Abstract
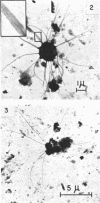
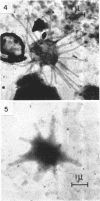
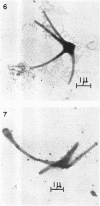
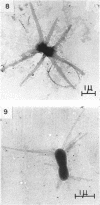
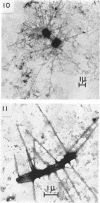
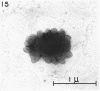
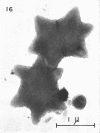
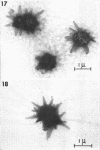
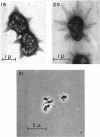
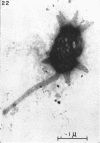
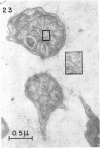
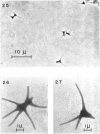
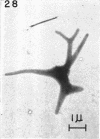
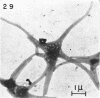
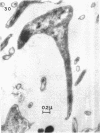
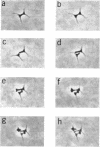
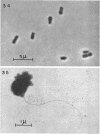
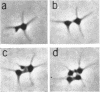
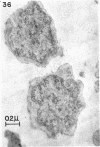
Direct microscopic examination of natural freshwater samples reveals a variety of small microorganisms having elaborate cellular appendages. Several strains have been isolated from crude cultures containing low concentrations of organic nutrients. All of the isolates are procaryotic. They are aerobic chemoorganotrophs that require vitamins for growth. Because they cannot be assigned to any of the existing bacterial genera, two new genera are proposed: Ancalomicrobium for organisms which have several long appendages and which reproduce by budding; Prosthecomicrobium for organisms which have many short appendages tapering toward a blunt tip and which reproduce by binary fission. Gas vacuoles have been found in strains of each genus. The term prostheca is proposed for the rigid appendages of procaryotic cells bounded by the cell wall, and is defined to include the structures on these new bacteria, as well as the stalks of the caulobacters and the hyphae of the hyphomicrobia.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLEN M. B. Excretion of organic compounds by Chlamydomonas. Arch Mikrobiol. 1956;24(2):163–168. doi: 10.1007/BF00408630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOATMAN E. S., DOUGLAS H. C. Fine structure of the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodomicrobium vannielii. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Nov;11:469–483. doi: 10.1083/jcb.11.2.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen C. C., Jensen T. E. Blue-Green Algae: Fine Structure of the Gas Vacuoles. Science. 1965 Mar 19;147(3664):1460–1462. doi: 10.1126/science.147.3664.1460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN-BAZIRE G., SISTROM W. R., STANIER R. Y. Kinetic studies of pigment synthesis by non-sulfur purple bacteria. J Cell Physiol. 1957 Feb;49(1):25–68. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030490104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONTI S. F., HIRSCH P. BIOLOGY OF BUDDING BACTERIA. 3. FINE STRUCTURE OF RHODOMICROBIUM AND HYPHOMICROBIUM SPP. J Bacteriol. 1965 Feb;89:503–512. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.2.503-512.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRULA E. A., WEAVER R. H., EDWARDS O. F. Studies on a strain of Caulobacter from water. II. Nutrition, with implications for cytology. J Bacteriol. 1954 Aug;68(2):201–206. doi: 10.1128/jb.68.2.201-206.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOUWINK A. L. Caulobacter versus Bacillus spec. div. Nature. 1951 Oct 13;168(4276):654–655. doi: 10.1038/168654b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOUWINK A. L. Flagella, gas vacuoles and cell-wall structure in Halobacterium halobium; an electron microscope study. J Gen Microbiol. 1956 Aug;15(1):146–150. doi: 10.1099/00221287-15-1-146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGH R., LEIFSON E. The taxonomic significance of fermentative versus oxidative metabolism of carbohydrates by various gram negative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1953 Jul;66(1):24–26. doi: 10.1128/jb.66.1.24-26.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henrici A. T., Johnson D. E. Studies of Freshwater Bacteria: II. Stalked Bacteria, a New Order of Schizomycetes. J Bacteriol. 1935 Jul;30(1):61–93. doi: 10.1128/jb.30.1.61-93.1935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henrici A. T. Studies of Freshwater Bacteria: I. A Direct Microscopic Technique. J Bacteriol. 1933 Mar;25(3):277–287. doi: 10.1128/jb.25.3.277-287.1933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEIFSON E. HYPHOMICROBIUM NEPTUNIUM SP. N. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1964;30:249–256. doi: 10.1007/BF02046730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POINDEXTER J. S. BIOLOGICAL PROPERTIES AND CLASSIFICATION OF THE CAULOBACTER GROUP. Bacteriol Rev. 1964 Sep;28:231–295. doi: 10.1128/br.28.3.231-295.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pate J. L., Ordal E. J. The fine structure of two unusual stalked bacteria. J Cell Biol. 1965 Oct;27(1):133–150. doi: 10.1083/jcb.27.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfennig N. Photosynthetic bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1967;21:285–324. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.21.100167.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYTER A., KELLENBERGER E., BIRCHANDERSEN A., MAALOE O. Etude au microscope électronique de plasmas contenant de l'acide désoxyribonucliéique. I. Les nucléoides des bactéries en croissance active. Z Naturforsch B. 1958 Sep;13B(9):597–605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHILDKRAUT C. L., MARMUR J., DOTY P. Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its buoyant density in CsCl. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jun;4:430–443. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STANIER R. Y., VAN NIEL C. B. The concept of a bacterium. Arch Mikrobiol. 1962;42:17–35. doi: 10.1007/BF00425185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOLP H., STARR M. P. BDELLOVIBRIO BACTERIOVORUS GEN. ET SP. N., A PREDATORY, ECTOPARASITIC, AND BACTERIOLYTIC MICROORGANISM. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1963;29:217–248. doi: 10.1007/BF02046064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOVEPOINDEXTER J. L., COHEN-BAZIRE G. THE FINE STRUCTURE OF STALKED BACTERIA BELONGING TO THE FAMILY CAULOBACTERACEAE. J Cell Biol. 1964 Dec;23:587–607. doi: 10.1083/jcb.23.3.587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M. The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 May;43(2):159–271. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckenius W., Rowen R. A morphological study of Halobacterium halobium and its lysis in media of low salt concentration. J Cell Biol. 1967 Jul;34(1):365–393. doi: 10.1083/jcb.34.1.365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VENABLE J. H., COGGESHALL R. A SIMPLIFIED LEAD CITRATE STAIN FOR USE IN ELECTRON MICROSCOPY. J Cell Biol. 1965 May;25:407–408. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.2.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]