Abstract
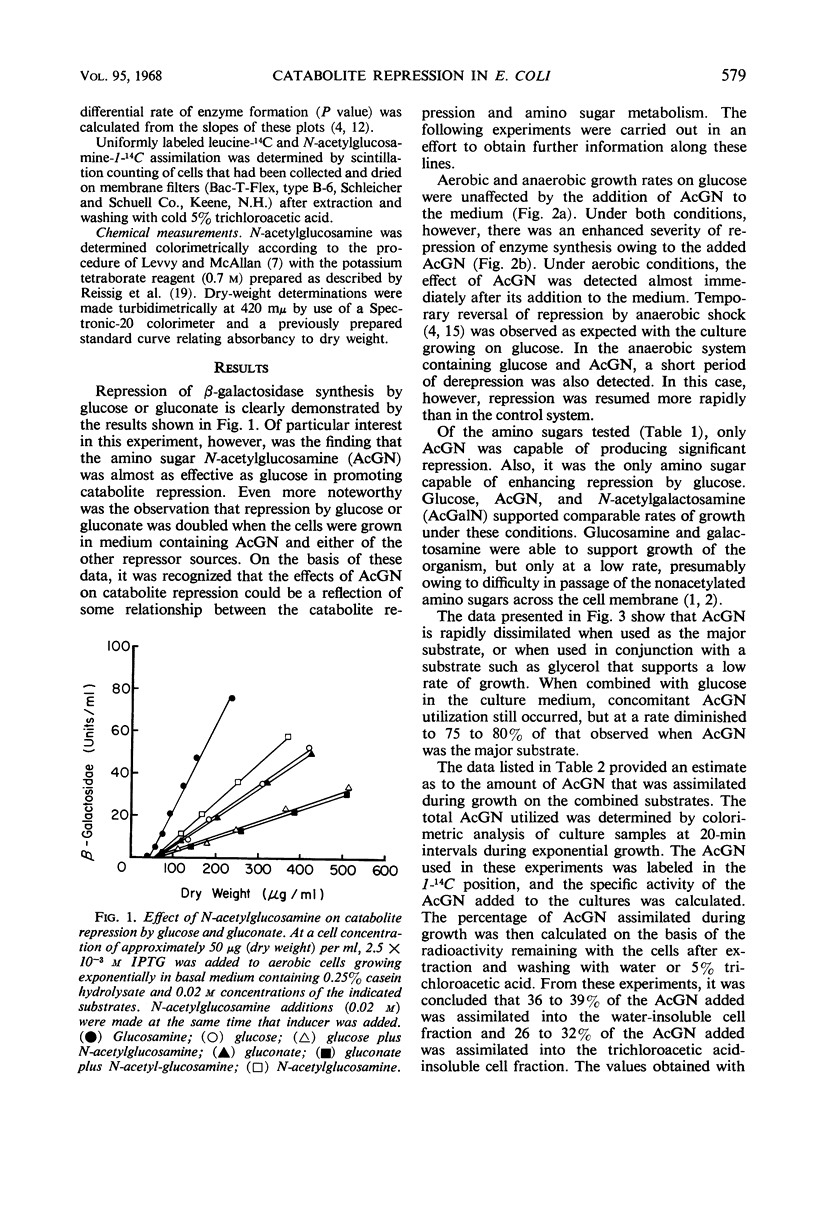
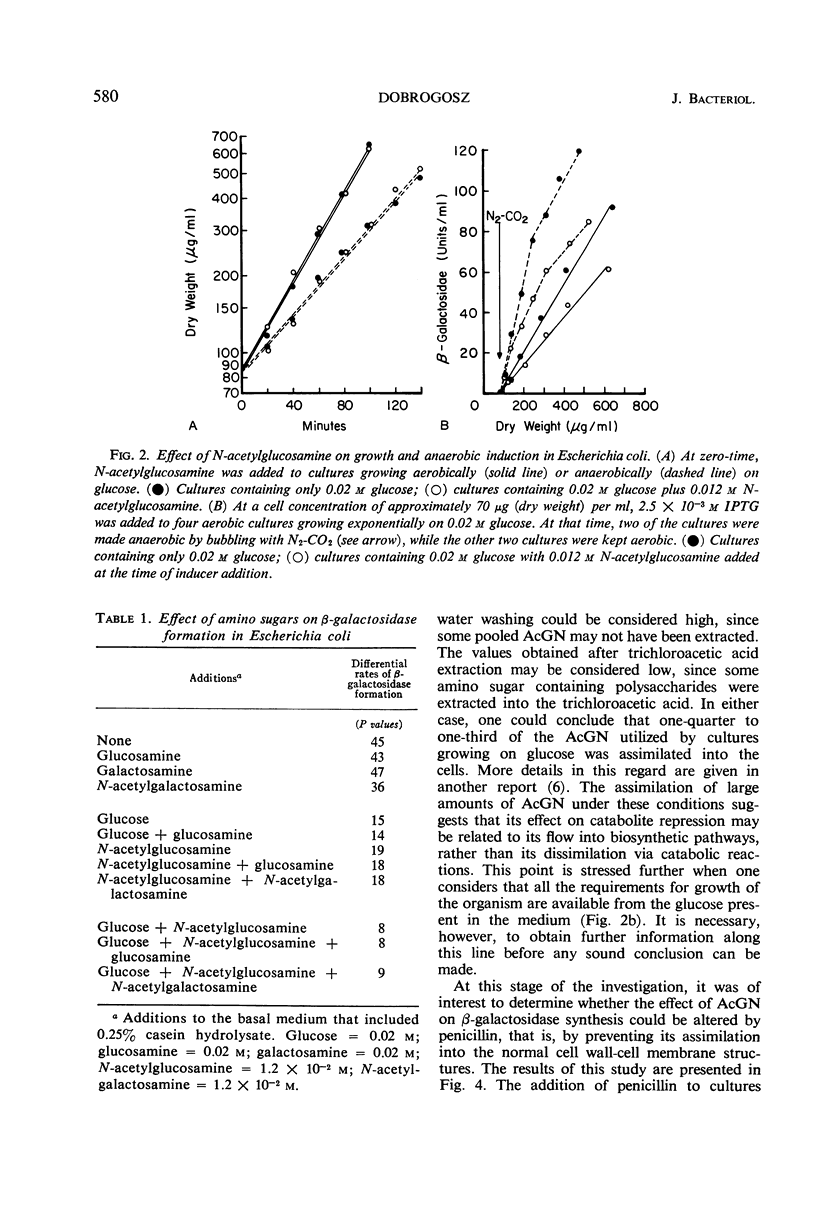
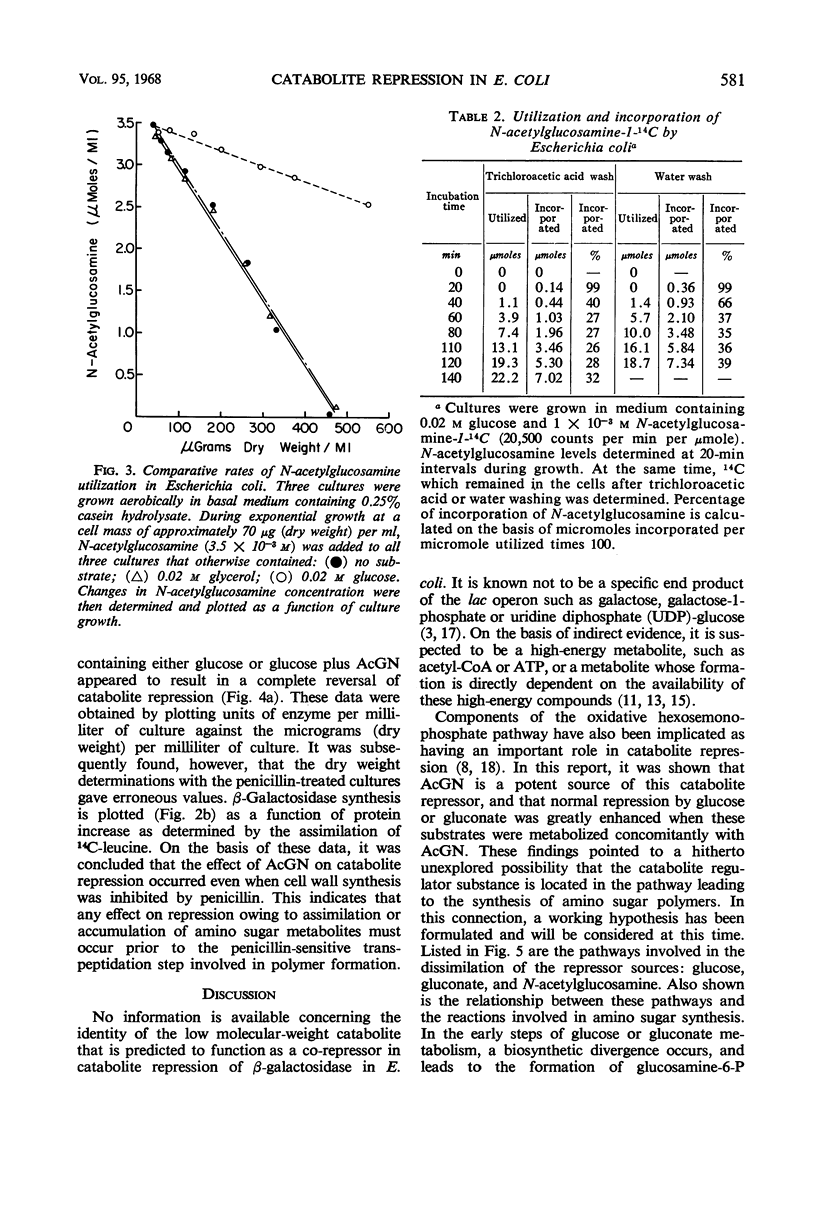
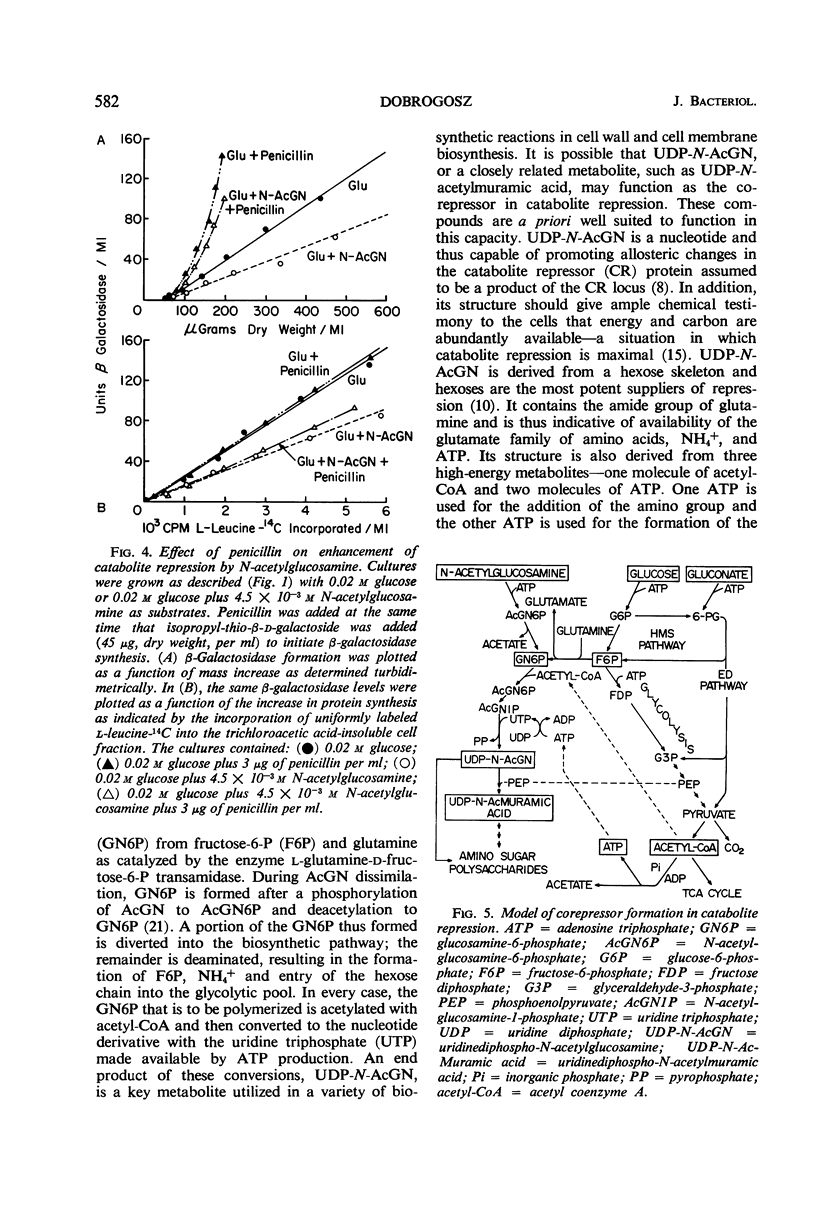
N-acetylglucosamine was found to be a good repressor source for catabolite repression of the β-galactosidase system in Escherichia coli. It was found capable of increasing the severity of repression by glucose or gluconate when included in the medium with either of these substrates. N-acetylglucosamine was shown to be assimilated under these conditions, but had no effect on culture growth rates. Its influence on catabolite repression was not altered by growth in the presence of inhibiting levels of penicillin. These findings indicated that catabolite repression may be associated with certain reactions of amino sugar metabolism. A working model has been formulated along these lines and will be used to explore this possible relationship further.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BATES C. J., PASTERNAK C. A. FURTHER STUDIES ON THE REGULATION OF AMINO SUGAR METABOLISM IN BACILLUS SUBTILIS. Biochem J. 1965 Jul;96:147–154. doi: 10.1042/bj0960147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BATES C. J., PASTERNAK C. A. THE INCORPORATION OF LABELLED AMINO SUGARS BY BACILLUS SUBTILIS. Biochem J. 1965 Jul;96:155–158. doi: 10.1042/bj0960155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beggs W. H., Rogers P. Galactose repression of beta-galactosidase induction in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):1869–1874. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.1869-1874.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN M., HORIBATA K. Physiology of the inhibition by glucose of the induced synthesis of the beta-galactosideenzyme system of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1959 Nov;78:624–635. doi: 10.1128/jb.78.5.624-635.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobrogosz W. J. Altered end-product patterns and catabolite repression in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jun;91(6):2263–2269. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.6.2263-2269.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobrogosz W. J. N-acetylglucosamine assimilation in Escherichia coli and its relation to catabolite repression. J Bacteriol. 1968 Feb;95(2):585–591. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.2.585-591.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVVY G. A., MCALLAN A. The N-acetylation and estimation of hexosamines. Biochem J. 1959 Sep;73:127–132. doi: 10.1042/bj0730127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loomis W. F., Jr, Magasanik B. Nature of the effector of catabolite repression of beta-galactosidase in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jul;92(1):170–177. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.1.170-177.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGASANIK B. Catabolite repression. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1961;26:249–256. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1961.026.01.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONOD J., PAPPENHEIMER A. M., Jr, COHEN-BAZIRE G. La cinétique de la biosynthèse de la beta-galactosidase chez E. coli considérée comme fonction de la croissance. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1952 Dec;9(6):648–660. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(52)90227-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses V., Prevost C. Catabolite repression of beta-galactosidase synthesis in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1966 Aug;100(2):336–353. doi: 10.1042/bj1000336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEIDHARDT F. C. Mutant of Aerobacter aerogenes lacking glucose repression. J Bacteriol. 1960 Oct;80:536–543. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.4.536-543.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okinaka R. T., Dobrogosz W. J. Catabolite repression and pyruvate metabolism in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 May;93(5):1644–1650. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.5.1644-1650.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okinaka R. T., Dobrogosz W. J. Catabolite repression and the Pasteur effect in Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1967 May;120(2):451–453. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(67)90263-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paigen K., Williams B., McGinnis J. Catabolite repression is not due to end-product repression in the gal operon. J Bacteriol. 1967 Aug;94(2):493–494. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.2.493-494.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prevost C., Moses V. Pool sizes of metabolic intermediates and their relation to glucose repression of beta-galactosidase synthesis in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1967 May;103(2):349–357. doi: 10.1042/bj1030349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uyeda K., Racker E. Regulatory mechanisms in carbohydrate metabolism. 8. The regulatory function of phosphate in glycolysis. J Biol Chem. 1965 Dec;240(12):4689–4693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMSON J. R. GLYCOLYTIC CONTROL MECHANISMS. I. INHIBITION OF GLYCOLYSIS BY ACETATE AND PYRUVATE IN THE ISOLATED, PERFUSED RAT HEART. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jun;240:2308–2321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


