Abstract
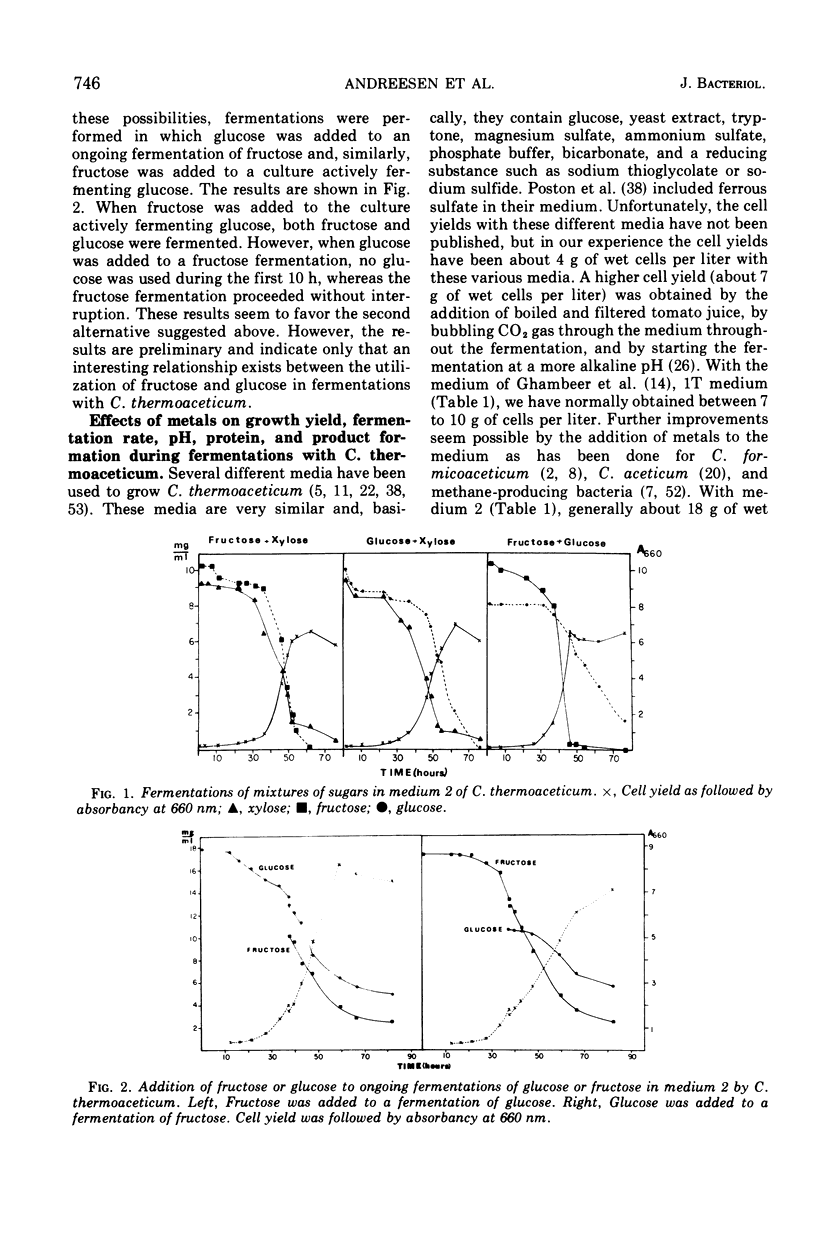
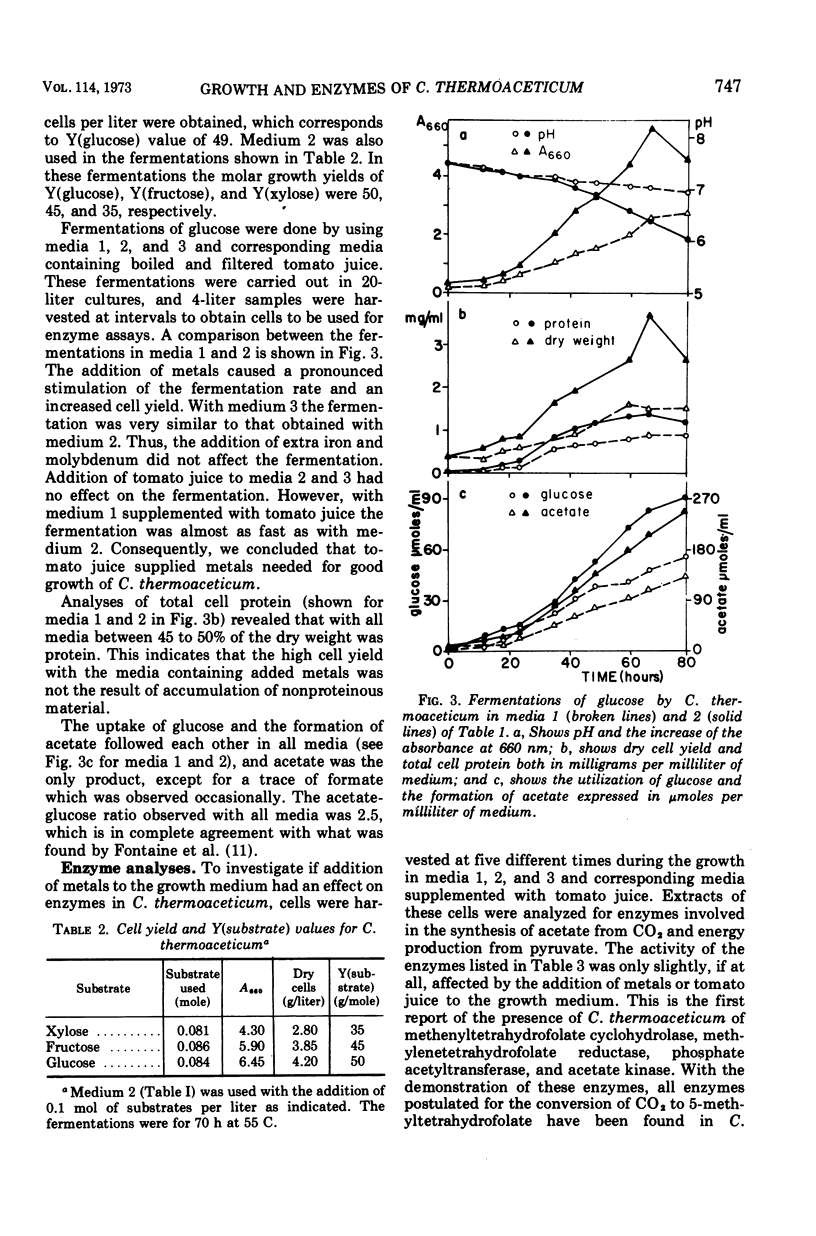
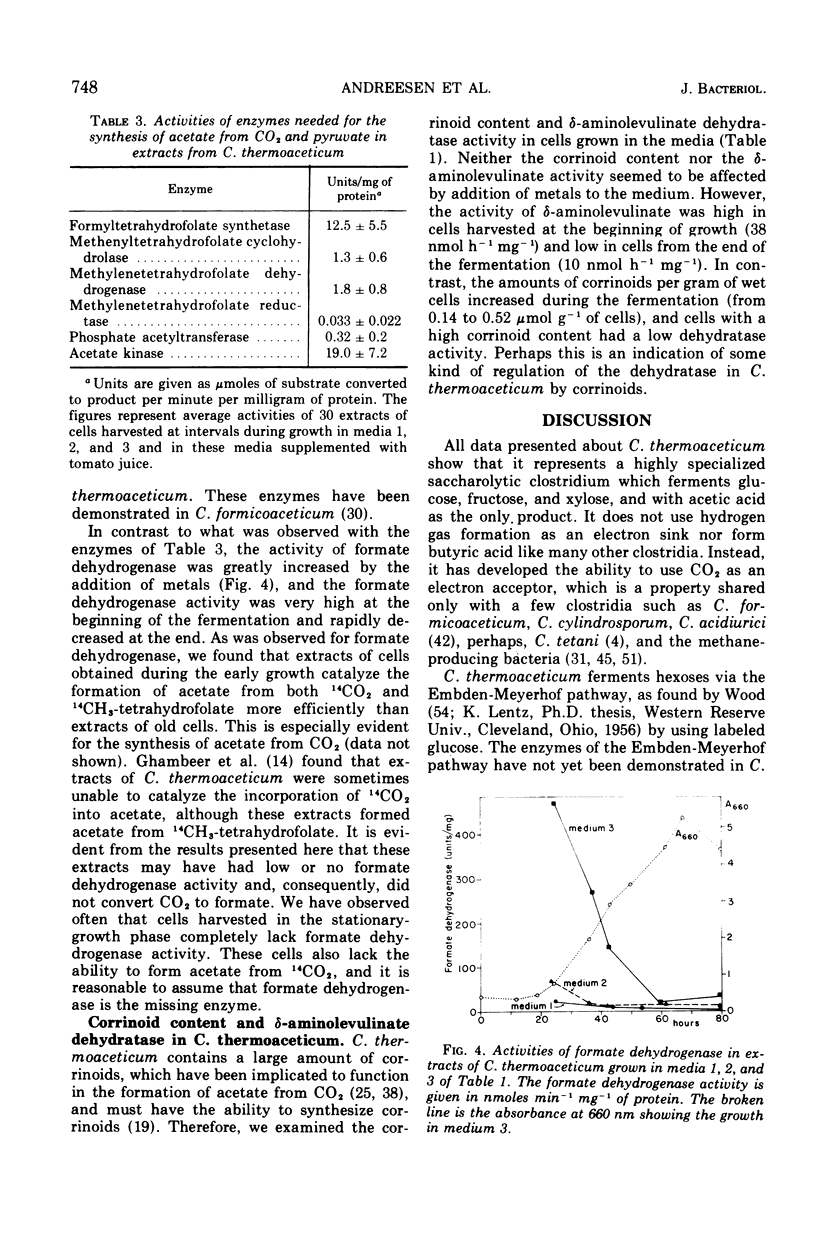
Clostridium thermoaceticum ferments xylose, fructose, and glucose with acetate as the only product. In fermentations with mixtures of the sugars, xylose is first fermented, then fructose, and last, glucose. Fructose inhibits the fermentation of glucose, and this inhibition appears to be due to a repression of the synthesis of an enzyme needed for glucose utilization. Addition of metals to the culture medium increases the cell yield drastically from about 7 to 18 g per liter, and Y(glucose) values between 40 and 50 are obtained. According to the postulated pathways of the fermentation of glucose and synthesis of acetate from CO2 by C. thermoaceticum, 3 mol of ATP are available as energy for growth. Thus a Y(adenosine 5′-triphosphate) of 13 to 16 is obtained. Because the normal Y(ATP) value is 10.5, this could mean that an additional source of ATP is available by an unknown mechanism. The addition of metals also increases the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-dependent formate dehydrogenase activity, the overall reaction (14CO2 → acetate), and the incorporation of the methyl group of 5-methyltetrahydrofolate into acetate. These reactions are catalyzed very efficiently by cells harvested in early growth, whereas cells obtained at the end of a fermentation have very low formate dehydrogenase activity and capacity to incorporate CO2 into acetate. The following enzymes involved in the synthesis of acetate from CO2 and in the metabolism of pyruvate are present in extracts of C. thermoaceticum: 10-formyltetrahydrofolate synthetase, 5,10-methenyltetrahydrofolate cyclohydrolase, 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase, 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase, phosphate acetyltransferase, and acetate kinase. These enzymes are not or are very little affected by the addition of metals to the growth medium.
The amount of corrinoids in cells from early growth is low, whereas it is high in cells harvested late in growth. The opposite is found for the activity of δ-aminolevulinate dehydratase, which is high at the beginning of growth and low at the end.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLEN S. H., KELLERMEYER R. W., STJERNHOLM R. L., WOOD H. G. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF ENZYMES INVOLVED IN THE PROPIONIC ACID FERMENTATION. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jan;87:171–187. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.1.171-187.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreesen J. R., Gottschalk G., Schlegel H. G. Clostridium formicoaceticum nov. spec. isolation, description and distinction from C. aceticum and C. thermoaceticum. Arch Mikrobiol. 1970;72(2):154–174. doi: 10.1007/BF00409521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAUCHOP T., ELSDEN S. R. The growth of micro-organisms in relation to their energy supply. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Dec;23:457–469. doi: 10.1099/00221287-23-3-457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker H. A., Kamen M. D. Carbon Dioxide Utilization in the Synthesis of Acetic Acid by Clostridium Thermoaceticum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1945 Aug;31(8):219–225. doi: 10.1073/pnas.31.8.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enoch H. G., Lester R. L. Effects of molybdate, tungstate, and selenium compounds on formate dehydrogenase and other enzyme systems in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jun;110(3):1032–1040. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.3.1032-1040.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontaine F. E., Peterson W. H., McCoy E., Johnson M. J., Ritter G. J. A New Type of Glucose Fermentation by Clostridium thermoaceticum. J Bacteriol. 1942 Jun;43(6):701–715. doi: 10.1128/jb.43.6.701-715.1942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuyama T., Ordal E. J. Induced Biosynthesis of Formic Hydrogenlyase in Iron-Deficient Cells of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1965 Sep;90(3):673–680. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.3.673-680.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghambeer R. K., Wood H. G., Schulman M., Ljungdahl L. Total synthesis of acetate from CO2. 3. Inhibition by alkylhalides of the synthesis from CO2, methyltetrahydrofolate, and methyl-B12 by Clostridium thermoaceticum. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Apr;143(2):471–484. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90232-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOBSON P. N. CONTINUOUS CULTURE OF SOME ANEROBIC AND FACULTATIVELY ANAEROBIC RUMEN BACTERIA. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Feb;38:167–180. doi: 10.1099/00221287-38-2-167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irion E., Ljungdahl L. Isolation of factor 3m coenzyme and cobyric acid coenzyme plus other B12 factors from Clostridium thermoaceticum. Biochemistry. 1965 Dec;4(12):2780–2790. doi: 10.1021/bi00888a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson J. L., Volcani B. E., Barker H. A. The Nutritional Requirements of Clostridium aceticum. J Bacteriol. 1948 Dec;56(6):781–782. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight E., Jr, D'Eustachio A. J., Hardy R. W. Flavodoxin: a flavoprotein with ferredoxin activity from Clostrium pasteurianum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Mar 7;113(3):626–628. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(66)80025-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LENTZ K., WOOD H. G. Synthesis of acetate from formate and carbon dioxide by Clostridium thermoaceticum. J Biol Chem. 1955 Aug;215(2):645–654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LJUNGDAHL L., WOOD H. G. INCORPORATION OF C14 FROM CARBON DIOXIDE INTO SUGAR PHOSPHATES, CARBOXYLIC ACIDS, AND AMINO ACIDS BY CLOSTRIDIUM THERMOACETICUM. J Bacteriol. 1965 Apr;89:1055–1064. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.4.1055-1064.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester R. L., DeMoss J. A. Effects of molybdate and selenite on formate and nitrate metabolism in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;105(3):1006–1014. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.3.1006-1014.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li L. F., Ljungdahl L., Wood H. G. Properties of Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate-Dependent Formate Dehydrogenase from Clostridium thermoaceticum. J Bacteriol. 1966 Aug;92(2):405–412. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.2.405-412.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungdahl L. G. Total synthesis of acetate from CO2 by heterotrophic bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1969;23:515–538. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.23.100169.002503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungdahl L., Irion E., Wood H. G. Total synthesis of acetate from CO2. I. Co-methylcobyric acid and CO-(methyl)-5-methoxybenzimidazolylcobamide as intermediates with Clostridium thermoaceticum. Biochemistry. 1965 Dec;4(12):2771–2780. doi: 10.1021/bi00888a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nandi D. L., Baker-Cohen K. F., Shemin D. Delta-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. J Biol Chem. 1968 Mar 25;243(6):1224–1230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien W. E., Ljungdahl L. G. Fermentation of fructose and synthesis of acetate from carbon dioxide by Clostridium formicoaceticum. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):626–632. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.626-632.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PECK H. D., Jr, GEST H. Formic dehydrogenase and the hydrogenlyase enzyme complex in coli-aerogenes bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1957 Jun;73(6):706–721. doi: 10.1128/jb.73.6.706-721.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PINSENT J. The need for selenite and molybdate in the formation of formic dehydrogenase by members of the coli-aerogenes group of bacteria. Biochem J. 1954 May;57(1):10–16. doi: 10.1042/bj0570010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker D. J., Wood H. G., Ghambeer R. K., Ljungdahl L. G. Total synthesis of acetate from carbon dioxide. Retention of deuterium during carboxylation of trideuteriomethyltetrahydrofolate or trideuteriomethylcobalamin. Biochemistry. 1972 Aug 1;11(16):3074–3080. doi: 10.1021/bi00766a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker D. J., Wu T. F., Wood H. G. Total synthesis of acetate from CO 2 : methyltetrahydrofolate, an intermediate, and a procedure for separation of the folates. J Bacteriol. 1971 Nov;108(2):770–776. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.2.770-776.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne W. J. Energy yields and growth of heterotrophs. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1970;24:17–52. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.24.100170.000313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck H. D., Jr Energy-coupling mechanisms in chemolithotrophic bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1968;22:489–518. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.22.100168.002421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poston J. M., Kuratomi K., Stadtman E. R. The conversion of carbon dioxide to acetate. I. The use of cobalt-methylcobalamin as a source of methyl groups for the synthesis of acetate by cell-free extracts of Clostridium thermoaceticum. J Biol Chem. 1966 Sep 25;241(18):4209–4216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poston J. M., Stadtman E. R. The conversion of carbon dioxide to acetate. 3. Demonstration of ferredoxin in the system converting Co-14Ch3-cobalamin to acetate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Mar 9;26(5):550–555. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90100-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raeburn S., Rabinowitz J. C. Pyruvate: ferredoxin oxidoreductase. I. The pyruvate-CO 2 exchange reaction. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Sep;146(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(71)80036-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STICKLAND L. H. The determination of small quantities of bacteria by means of the biuret reaction. J Gen Microbiol. 1951 Oct;5(4):698–703. doi: 10.1099/00221287-5-4-698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWIM H. E., KRAMPITZ L. O. Acetic acid oxidation by Escherichia coli; evidence for the occurrence of a tricarboxylic acid cycle. J Bacteriol. 1954 Apr;67(4):419–425. doi: 10.1128/jb.67.4.419-425.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman M., Parker D., Ljungdahl L. G., Wood H. G. Total synthesis of acetate from CO 2 . V. Determination by mass analysis of the different types of acetate formed from 13 CO 2 by heterotrophic bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):633–644. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.633-644.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman M., Wood H. G. Determination and degradation of microquantities of acetate. Anal Biochem. 1971 Feb;39(2):505–520. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90441-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shum A. C., Murphy J. C. Effects of selenium compounds on formate metabolism and coincidence of selenium-75 incorporation and formic dehydrogenase activity in cell-free preparations of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Apr;110(1):447–449. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.1.447-449.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadtman T. C. Methane fermentation. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1967;21:121–142. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.21.100167.001005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLIN E. A., WOLIN M. J., WOLFE R. S. FORMATION OF METHANE BY BACTERIAL EXTRACTS. J Biol Chem. 1963 Aug;238:2882–2886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOD H. G. A study of carbon dioxide fixation by mass determination of the types of C13-acetate. J Biol Chem. 1952 Feb;194(2):905–931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOD H. G. Fermentation of 3, 4-C14-and 1-C14-labeled glucose by Clostridium thermoaceticum. J Biol Chem. 1952 Dec;199(2):579–583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe R. S. Microbial formation of methane. Adv Microb Physiol. 1971;6:107–146. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60068-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Ghazzawi E., Schmidt K. Hexosen-Umwandlungen in Nährlösungen: Fructose-Verwertung durch Clostridium acetium Wieringa. Zentralbl Bakteriol Parasitenkd Infektionskr Hyg. 1967;121(6):569–575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


