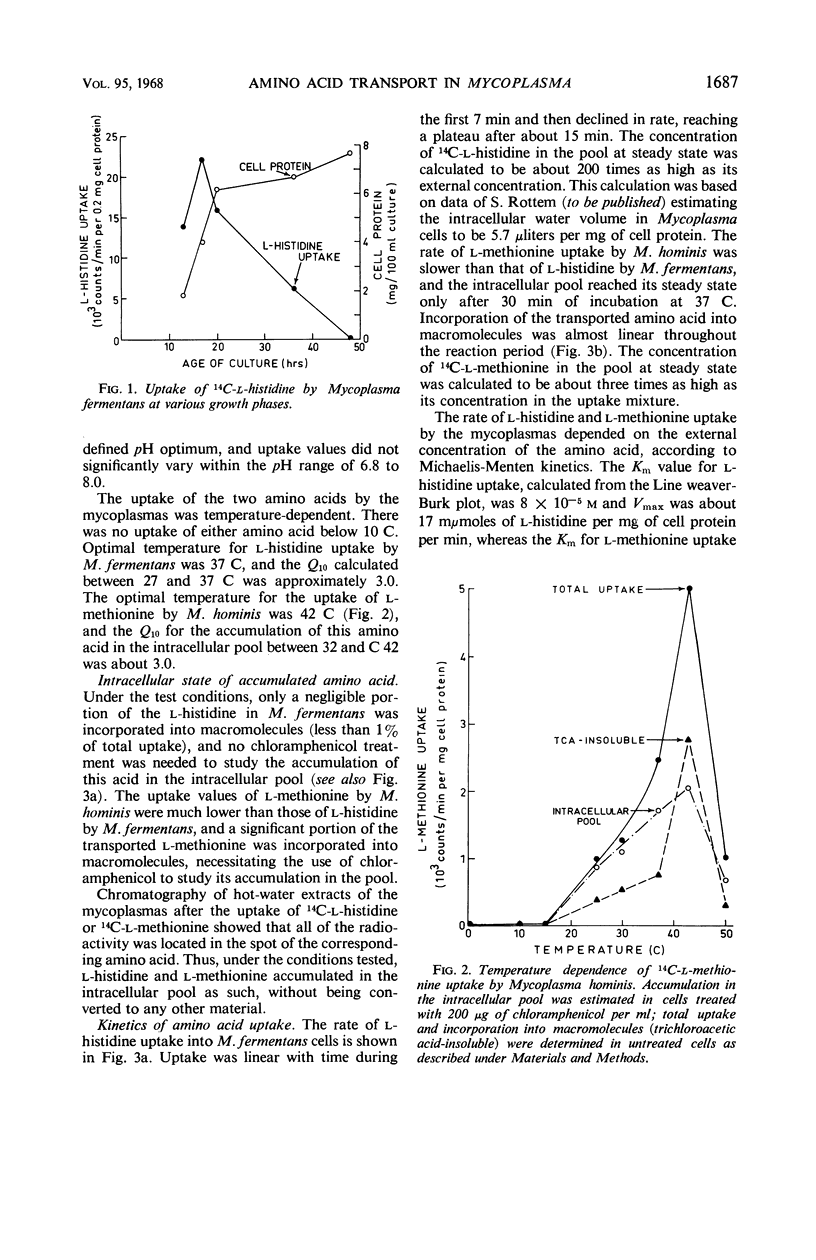
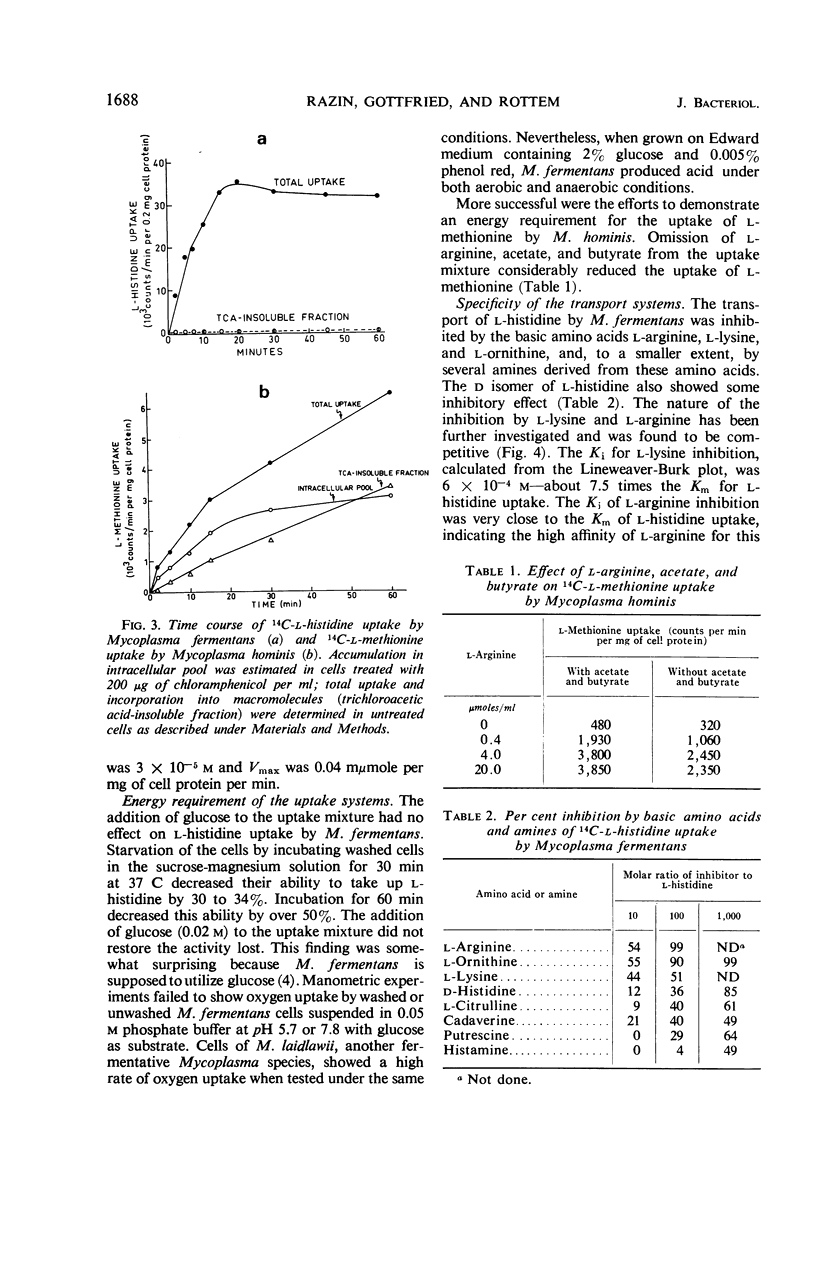
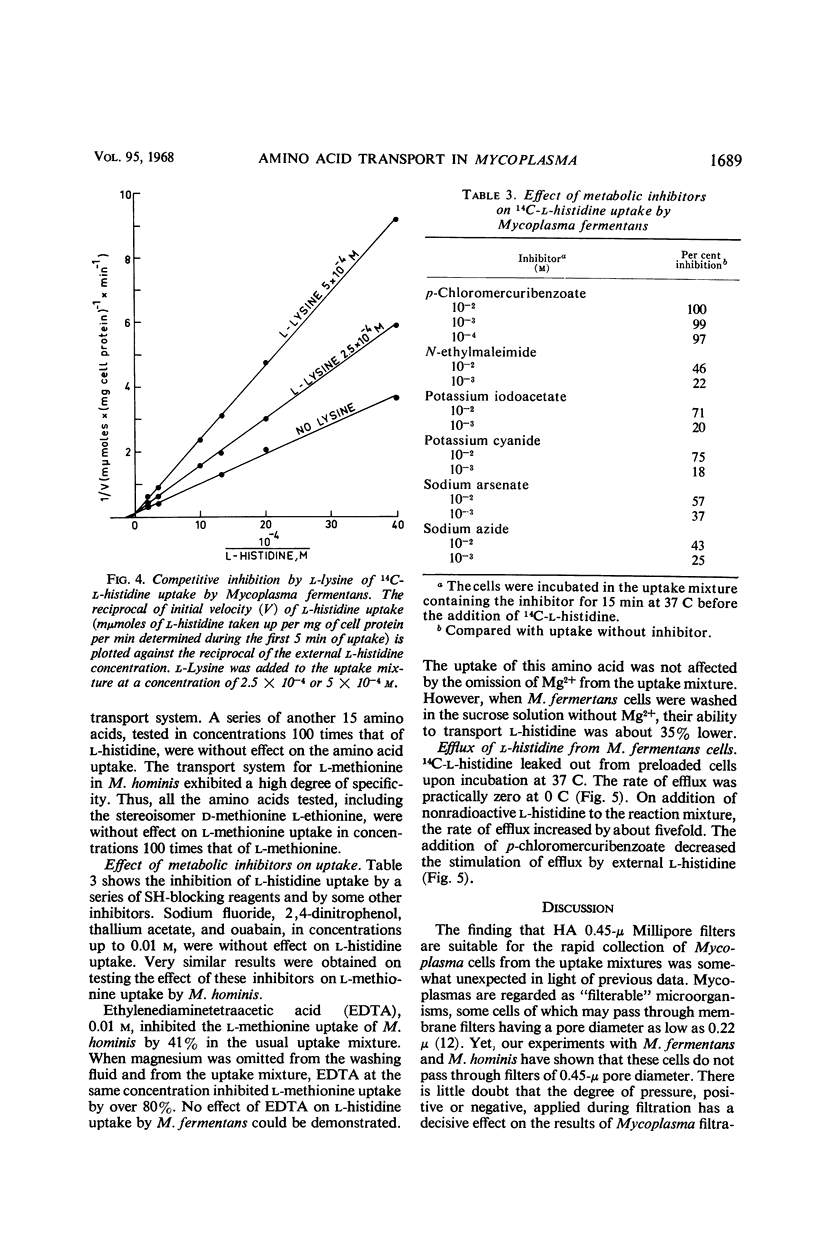
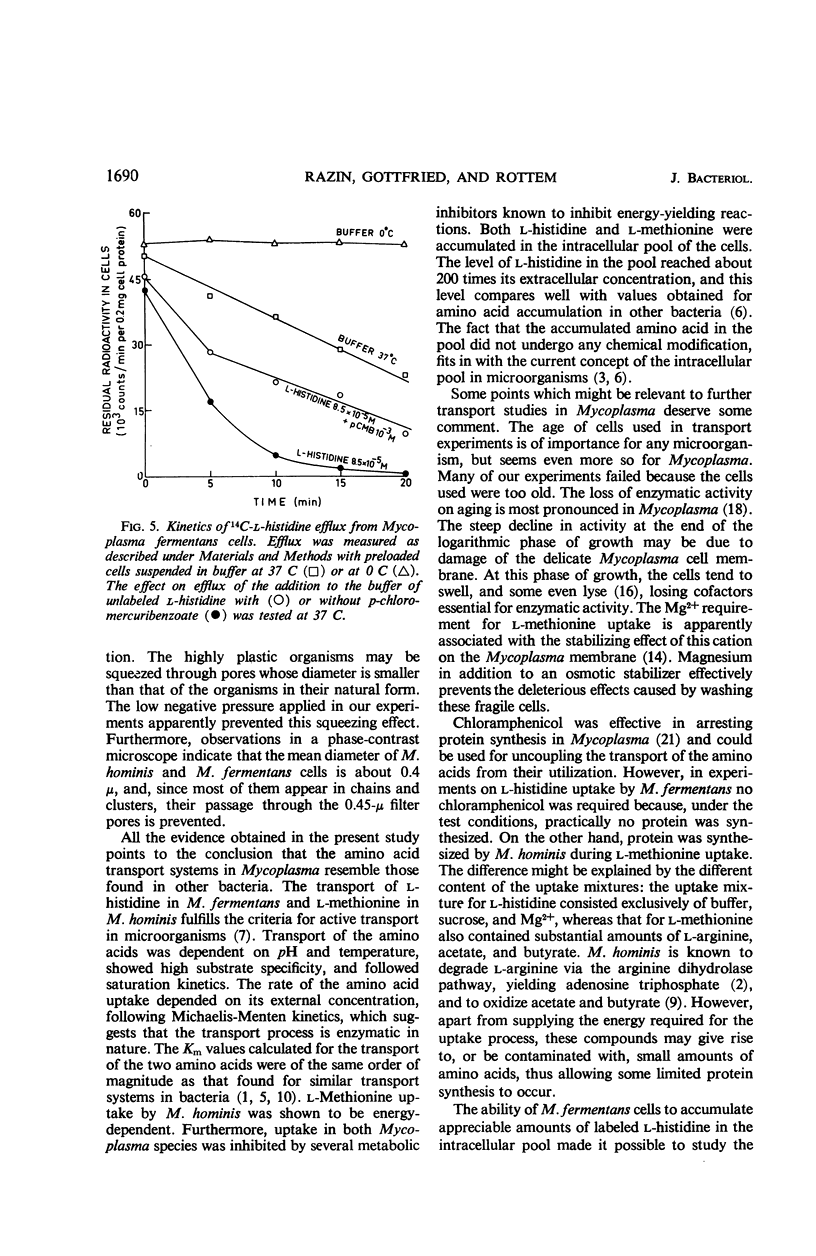
Abstract
The uptake of l-histidine by Mycoplasma fermentans and l-methionine by M. hominis was found to be dependent on temperature and pH and to follow saturation kinetics. Several metabolic inhibitors inhibited this uptake. The transport system for l-methionine was highly specific. The l-histidine transport system was less specific, and the uptake was competitively inhibited by l-arginine and l-lysine. l-Histidine accumulated in the intracellular pool of M. fermentans at a concentration about 200 times that found in the medium. Efflux of accumulated l-histidine was demonstrated at 37 C, but not at 0 C. The rate of efflux was greatly accelerated by addition of l-histidine to the medium. The findings indicate that the Mycoplasma cell membrane contains specific transport systems resembling the permease systems of other microorganisms.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMES G. F. UPTAKE OF AMINO ACIDS BY SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Jan;104:1–18. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(64)80028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barile M. F., Schimke R. T., Riggs D. B. Presence of the arginine dihydrolase pathway in Mycoplasma. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):189–192. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.1.189-192.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halpern Y. S., Even-Shoshan A. Properties of the glutamate transport system in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Mar;93(3):1009–1016. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.3.1009-1016.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LYNN R. J. Oxidative metabolism of pleuropneumonialike organisms. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Jan 15;79:538–542. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb42720.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morowitz H. J., Bode H. R., Kirk R. G. The nucleic acids of mycoplasma. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):110–114. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27650.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morowitz H. J., Tourtellotte M. E., Pollack M. E. USE OF POROUS CELLULOSE ESTER MEMBRANES IN THE PRIMARY ISOLATION AND SIZE DETERMINATION OF PLEUROPNEUMONIA-LIKE ORGANISMS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jan;85(1):134–136. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.1.134-136.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAZIN S. FACTORS INFLUENCING OSMOTIC FRAGILITY OF MYCOPLASMA. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 Sep;36:451–459. doi: 10.1099/00221287-36-3-451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAZIN S. OSMOTIC LYSIS OF MYCOPLASMA. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Dec;33:471–475. doi: 10.1099/00221287-33-3-471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S., Cosenza B. J. Growth phases of Mycoplasma in liquid media observed with phase-contrast microscope. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):858–869. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.858-869.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S. The cell membrane of mycoplasma. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):115–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27651.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottem S., Razin S. Adenosine triphosphatase activity of mycoplasma membranes. J Bacteriol. 1966 Sep;92(3):714–722. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.3.714-722.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimke R. T., Berlin C. M., Sweeney E. W., Carroll W. R. The generation of energy by the arginine dihydrolase pathway in Mycoplasma hominis 07. J Biol Chem. 1966 May 25;241(10):2228–2236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tourtellotte M. E., Pollack M. E., Nalewaik R. P. Protein synthesis in mycoplasma. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):130–138. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27652.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


