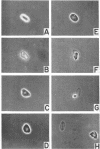
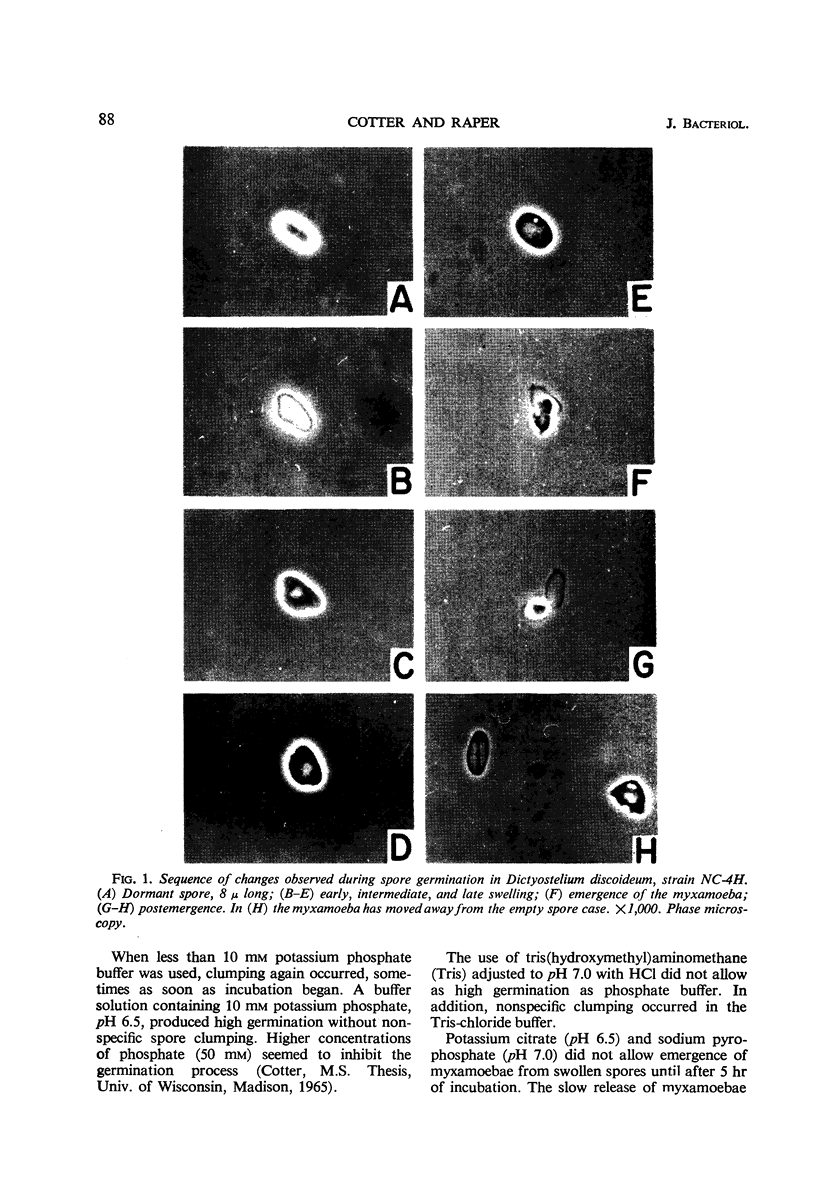
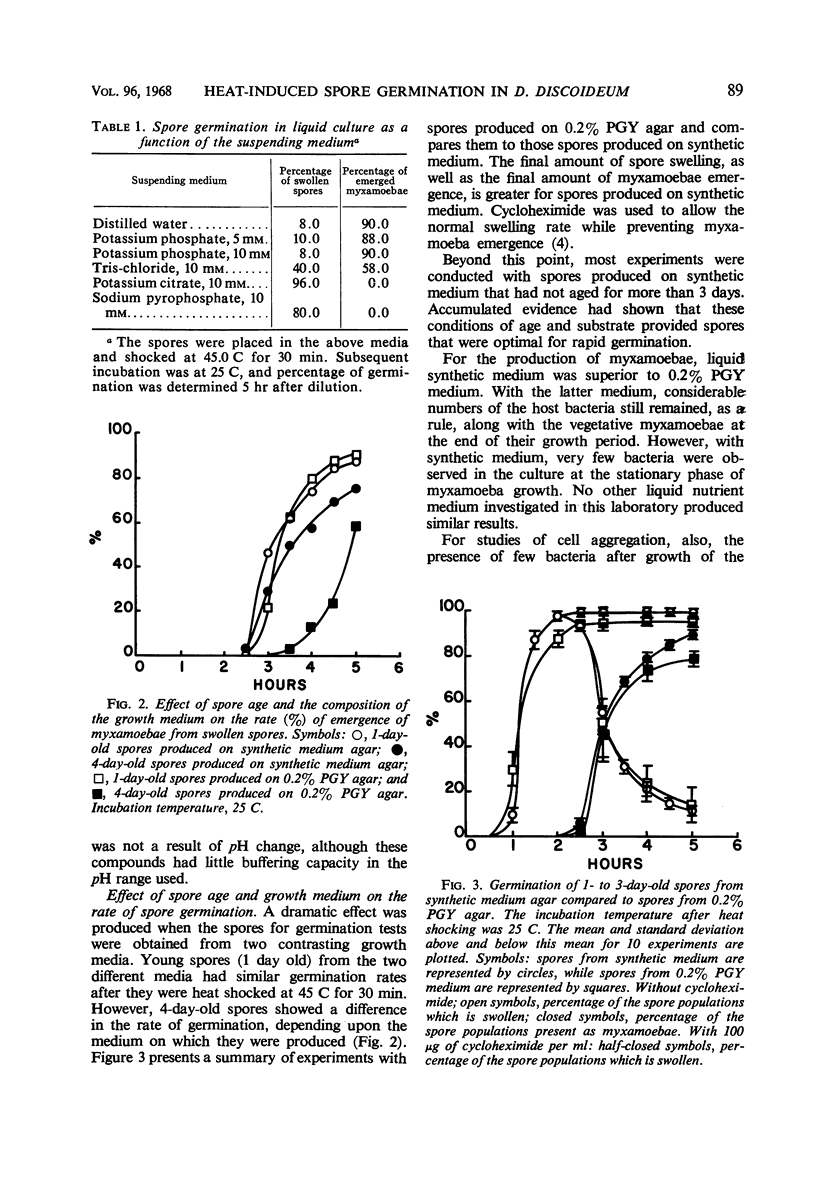
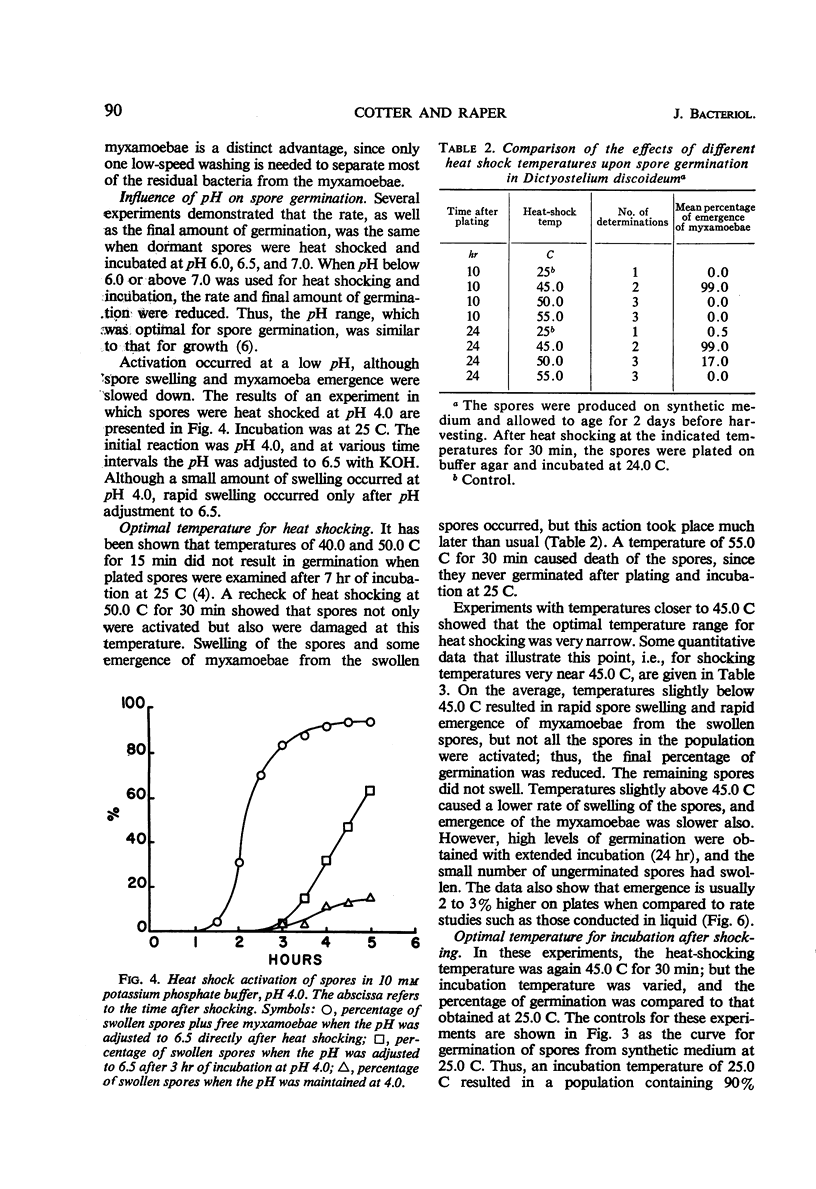
Abstract
Washed spores of Dictyostelium discoideum, strains NC-4H, NC-4D, and V-12, germinated rapidly after being heat shocked at or near 45.0 C for 30 min. Cultures of the slime molds were grown in association with Escherichia coli B/r as the host bacterium; spores taken from plates of synthetic medium had a higher final germination value than spores from complex medium containing peptone and yeast extract. Young spores germinated more rapidly than older spores. Optimal germination occurred between pH 6.0 and 7.0, and, of the buffers tested, potassium phosphate allowed the most rapid germination. After heat shocking, spores were diluted into fresh oxygenated buffer to provide enough oxygen for completion of germination. Germination occurred most rapidly between incubation temperatures of 22 and 25 C.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cotter D. A., Raper K. B. Spore germination in Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Sep;56(3):880–887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.3.880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inselburg J., Sussman M. Incorporation of 3H-uridine into RNA during cellular slime mould development. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Jan;46(1):59–64. doi: 10.1099/00221287-46-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]