Abstract
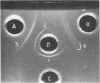
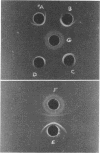
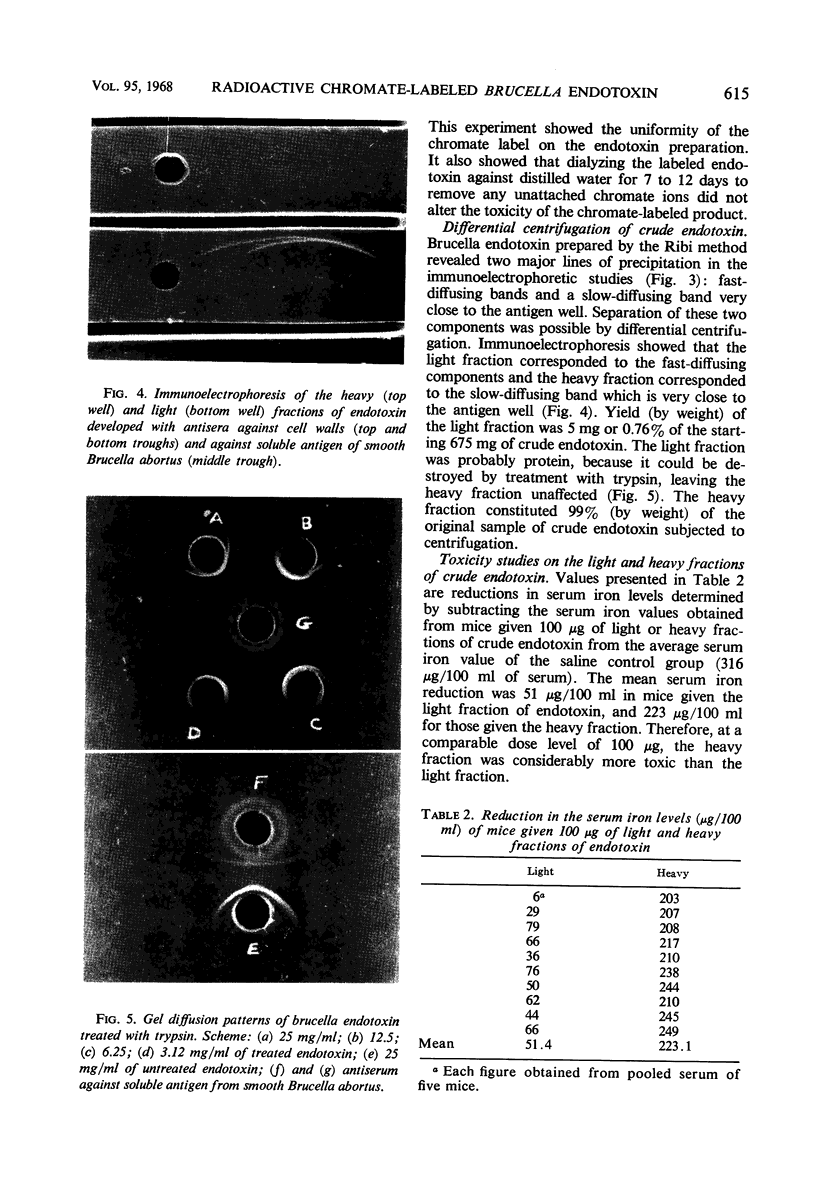
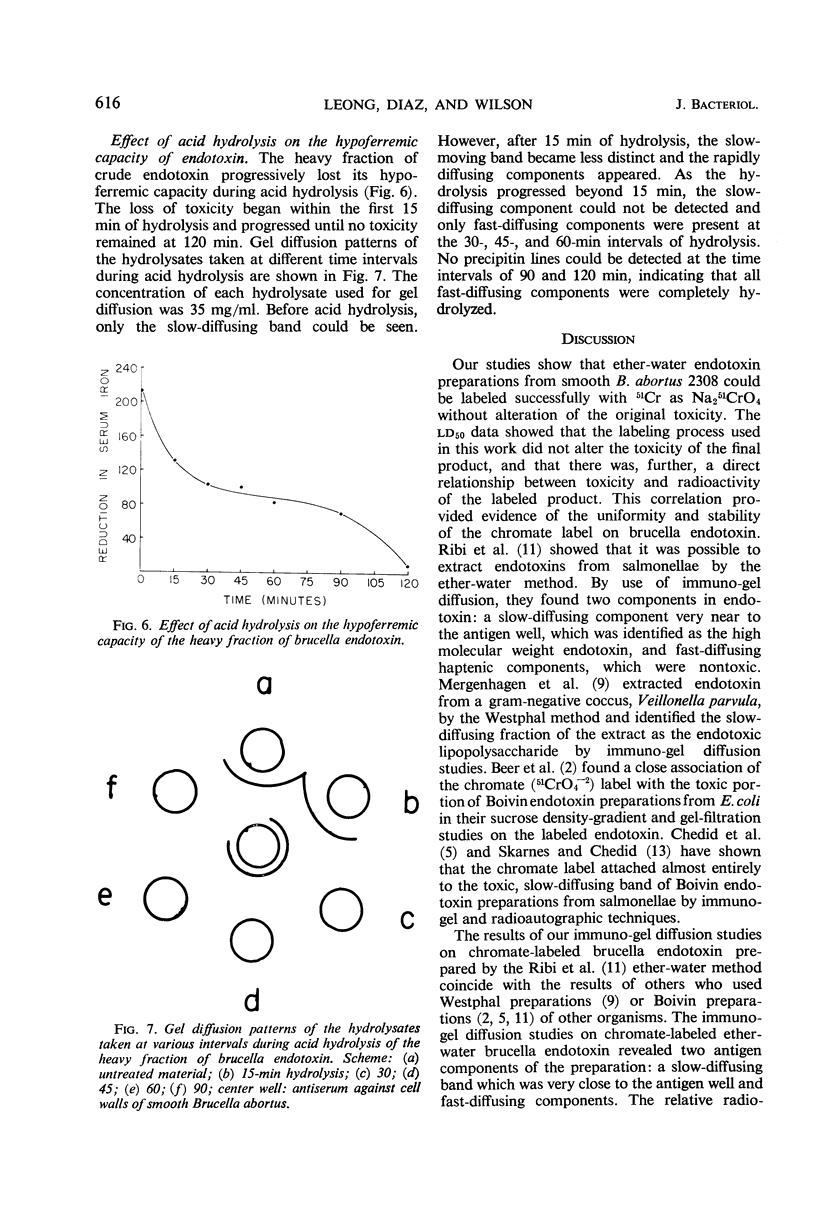
The evidence obtained from immuno-gel diffusion, centrifugation, and toxicity studies employing the serum iron assay proved that most of the toxicity in an ether-water brucella endotoxin preparation lies in the slow-diffusing component identified as the biologically active endotoxin. Subsequent destruction of the slow-diffusing component by acid hydrolysis resulted in a corresponding loss of toxicity. Chromate-51 was found to attach almost entirely on the slow-diffusing biologically active component and, hence, is a valid label for endotoxin derived from smooth Brucella abortus by the ether-water method.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEER H., STAEHELIN T., DOUGLAS H., BRAUDE A. I. RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN PARTICLE SIZE AND BIOLOGICAL ACTIVITY OF E. COLI BOIVIN ENDOTOXIN. J Clin Invest. 1965 Apr;44:592–602. doi: 10.1172/JCI105172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAUDE A. I., CAREY F. J., SUTHERLAND D., ZALESKY M. Studies with radioactive endotoxin. I. The use of Cr51 to label endotoxin of Escherichia coli. J Clin Invest. 1955 Jun;34(6):850–857. doi: 10.1172/JCI103140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. J., Wilson J. B. Hypoferremia in mice and its application to the bioassay of endotoxin. J Bacteriol. 1965 Oct;90(4):903–910. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.4.903-910.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHEDID L., SKARNES R. C., PARANT M. Characterization of a Cr51-labeled endotoxin and its identification in plasma and urine after parenteral administration. J Exp Med. 1963 Apr 1;117:561–571. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.4.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHORDI A., WALLS K. W., KAGAN I. G. STUDIES ON THE SPECIFICITY OF THE INDIRECT HEMAGGLUTINATION TEST FOR TOXOPLASMOSIS. J Immunol. 1964 Dec;93:1024–1033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz R., Jones L. M., Wilson J. B. Antigenic relationship of Brucella ovis and Brucella melitensis. J Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(4):1262–1268. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.4.1262-1268.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAMPSCHMIDT R. F., UPCHURCH H. F. Effects of bacteria endotoxin on plasma iron. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 May;110:191–193. doi: 10.3181/00379727-110-27463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mergenhagen S. E., Bladen H. A., Hsu K. C. Electron microscopic localization of endotoxic lipopolysaccharide in gram-negative organisms. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jun 30;133(2):279–291. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb52371.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIBI E., HASKINS W. T., MILNER K. C., ANACKER R. L., RITTER D. B., GOODE G., TRAPANI R. J., LANDY M. Physicochemical changes in endotoxin associated with loss of biological potency. J Bacteriol. 1962 Oct;84:803–814. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.4.803-814.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIBI E., MILNER K. C., PERRINE T. D. Endotoxic and antigenic fractions from the cell wall of Salmonella enteritidis; methods for separation and some biologic activities. J Immunol. 1959 Jan;82(1):75–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]