Abstract
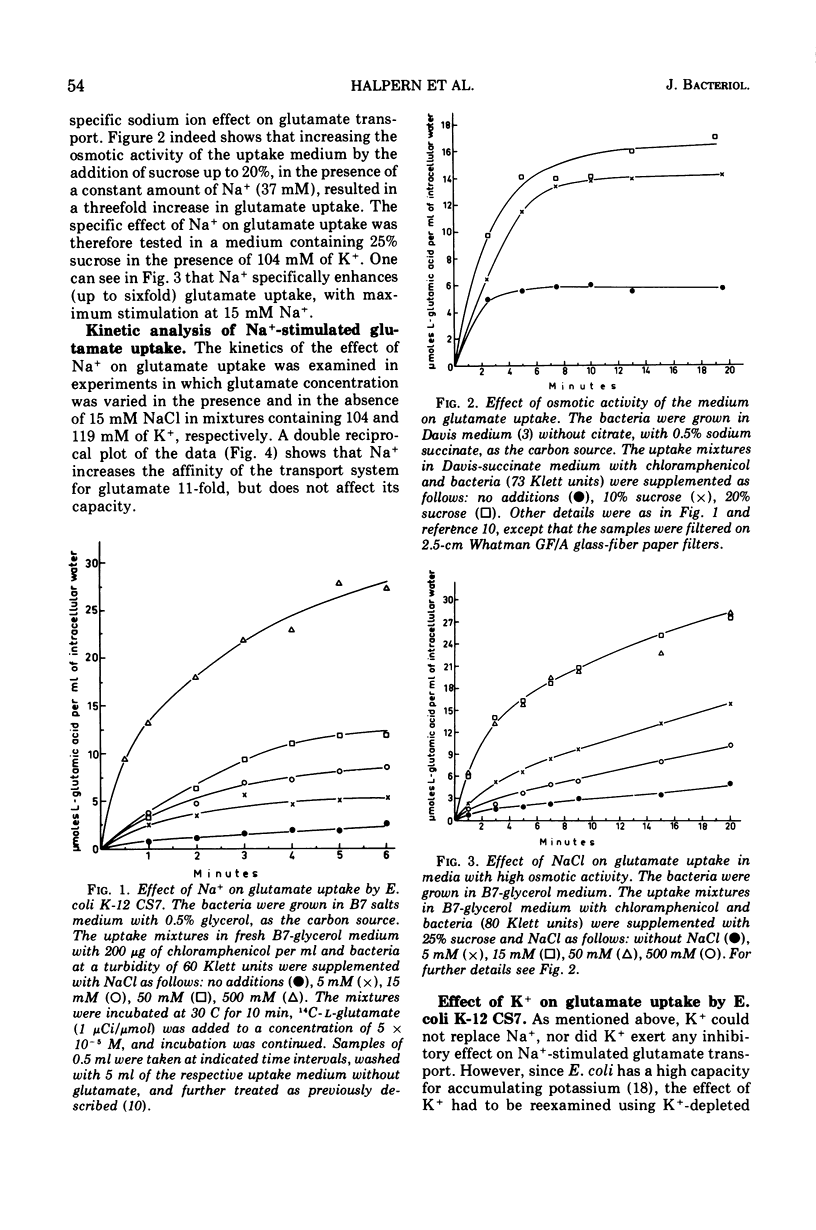
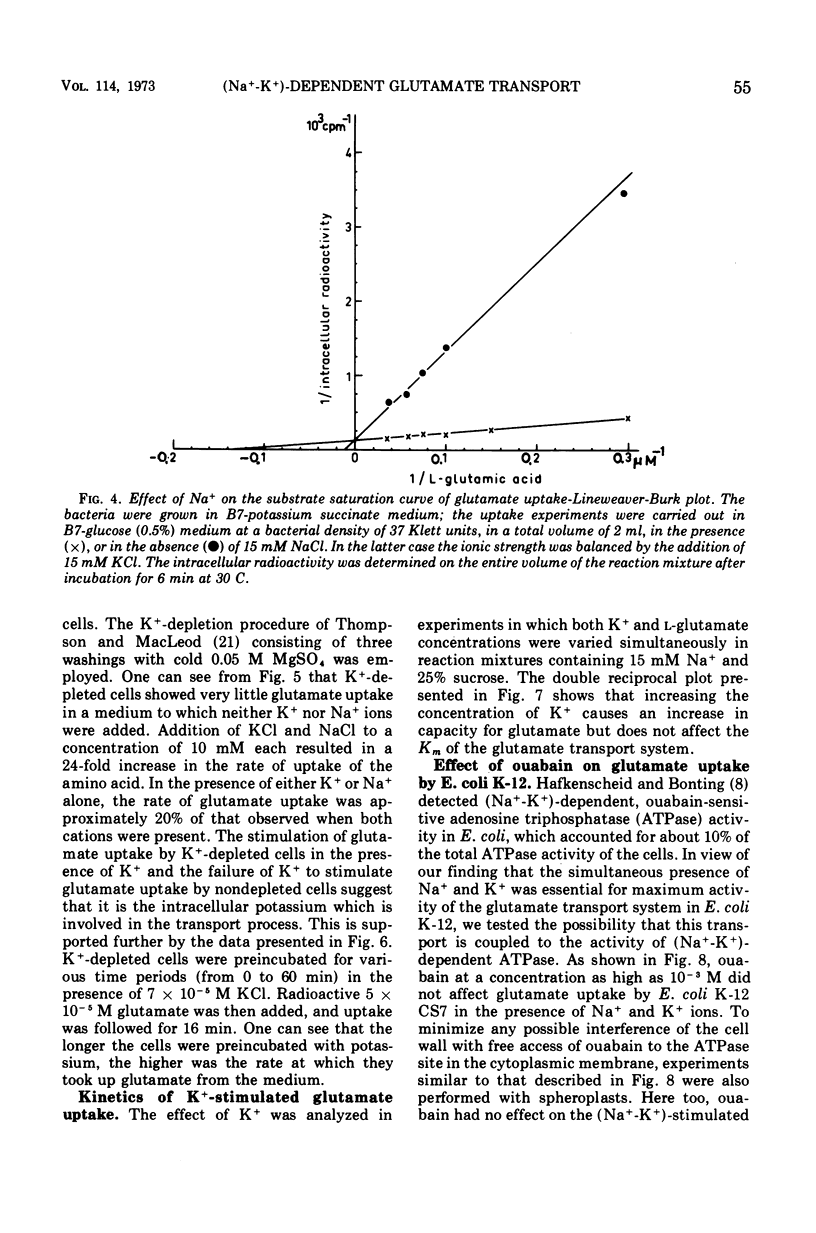
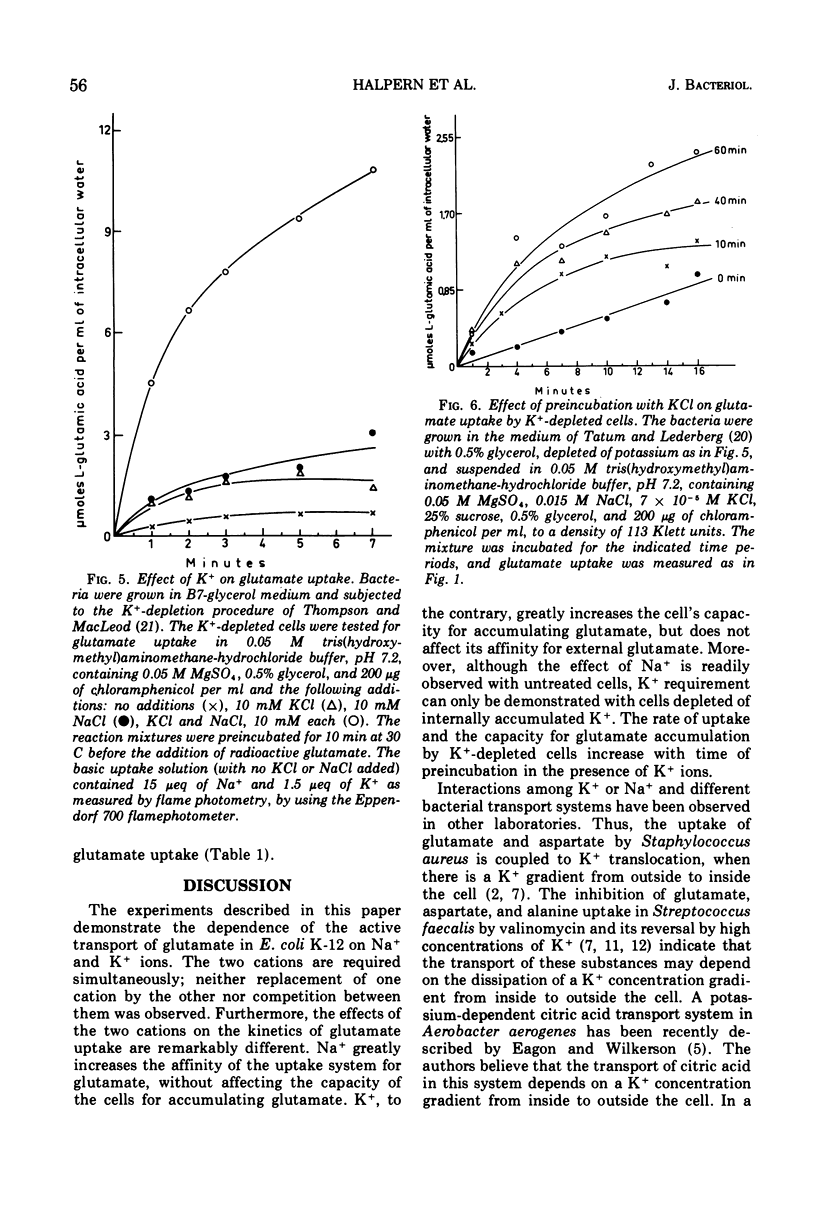
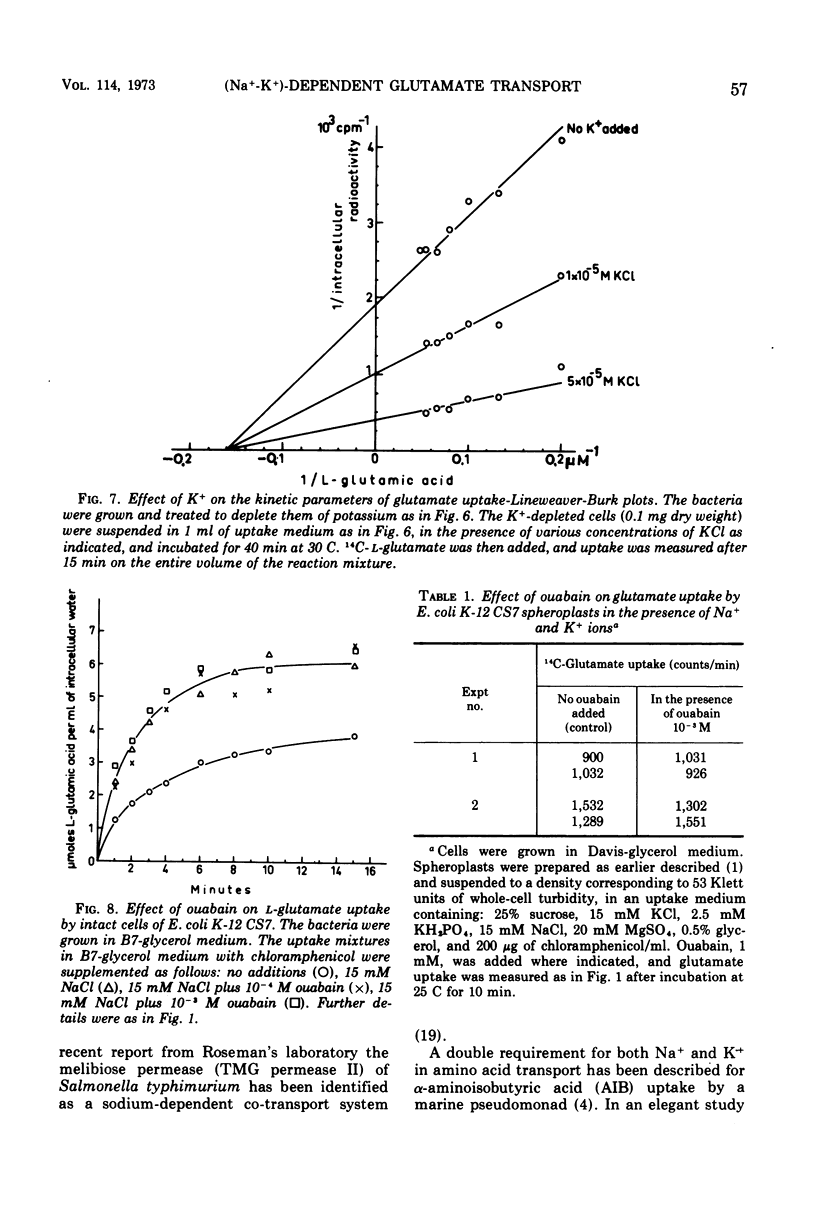
Active transport of glutamate by Escherichia coli K-12 requires both Na+ and K+ ions. Increasing the concentration of Na+ in the medium results in a decrease in the Km of the uptake system for glutamate; the capacity is not affected. Glutamate uptake by untreated cells is not stimulated by K+. K+-depleted cells show a greatly reduced capacity for glutamate uptake. Preincubation of such cells in the presence of K+ fully restores their capacity for glutamate uptake when Na+ ions are also present in the uptake medium. Addition of either K+ or Na+ alone restores glutamate uptake to only about 20% of its maximum capacity in the presence of both cations. Changes in K+ concentration affect the capacity for glutamate uptake but have no effect on the Km of the glutamate transport system. Ouabain does not inhibit the (Na+-K+)-stimulated glutamate uptake by intact cells or spheroplasts of E. coli K-12.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barash H., Halpern Y. S. Glutamate-binding protein and its relation to glutamate transport in Escherichia coli K-12. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Nov 5;45(3):681–688. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90470-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIES R., FOLKES J. P., GALE E. F., BIGGER L. C. The assimilation of amino-acids by micro-organisms. XVI. Changes in sodium and potassium accompanying the accumulation of glutamic acid or lysine by bacteria and yeast. Biochem J. 1953 Jun;54(3):430–437. doi: 10.1042/bj0540430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. D., MINGIOLI E. S. Mutants of Escherichia coli requiring methionine or vitamin B12. J Bacteriol. 1950 Jul;60(1):17–28. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.1.17-28.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapeau G. R., Matula T. I., MacLeod R. A. Nutrition and metabolism of marine bacteria. XV. Relation of Na+-activated transport to the Na+ requirement of a marine pseudomonad for growth. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jul;92(1):63–71. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.1.63-71.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eagon R. G., Wilkerson L. S. A potassium-dependent citric acid transport system in Aerobacter aerogenes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Mar 10;46(5):1944–1950. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90074-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank L., Hopkins I. Sodium-stimulated transport of glutamate in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):329–336. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.329-336.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gale E. F. 'Don't talk to me about permeability'. The tenth Marjory Stephenson memorial lecture. J Gen Microbiol. 1971 Sep;68(1):1–14. doi: 10.1099/00221287-68-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafkenscheid J. C., Bonting S. L. Studies on (Na+-K+)-activated ATPase. XIX. Occurrence and properties of a (Na+-K+)-activated ATPase in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jan 8;151(1):204–211. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(68)90175-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halpern Y. S., Even-Shoshan A. Properties of the glutamate transport system in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Mar;93(3):1009–1016. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.3.1009-1016.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halpern Y. S., Lupo M. Glutamate transport in wild-type and mutant strains of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1965 Nov;90(5):1288–1295. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.5.1288-1295.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M., Baarda J. R. Gramicidin, valinomycin, and cation permeability of Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):53–60. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.1.53-60.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M., Pavlasová E., Baarda J. R. A transmembrane pH gradient in Streptococcus faecalis: origin, and dissipation by proton conductors and N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodimide. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970;196(2):235–244. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KESSEL D., LUBIN M. STABILITY OF ALPHA-HYDROGEN OF AMINO ACIDS DURING ACTIVE TRANSPORT. Biochemistry. 1965 Mar;4:561–565. doi: 10.1021/bi00879a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus M., Halpern Y. S. Genetic analysis of glutamate transport and glutamate decarboxylase in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(4):1409–1415. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.4.1409-1415.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus M., Halpern Y. S. Genetic analysis of the glutamate permease in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1118–1128. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1118-1128.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REPASKE R. Lysis of gram-negative bacteria by lysozyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1956 Oct;22(1):189–191. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(56)90240-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHULTZ S. G., SOLOMON A. K. Cation transport in Escherichia coli. I. Intracellular Na and K concentrations and net cation movement. J Gen Physiol. 1961 Nov;45:355–369. doi: 10.1085/jgp.45.2.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz S. G., Curran P. F. Coupled transport of sodium and organic solutes. Physiol Rev. 1970 Oct;50(4):637–718. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1970.50.4.637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J., Roseman S. A sodium-dependent sugar co-transport system in bacteria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jul 2;44(1):132–138. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(71)80168-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatum E. L., Lederberg J. Gene Recombination in the Bacterium Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1947 Jun;53(6):673–684. doi: 10.1128/jb.53.6.673-684.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., MacLeod R. A. Functions of Na+ and K+ in the active transport of -aminoisobutyric acid in a marine pseudomonad. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jun 25;246(12):4066–4074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. T., Thompson J., MacLeod R. A. Nutrition and metabolism of marine bacteria. XVII. Ion-dependent retention of alpha-aminoisobutyric acid and its relation to Na+ dependent transport in a marine pseudomonad. J Biol Chem. 1969 Feb 10;244(3):1016–1025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


