTER A., SECHAUD J. Electron microscope study of DNA-containing plasms. II. Vegetative and mature phage DNA as compared with normal bacterial nucleoids in different physiological states. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Nov 25;4(6):671–678. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.6.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KING T. E., CHELDELIN V. H. Sources of energy and the dinitrophenol effect in the growth of Acetobacter suboxydans. J Bacteriol. 1953 Nov;66(5):581–584. doi: 10.1128/jb.66.5.581-584.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KITOS P. A., WANG C. H., MOHLER B. A., KING T. E., CHELDELIN V. H. Glucose and gluconate dissimilation in Acetobacter suboxydans. J Biol Chem. 1958 Dec;233(6):1295–1298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURRAY R. G., WATSON S. W. STRUCTURE OF NITROSOCYSTIS OCEANUS AND COMPARISON WITH NITROSOMONAS AND NITROBACTER. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jun;89:1594–1609. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.6.1594-1609.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallette M. F. A pH 7 buffer devoid of nitrogen, sulfur, and phosphorus for use in bacteriological systems. J Bacteriol. 1967 Aug;94(2):283–290. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.2.283-290.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remsen C. C., Valois F. W., Watson S. W. Fine structure of the cytomembranes of Nitrosocystis oceanus. J Bacteriol. 1967 Aug;94(2):422–433. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.2.422-433.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remsen C. C., Watson S. W., Waterbury J. B., Trüper H. G. Fine structure of Ectothiorhodospira mobilis Pelsh. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2374–2392. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2374-2392.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shively J. M., Decker G. L., Greenawalt J. W. Comparative ultrastructure of the thiobacilli. J Bacteriol. 1970 Feb;101(2):618–627. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.2.618-627.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurr A. R. A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Jan;26(1):31–43. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien H. C., Lambert R., Laudelout H. Fine structure and the localization of the nitrite oxidizing system in Nitrobacter winogradskyi. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1968;34(4):483–494. doi: 10.1007/BF02046470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VENABLE J. H., COGGESHALL R. A SIMPLIFIED LEAD CITRATE STAIN FOR USE IN ELECTRON MICROSCOPY. J Cell Biol. 1965 May;25:407–408. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.2.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiebe W. J., Chapman G. B. Variation in the fine structure of a marine achromobacter and a marine pseudomonad grown under selected nutritional and temperature regimes. J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1874–1886. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1874-1886.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Gool A. P., Lambert R., Laudelout H. The fine structure of frozen etched nitrobacter cells. Arch Mikrobiol. 1969;69(4):281–293. doi: 10.1007/BF00408570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]