Abstract
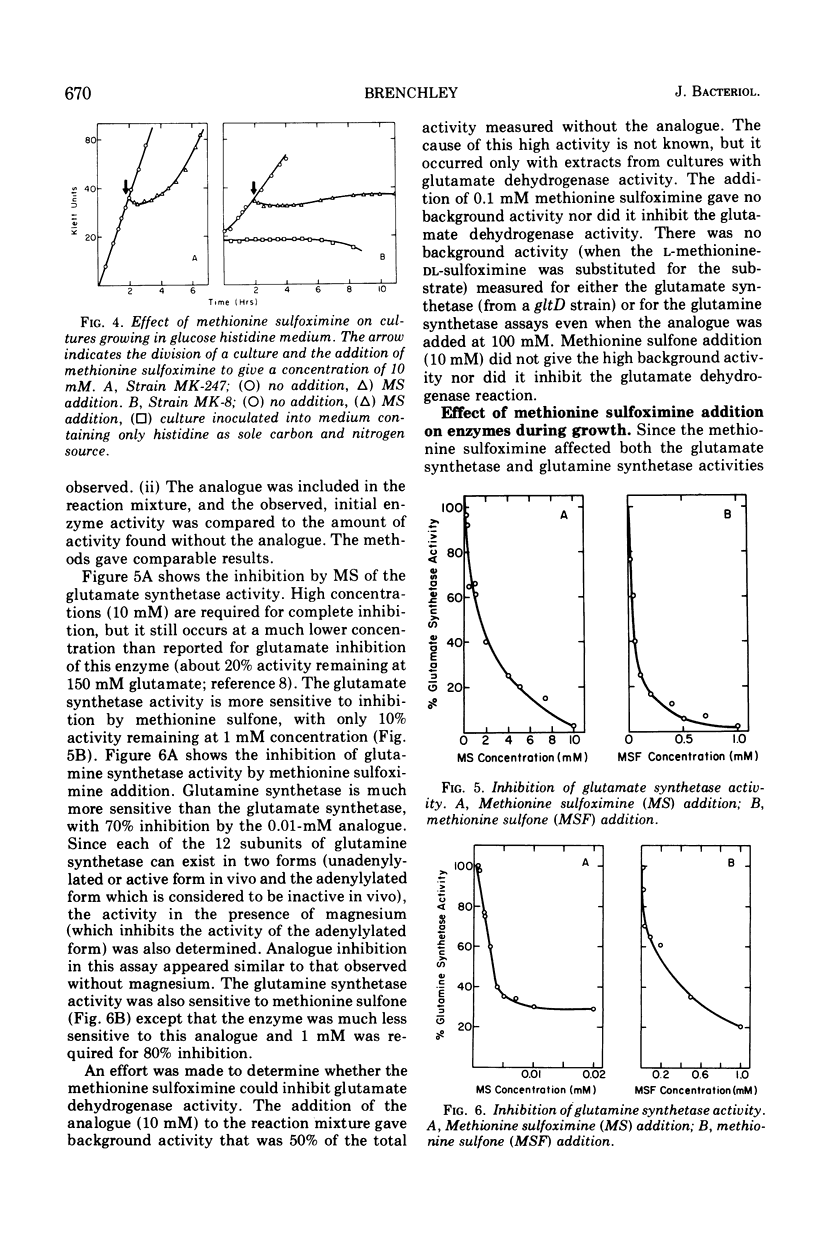
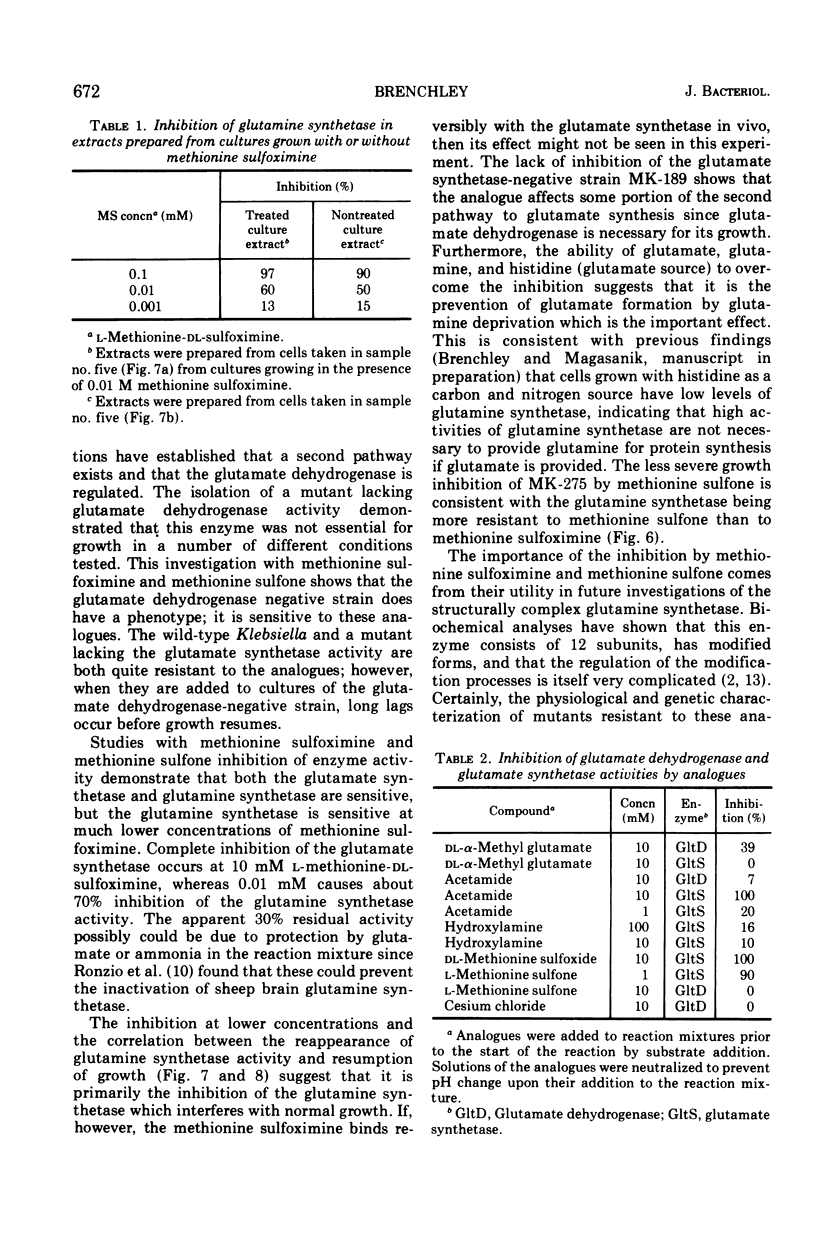
At least two pathways exist in Klebsiella aerogenes for glutamate synthesis. A mutant blocked in one pathway due to the loss of glutamate dehydrogenase (gltD) does not require glutamate and has the same growth characteristics as the parent strain in most media; however, its growth is inhibited by the analogues methionine sulfoximine and methionine sulfone. Wild-type Klebsiella is resistant to 0.1 M methionine sulfoximine or methionine sulfone, whereas the gltD mutant is sensitive to 1 mM concentrations. Either glutamate or glutamine is effective in overcoming this inhibition. Activities of both glutamine synthetase and glutamate synthetase, two enzymes involved in the second pathway of glutamate synthesis, are inhibited by methionine sulfoximine and methionine sulfone. The primary effect of methionine sulfoximine appears to be the prevention of glutamine production necessary for subsequent glutamate synthesis via glutamate synthetase enzyme.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brill W. J., Magasanik B. Genetic and metabolic control of histidase and urocanase in Salmonella typhimurium, strain 15-59. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 10;244(19):5392–5402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Segal A., Stadtman E. R. Modulation of glutamine synthetase adenylylation and deadenylylation is mediated by metabolic transformation of the P II -regulatory protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):2949–2953. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.2949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEATHCOTE J. G., PACE J. Inhibition of the growth of Leuconostoc mesenteroides by the toxic factor from "agenized" zein: reversal by l-glutamine. Nature. 1950 Aug 26;166(4217):353–354. doi: 10.1038/166353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hrebícek J., Kolousek J., Wiederman M., Charamza O. Changes of the incorporation of [75 Se]methionine and of the electrical activity in various brain structures of the cat after administration of methionine sulphoximine. Brain Res. 1971 Apr 16;28(1):109–117. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90528-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacPhee D. G., Sutherland I. W., Wilkinson J. F. Transduction in Klebsiella. Nature. 1969 Feb 1;221(5179):475–476. doi: 10.1038/221475a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning J. M., Moore S., Rowe W. B., Meister A. Identification of L-methionine S-sulfoximine as the diastereoisomer of L-methionine SR-sulfoximine that inhibits glutamine synthetase. Biochemistry. 1969 Jun;8(6):2681–2685. doi: 10.1021/bi00834a066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meers J. L., Tempest D. W., Brown C. M. 'Glutamine(amide):2-oxoglutarate amino transferase oxido-reductase (NADP); an enzyme involved in the synthesis of glutamate by some bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Dec;64(2):187–194. doi: 10.1099/00221287-64-2-187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PACE J., McDERMOTT E. E. Methionine sulphoximine and some enzyme systems in volving glutamine. Nature. 1952 Mar 8;169(4297):415–416. doi: 10.1038/169415a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronzio R. A., Rowe W. B., Meister A. Studies on the mechanism of inhibition of glutamine synthetase by methionine sulfoximine. Biochemistry. 1969 Mar;8(3):1066–1075. doi: 10.1021/bi00831a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. B., Meister A. Identification of L-methionine-S-sulfoximine as the convulsant isomer of methionine sulfoximine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jun;66(2):500–506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.2.500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. B., Ronzio R. A., Meister A. Inhibition of glutamine synthetase by methionine sulfoximine. Studies on methionine sulfoximine phosphate. Biochemistry. 1969 Jun;8(6):2674–2680. doi: 10.1021/bi00834a065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro B. M., Stadtman E. R. The regulation of glutamine synthesis in microorganisms. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1970;24:501–524. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.24.100170.002441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadtman E. R., Ginsburg A., Ciardi J. E., Yeh J., Hennig S. B., Shapiro B. M. Multiple molecular forms of glutamine synthetase produced by enzyme catalyzed adenylation and deadenylylation reactions. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1970;8:99–118. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(70)90011-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


