Abstract
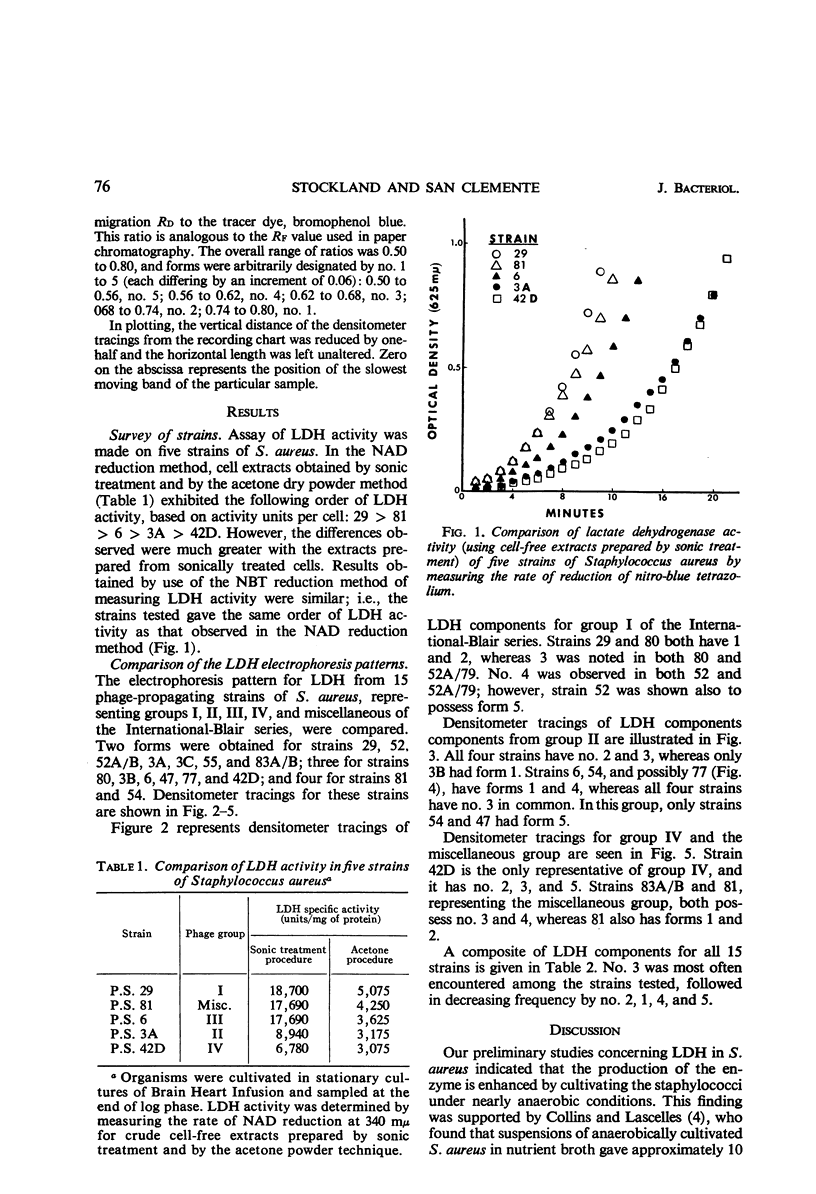
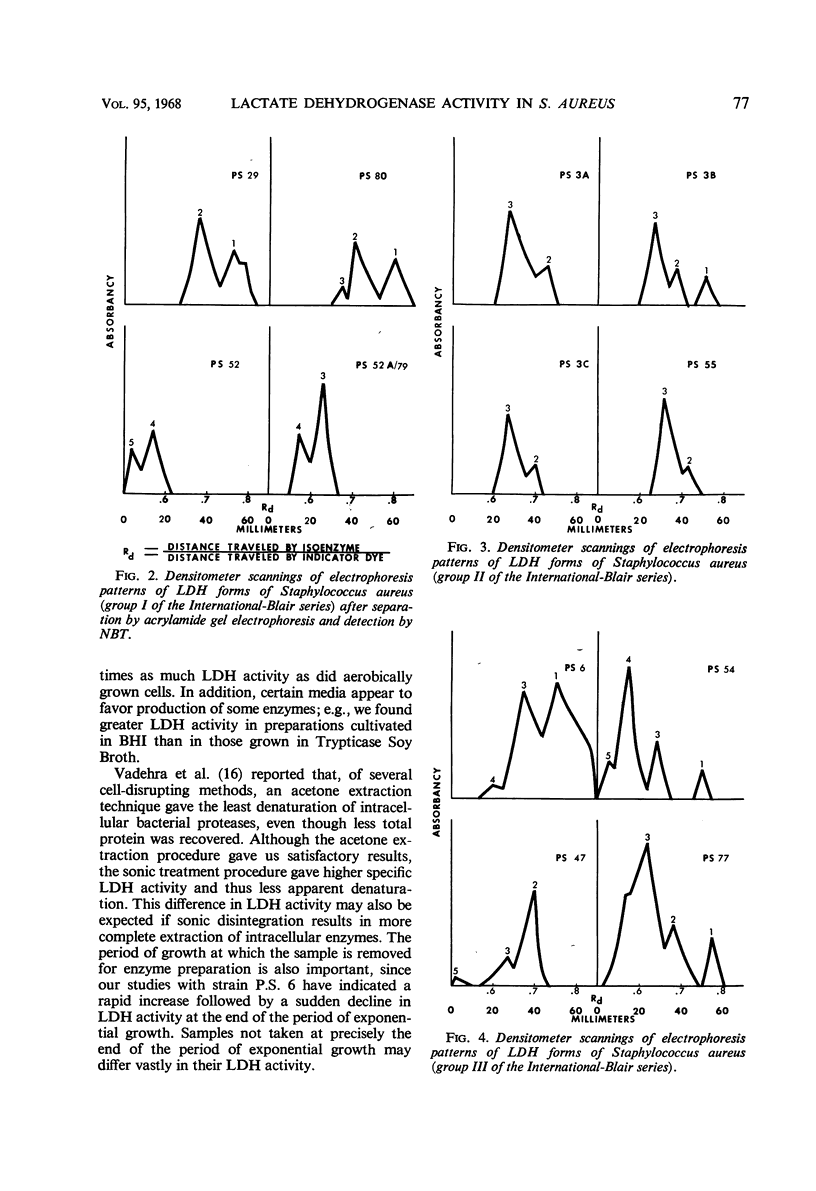
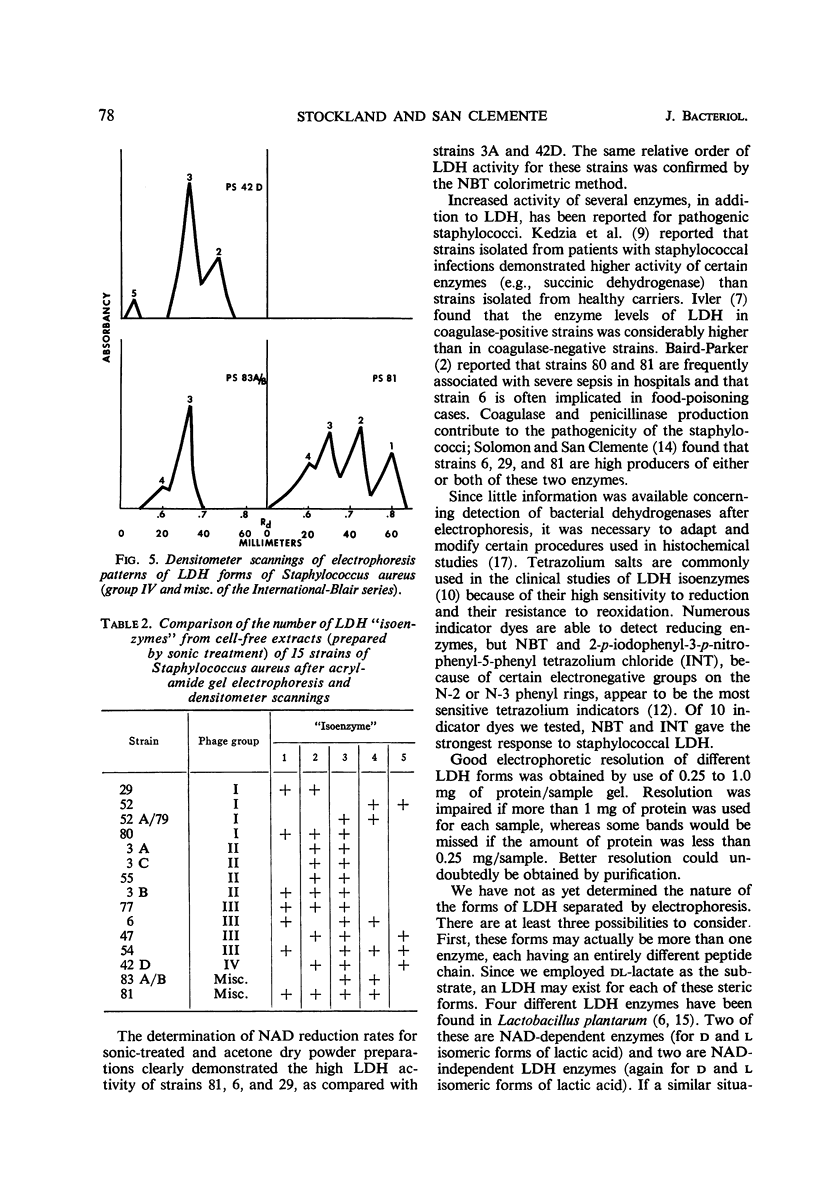
Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) was studied in phage-propagating strains 29, 3A, 6, 81, and 42D of Staphylococcus aureus selected from the five groups in the International-Blair series. Cells were cultivated in Brain Heart Infusion (Difco) under nearly anaerobic conditions and were harvested near the end of the log phase. LDH activity was maximal at the end of the exponential growth period and was measured spectrophotometrically by reduction of p-nitro-blue tetrazolium, with phenazine methosulfate as a coupling agent. Crude enzyme extracts were prepared both by an acetone extraction technique and by sonic treatment. LDH activity for these enzyme preparations was determined by the colorimetric method mentioned and also by measuring the rate of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide reduction at 340 mμ. The order of activity observed, by use of both assay methods, was 29 > 81 > 6 > 3A > 42D. LDH forms (possibly isoenzymes) for each of 15 strains, which represent the five phage-propagating groups of the International-Blair series, were separated by acrylamide gel electrophoresis. Five forms were distinguished and arbitrarily numbered on the basis of their rate of migration, no. 5 being the slowest component. No one strain had more than four, nor fewer than two, LDH forms. Form 3 appeared in 13 of the 15 strains and was followed in frequency by no. 2, 1, 4, and 5.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLEN J. M. Multiple forms of lactic dehydrogenase in tissues of the mouse: their specificity, cellular localization, and response to altered physiological conditions. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1961 Nov 2;94:937–951. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1961.tb35586.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLAIR J. E., CARR M. The techniques and interpretation of phage typing of staphylococci. J Lab Clin Med. 1960 Apr;55:650–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baird-Parker A. C. Staphylococci and their classification. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jul 23;128(1):4–25. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb11626.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLLINS F. M., LASCELLES J. The effect of growth conditions on oxidative and dehydrogenase activity in Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Nov;29:531–535. doi: 10.1099/00221287-29-3-531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DENNIS D., KAPLAN N. O. D- and L-lactic acid dehydrogenases in Lactobacillus plantarum. J Biol Chem. 1960 Mar;235:810–818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivler D. Comparative metabolism of virulent and avirulent staphylococci. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jul 23;128(1):62–80. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb11630.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLAN N. O., CIOTTI M. M. Evolution and differentiation of dehvdrogenases. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1961 Nov 2;94:701–722. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1961.tb35567.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedzia W., Musielak M., Kedzia B., Koniar H., Pniewska E. Enzymatic activity of coagulase-positive Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from patients and healthy carriers. Pathol Microbiol (Basel) 1966;29(3):307–323. doi: 10.1159/000161915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markert C. L., Faulhaber I. Lactate dehydrogenase isozyme patterns of fish. J Exp Zool. 1965 Aug;159(3):319–332. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401590304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NACHLAS M. M., MARGULIES S. I., SELIGMAN A. M. A colorimetric method for the estimation of succinic dehydrogenase activity. J Biol Chem. 1960 Feb;235:499–503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SNOSWELL A. M. OXIDIZED NICOTINAMIDE-ADENINE DINUCLEOTIDE-INDEPENDENT LACTATE DEHYDROGENASES OF LACTOBACILLUS ARABINOSUS 17.5. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Sep 3;77:7–9. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90464-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadehra D. V., Wallace D. L., Harmon L. G. Comparison of methods of extracting intracellular proteases from bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1965 Nov;13(6):1010–1013. doi: 10.1128/am.13.6.1010-1013.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIEME R. J., van SANDE, KARCHER D., LOWENTHAL A., van der HELM H. A modified technique for direct staining with nitro-blue tetrazolium of lactate dehydrogenase iso-enzymes upon agar gel electrophoresis. Clin Chim Acta. 1962 Nov;7:750–754. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(62)90054-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


