Abstract
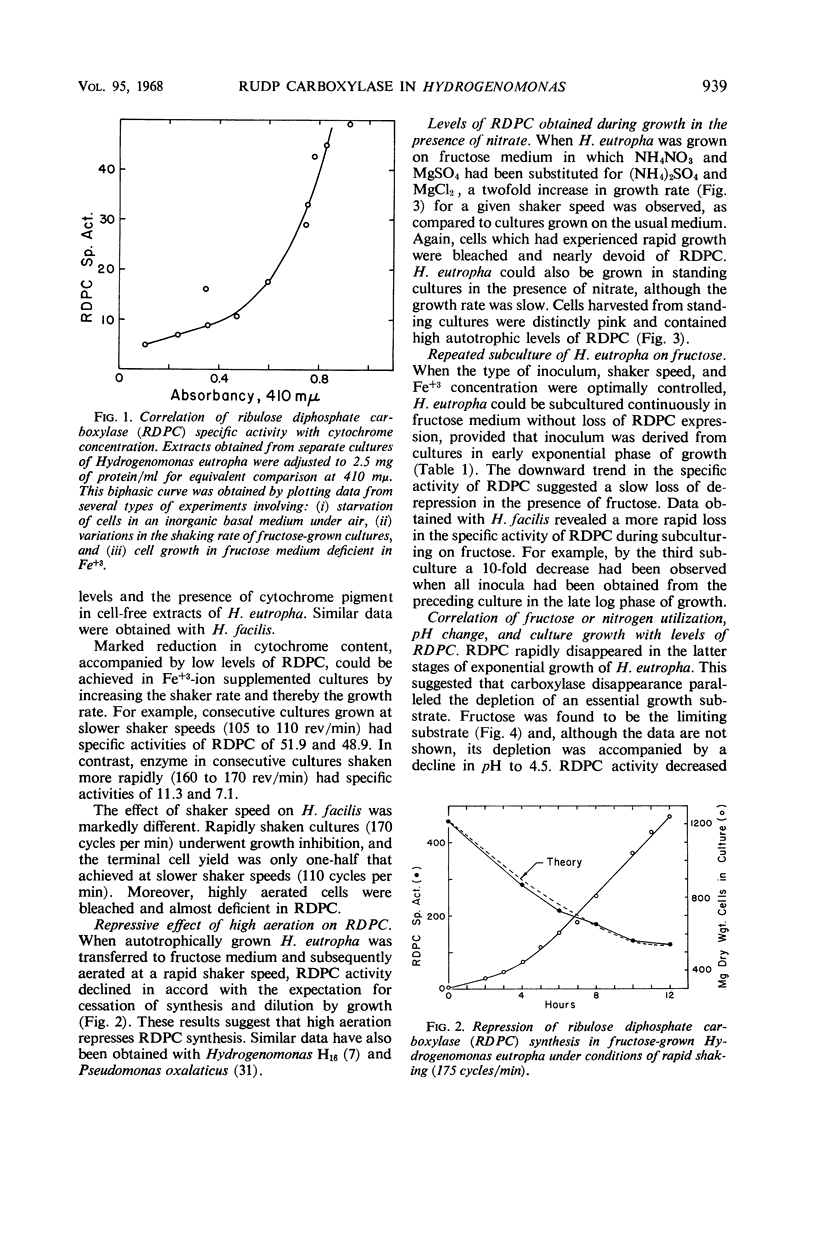
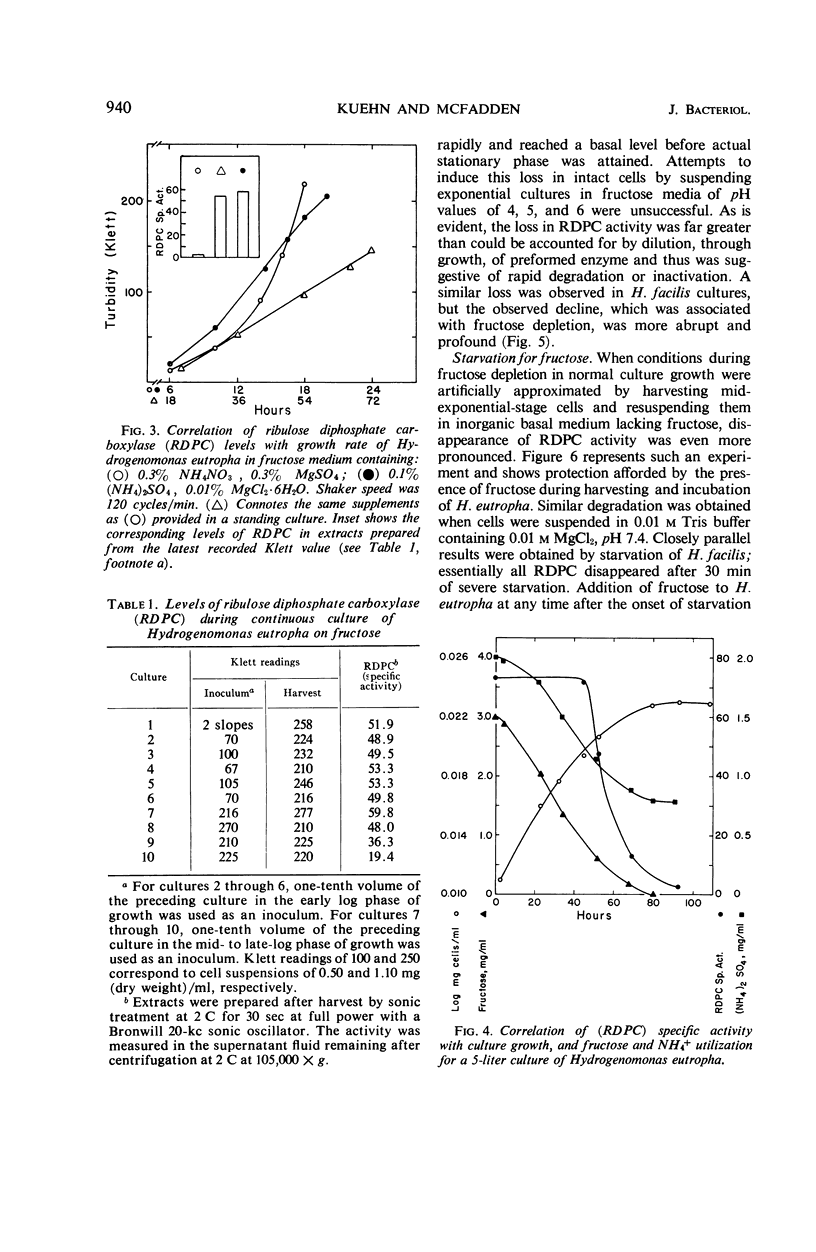
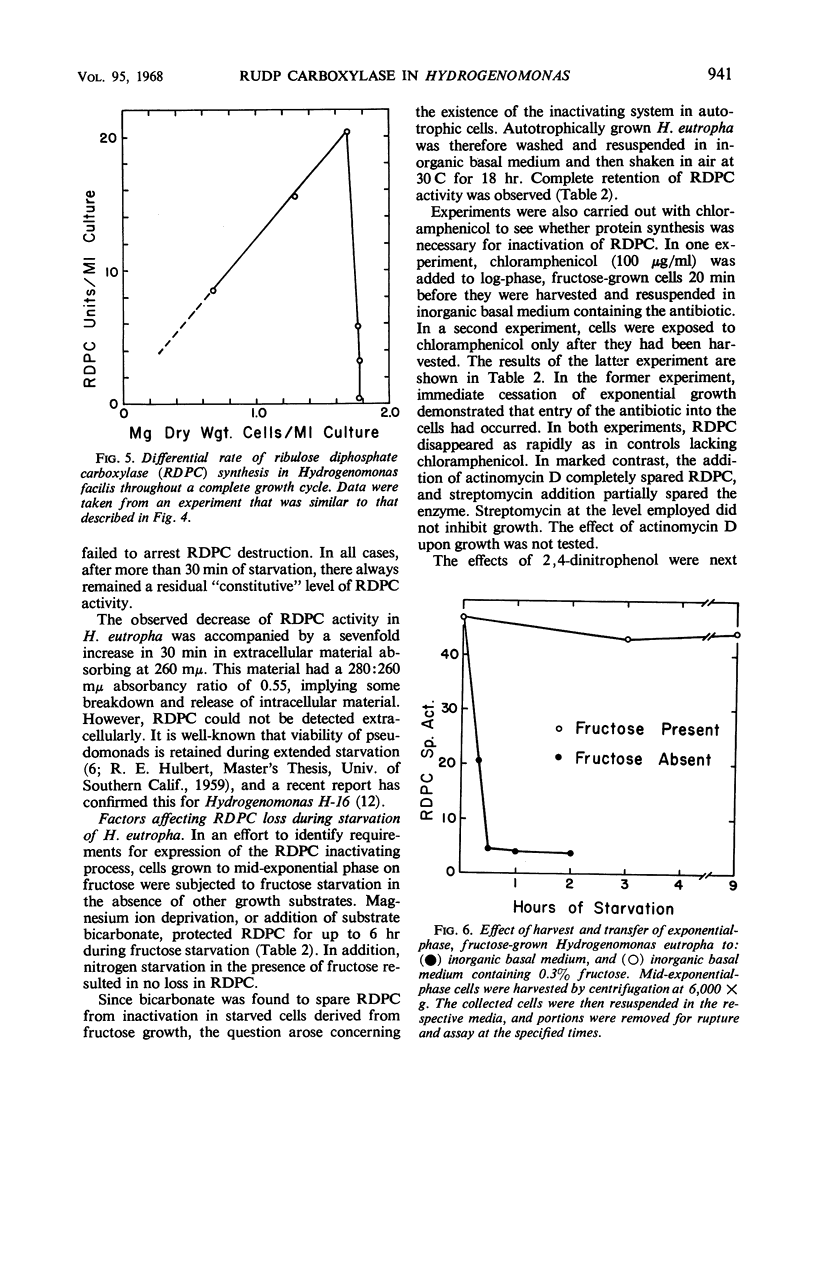
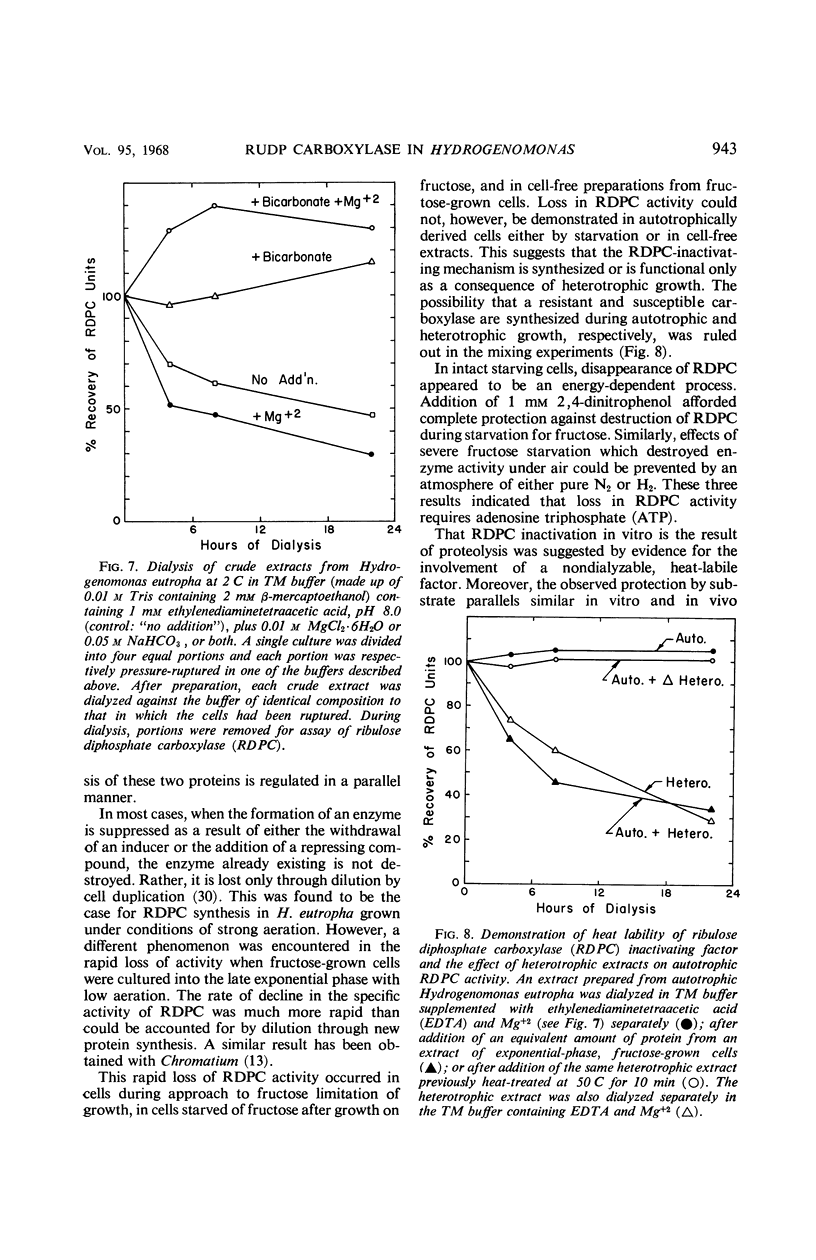
Hydrogenomonas facilis and H. eutropha cultured in fructose medium retained high levels of ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase only when the following conditions were fulfilled: low aeration, FeCl3 addition to fructose medium, and cell harvest at or prior to mid-exponential phase of growth. Repression of carboxylase synthesis was demonstrated under conditions of high oxygen tension during growth of H. eutropha on fructose. Upon depletion of fructose in the growth medium, carboxylase activity fell abruptly in both organisms. The decline could not be attributed to a repressive mechanism. Rapid inactivation of carboxylase was promoted by transfer of mid-exponential-phase H. eutropha to a basal salts medium lacking fructose. During severe fructose starvation, N2, H2, 80% H2 to 20% air, 2,4-dinitrophenol, actinomycin D, streptomycin, bicarbonate, and magnesium ion deficiency spared carboxylase. Nitrogen starvation or chloramphenicol afforded no protection during severe starvation. In vitro inactivation was also demonstrated in crude cell-free extracts from nonstarved, fructose-grown H. eutropha. Substrate bicarbonate protected against this loss. Inactivation of the carboxylase could not be demonstrated either by starvation of autotrophically grown cells or in autotrophic extracts. Autotrophic extracts mixed with heterotrophic extracts lost their carboxylase activity, but mixing with heterotrophic extracts that had been heated to 50 C resulted in no loss of activity. Mechanisms are proposed to accommodate these observations.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ATKINSON D. E., MCFADDEN B. A. The biochemistry of Hydrogenomonas. V. Factors affecting autotrophic fixation of carbon dioxide. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1957 Jan;66(1):16–22. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(57)90533-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aleem M. I., Huang E. Carbon dioxide fixation and carboxydismutase in Thiobacillus novellus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Aug 16;20(4):515–520. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90610-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson L., Fuller R. C. Photosynthesis in Rhodospirillum rubrum. 3. Metabolic control of reductive pentose phosphate and tricarboxylic acid cycle enzymes. Plant Physiol. 1967 Apr;42(4):497–509. doi: 10.1104/pp.42.4.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWES E. A., RIBBONS D. W. The endogenous metabolism of microorganisms. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1962;16:241–264. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.16.100162.001325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EGGMAN L., SINGER S. J., WILDMAN S. G. The proteins of green leaves. V. A cytoplasmic nucleoprotein from spinach and tobacco leaves. J Biol Chem. 1953 Dec;205(2):969–983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELSON D. Latent enzymic activity of a ribonucleoprotein isolated from Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Dec;36:372–386. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90179-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FULLER R. C., SMILLIE R. M., SISLER E. C., KORNBERG H. L. Carbon metabolism in Chromatium. J Biol Chem. 1961 Jul;236:2140–2149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronlund A. F., Campbell J. J. Enzymatic Degradation of Ribosomes During Endogenous Respiration of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jul;90(1):1–7. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.1.1-7.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HURLBERT R. E., LASCELLES J. RIBULOSE DIPHOSPHATE CARBOXYLASE IN THIORHODACEAE. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Dec;33:445–458. doi: 10.1099/00221287-33-3-445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hippe H. Abbau und Wiederverwertung von Poly-beta-hydroxybuttersäure durch Hydrogenomonas H 16. Arch Mikrobiol. 1967 Mar 29;56(3):248–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORNBERG H. L., COLLINS J. F., BIGLEY D. The influence of growth substrates on metabolic pathways in Micrococcus denitrificans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Mar 25;39:9–24. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90117-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingdon H. S., Shapiro B. M., Stadtman E. R. Regulation of glutamine synthetase. 8. ATP: glutamine synthetase adenylyltransferase, an enzyme that catalyzes alterations in the regulatory properties of glutamine synthetase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Oct;58(4):1703–1710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.4.1703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDELSTAM J. The intracellular turnover of protein and nucleic acids and its role in biochemical differentiation. Bacteriol Rev. 1960 Sep;24(3):289–308. doi: 10.1128/br.24.3.289-308.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDELSTAM J. Turnover of protein in growing and non-growing populations of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1958 May;69(1):110–119. doi: 10.1042/bj0690110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCFADDEN B. A., HOMANN H. R. CHARACTERISTICS AND INTERMEDIATES OF SHORT-TERM C-14-O-2 INCORPORATION DURING RIBOSE OXIDATION BY HYDROGENOMONAS FACILIS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Mar;89:839–847. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.3.839-847.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCFADDEN B. A., HOMANN H. R. QUANTITATIVE STUDIES OF THE EFFECT OF ORGANIC SUBSTRATES AND 2,4-DINITROPHENOL ON HETEROTROPHIC CARBON DIOXIDE FIXATION IN HYDROGENOMONAS FACILIS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Nov;86:971–977. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.5.971-977.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MENDIOLA L., AKAZAWA T. PARTIAL PURIFICATION AND THE ENZYMATIC NATURE OF FRACTION I PROTEIN OF RICE LEAVES. Biochemistry. 1964 Feb;3:174–179. doi: 10.1021/bi00890a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden B. A., Tu C. C. Regulation of autotrophic and heterotrophic carbon dioxide fixation in Hydrogenomonas facilis. J Bacteriol. 1967 Mar;93(3):886–893. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.3.886-893.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden B. A., Tu C. C. Ribulose diphosphate carboxylase and CO2 incorporation in extracts of Hydrogenomonas facilis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Jun 9;19(6):728–733. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90318-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pine M. J. Heterogeneity of protein turnover in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jul 8;104(2):439–456. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90349-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- QUAYLE J. R., KEECH D. B. Carboxydismutase activity in formate- and oxalate-grown Pseudomonas oxalacticus (strain OX1). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Feb;31(2):587–588. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90052-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REPASKE R. Nutritional requirements for Hydrogenomonas eutropha. J Bacteriol. 1962 Feb;83:418–422. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.2.418-422.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell G. K., Gibbs M. Regulation of Photosynthetic Capacity in Chlamydomonas mundana. Plant Physiol. 1966 May;41(5):885–890. doi: 10.1104/pp.41.5.885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHATZ A., BOVELL C., Jr Growth and hydrogenase activity of a new bacterium, Hydrogenomonas facilis. J Bacteriol. 1952 Jan;63(1):87–98. doi: 10.1128/jb.63.1.87-98.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar N. K. Effects of actinomycin D and mitomycin C on the degradation of deoxyribonucleic acid and polydeoxyribonucleotide by deoxyribonucleases and venom phosphodiesterase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Aug 22;145(1):174–177. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90669-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimke R. T., Sweeney E. W., Berlin C. M. Studies of the stability in vivo and in vitro of rat liver tryptophan pyrrolase. J Biol Chem. 1965 Dec;240(12):4609–4620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZITO R., ANTONINI E., WYMAN J. THE EFFECT OF OXYGENATION ON THE RATE OF DIGESTION OF HUMAN HEMOGLOBINS BY CARBOXYPEPTIDASES. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jun;239:1804–1808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


