Abstract
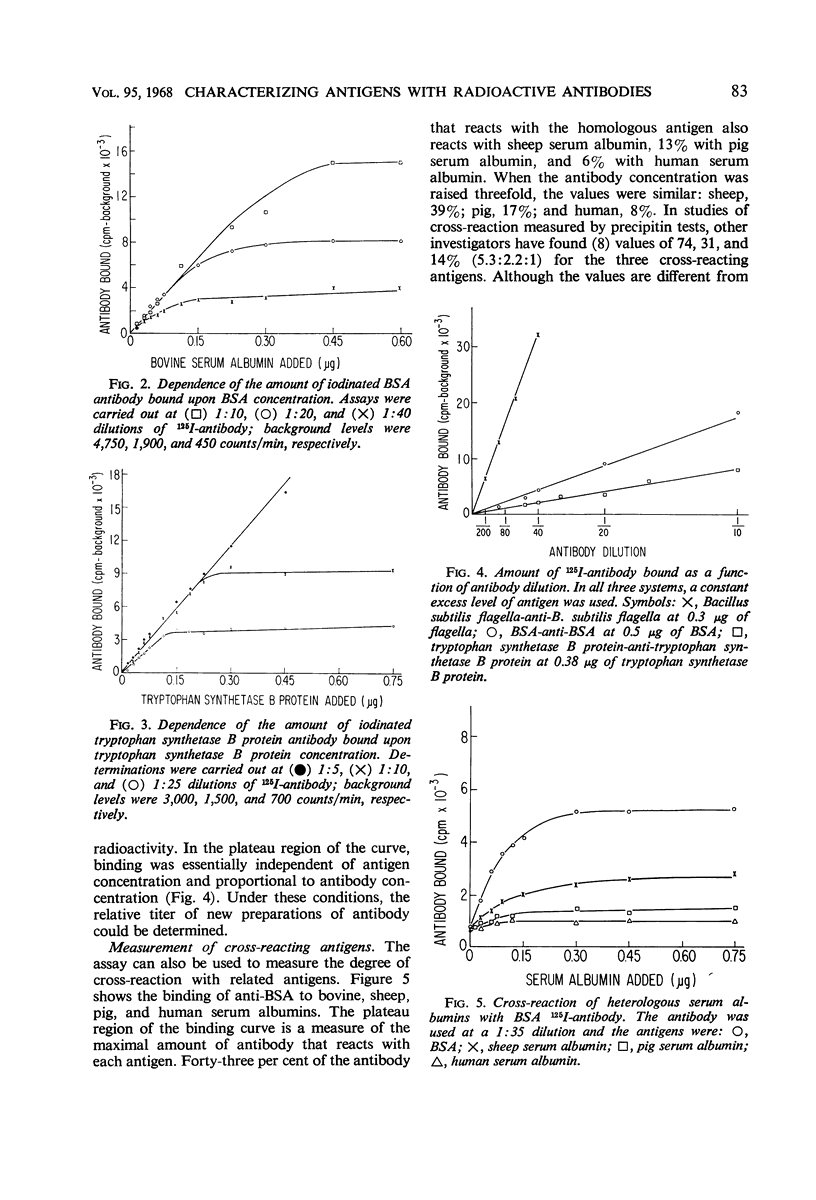
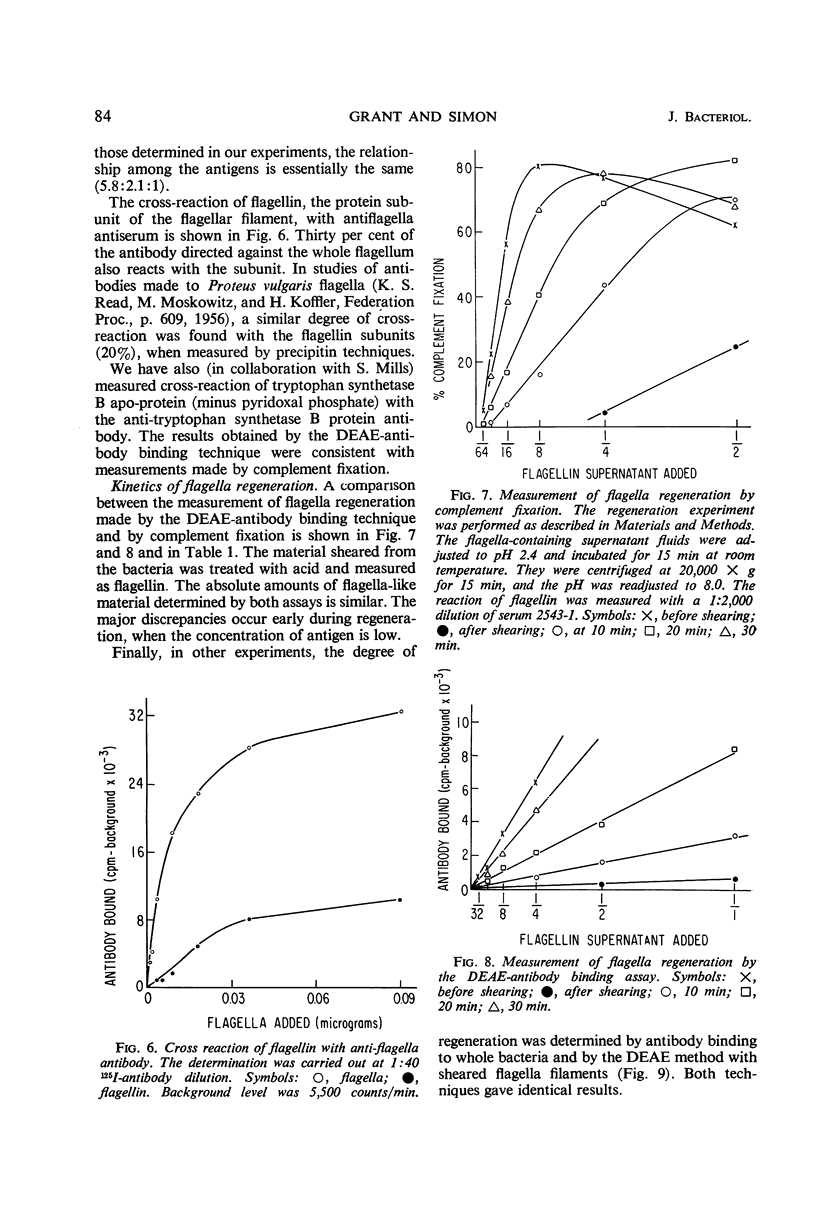
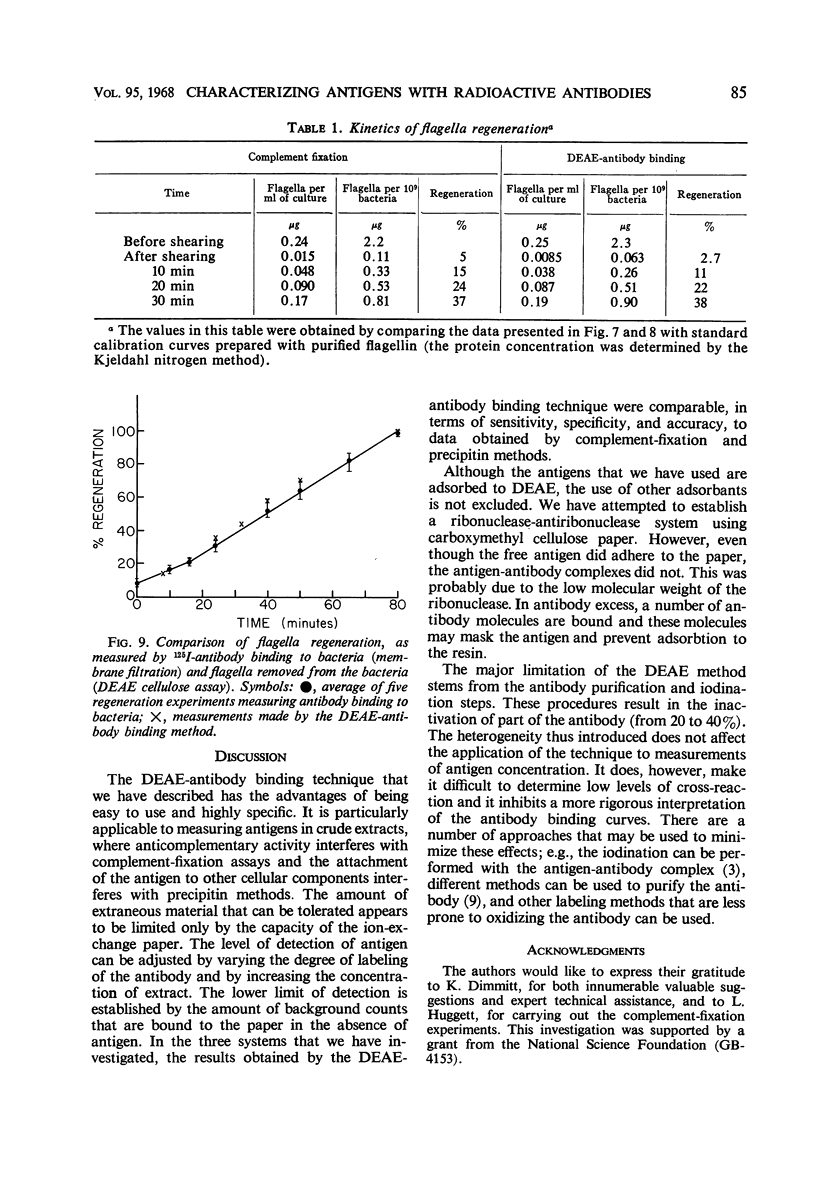
A simple rapid immunochemical procedure has been developed which provides information about the qualitative and quantitative nature of antigens. It involves the use of purified radioactive (125I-labeled) antibodies. The amount of antibody bound to the antigen is determined by filtering the mixture through diethylaminoethyl (DEAE)-cellulose paper. All of the antigen, as well as the antibody complexed with it, is trapped on the paper, whereas free antibody is removed by repeated washing. This technique has been applied to the study of three immune systems, bovine serum albumin, Escherichia coli tryptophan synthetase B protein, and Bacillus subtilis flagella. The results obtained by the DEAE-antibody binding technique were comparable, in terms of sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy, to data obtained by microcomplement fixation and precipitin methods. The assay was used to measure the kinetics of flagella regeneration in B. subtilis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Freedman M. H., Slobin L. I., Robbins J. B., Sela M. Soluble antigen-antibody complexes as intermediates in the purification of antibodies in 8 molar urea. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Sep 26;116(1):82–91. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KERRIDGE D. FLAGELLAR SYNTHESIS IN SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM: THE INCORPORATION OF ISOTOPICALLY-LABELLED AMINO ACIDS INTO FLAGELLIN. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Oct;33:63–76. doi: 10.1099/00221287-33-1-63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langenberg W. G., Schlegel D. E. Autoradiography with 125-I-labeled antibodies as a means of localizing TMV antigen in plant cells. Virology. 1967 May;32(1):167–171. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90266-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOCKER B. A., CAMPBELL J. C. The effect of non-lethal deflagellation on bacterial motility and observations on flagellar regeneration. J Gen Microbiol. 1959 Jun;20(3):670–685. doi: 10.1099/00221287-20-3-670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spizizen J. TRANSFORMATION OF BIOCHEMICALLY DEFICIENT STRAINS OF BACILLUS SUBTILIS BY DEOXYRIBONUCLEATE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1958 Oct 15;44(10):1072–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.44.10.1072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WASSERMAN E., LEVINE L. Quantitative micro-complement fixation and its use in the study of antigenic structure by specific antigen-antibody inhibition. J Immunol. 1961 Sep;87:290–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIGLE W. O. Immunochemical properties of the cross-reactions between anti-BSA and heterologous albumins. J Immunol. 1961 Nov;87:599–607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELIKY N., WEETALL H. H., GILDEN R. V., CAMPBELL D. H. THE SYNTHESIS AND USE OF SOME INSOLUBLE IMMUNOLOGICALLY SPECIFIC ADSORBENTS. Immunochemistry. 1964 Oct;1:219–229. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(64)90045-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


