Abstract
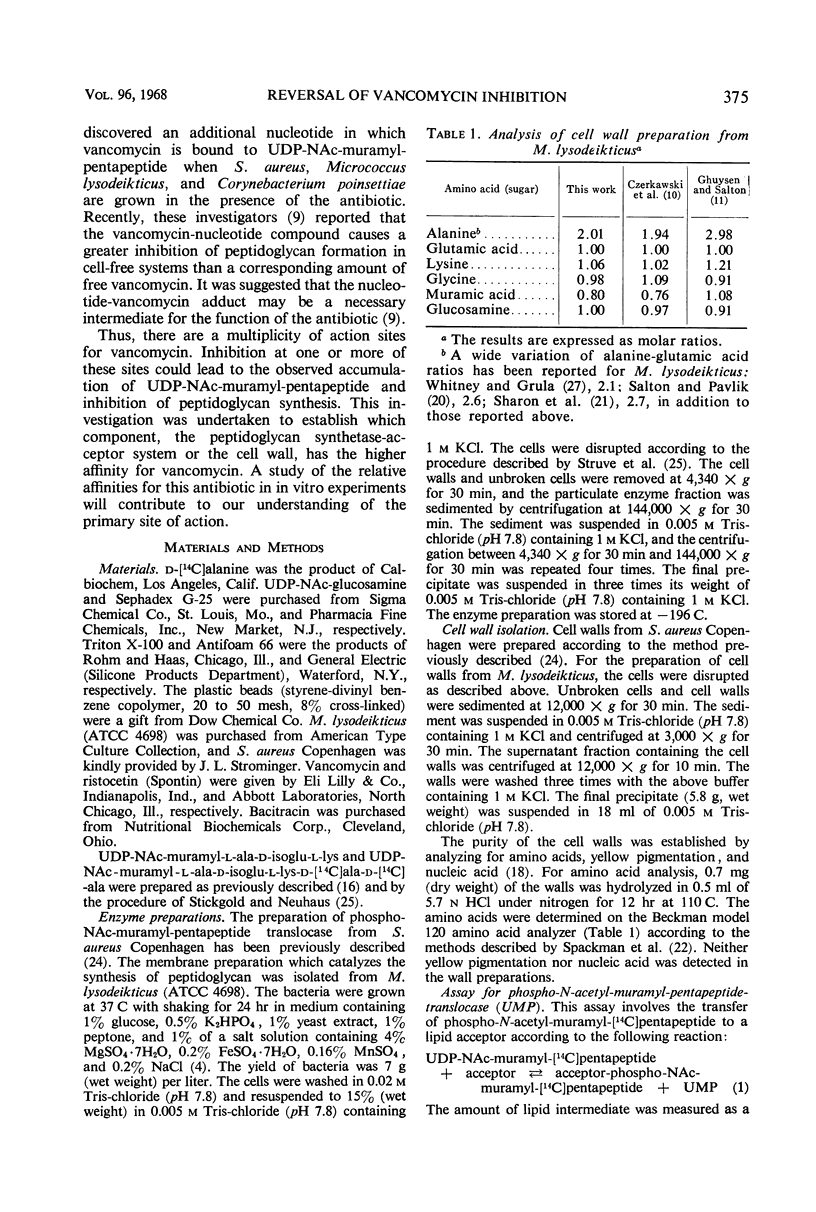
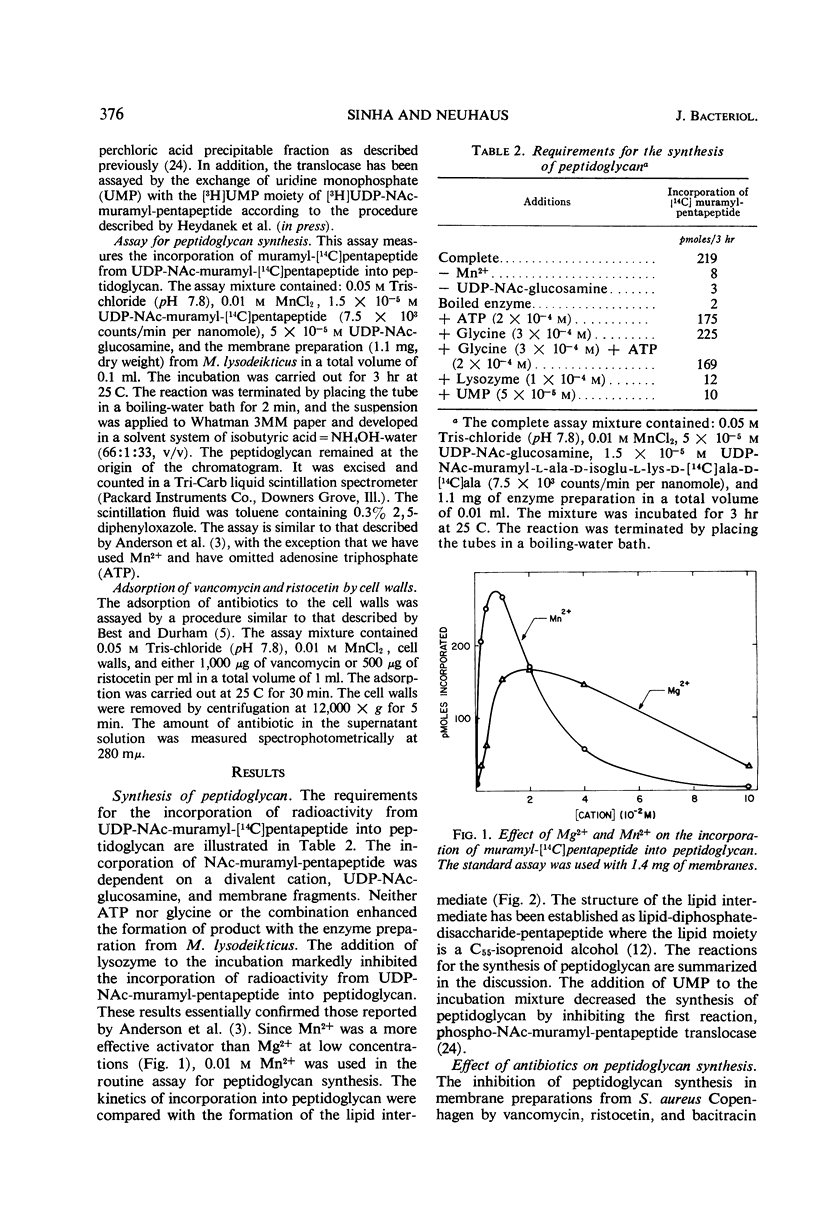
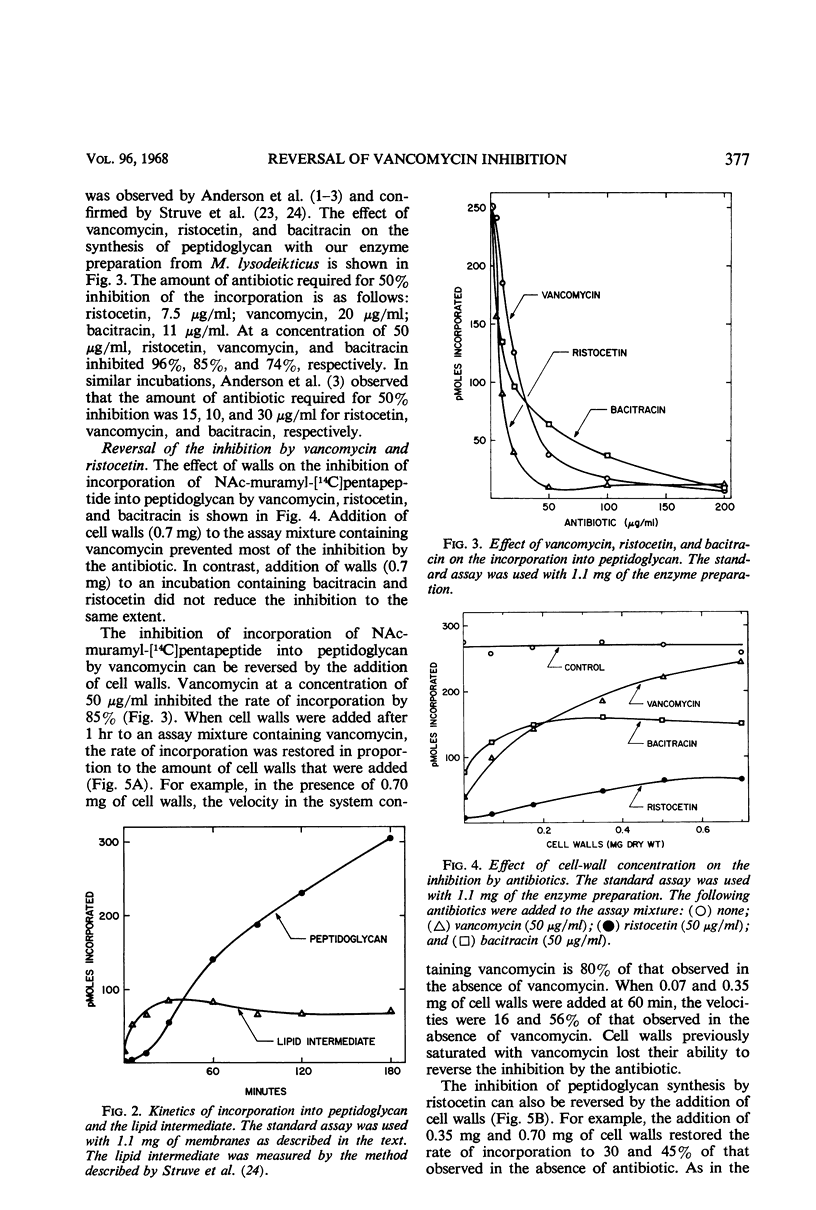
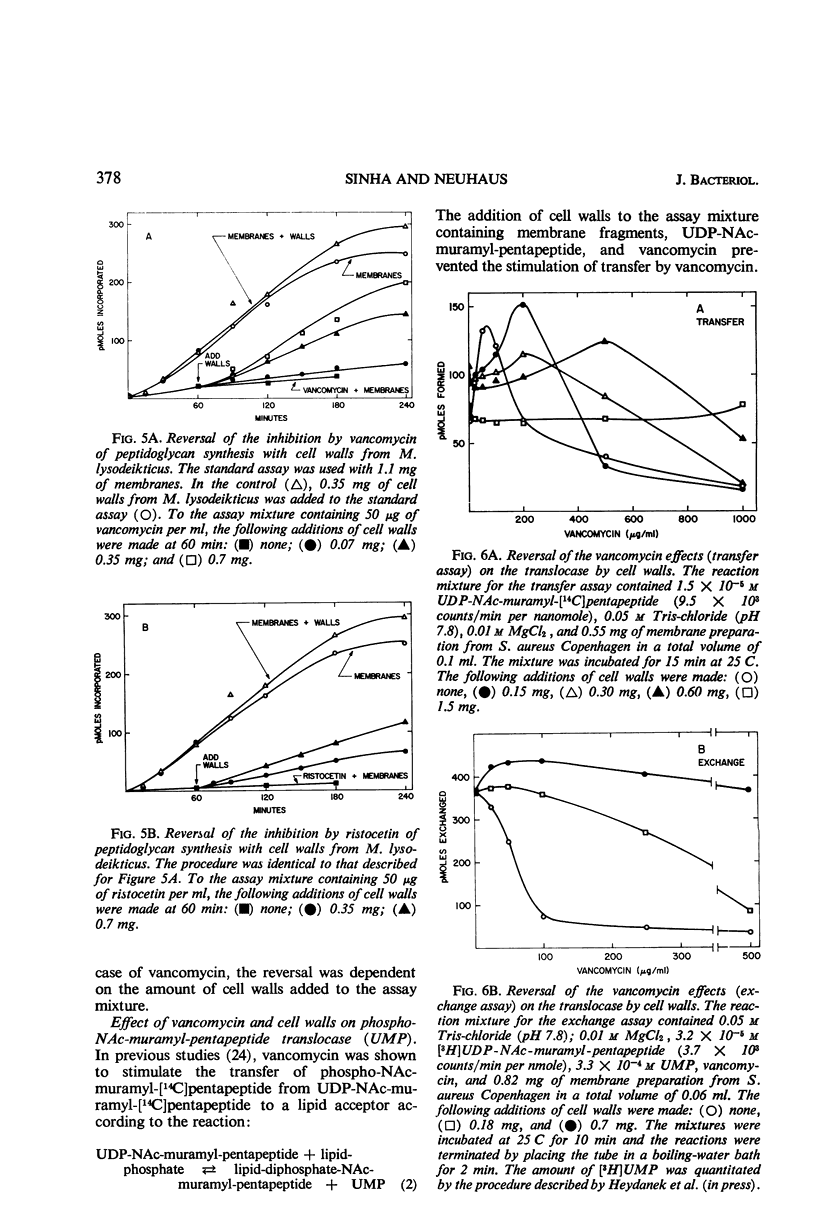
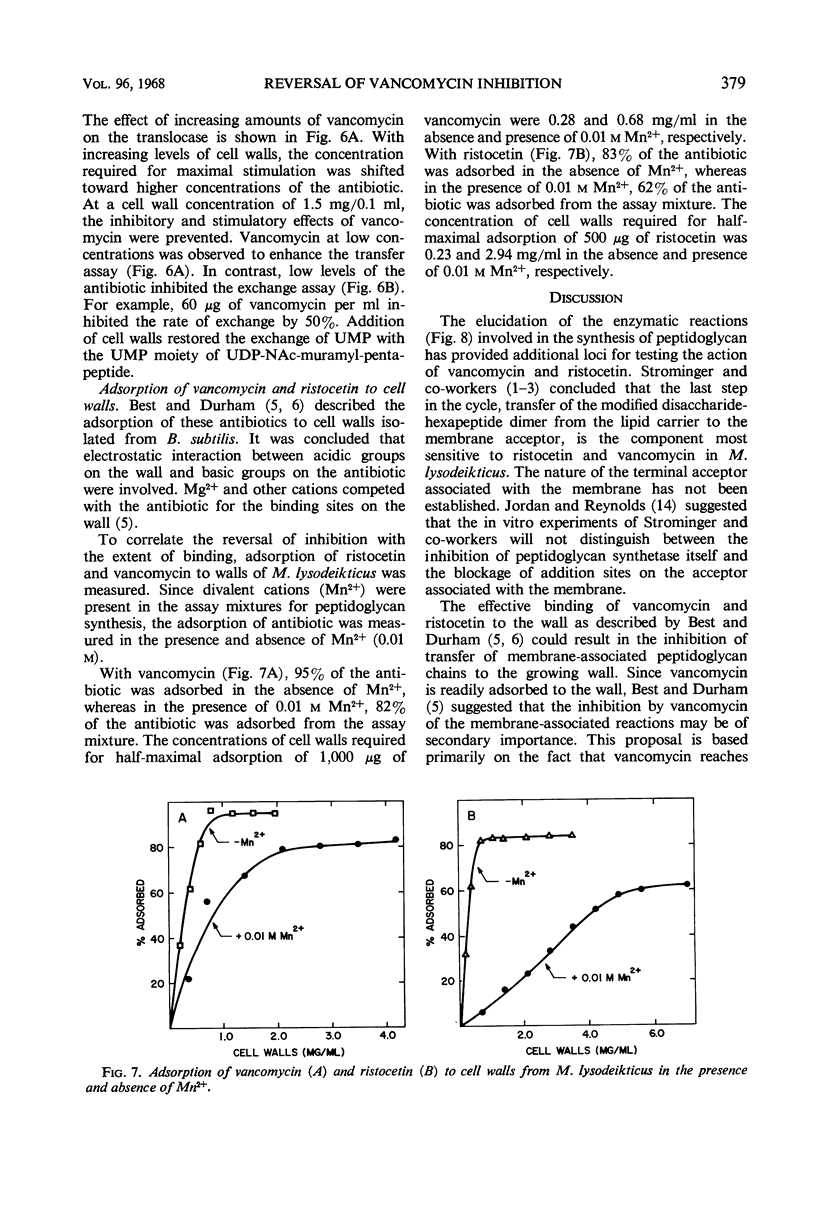
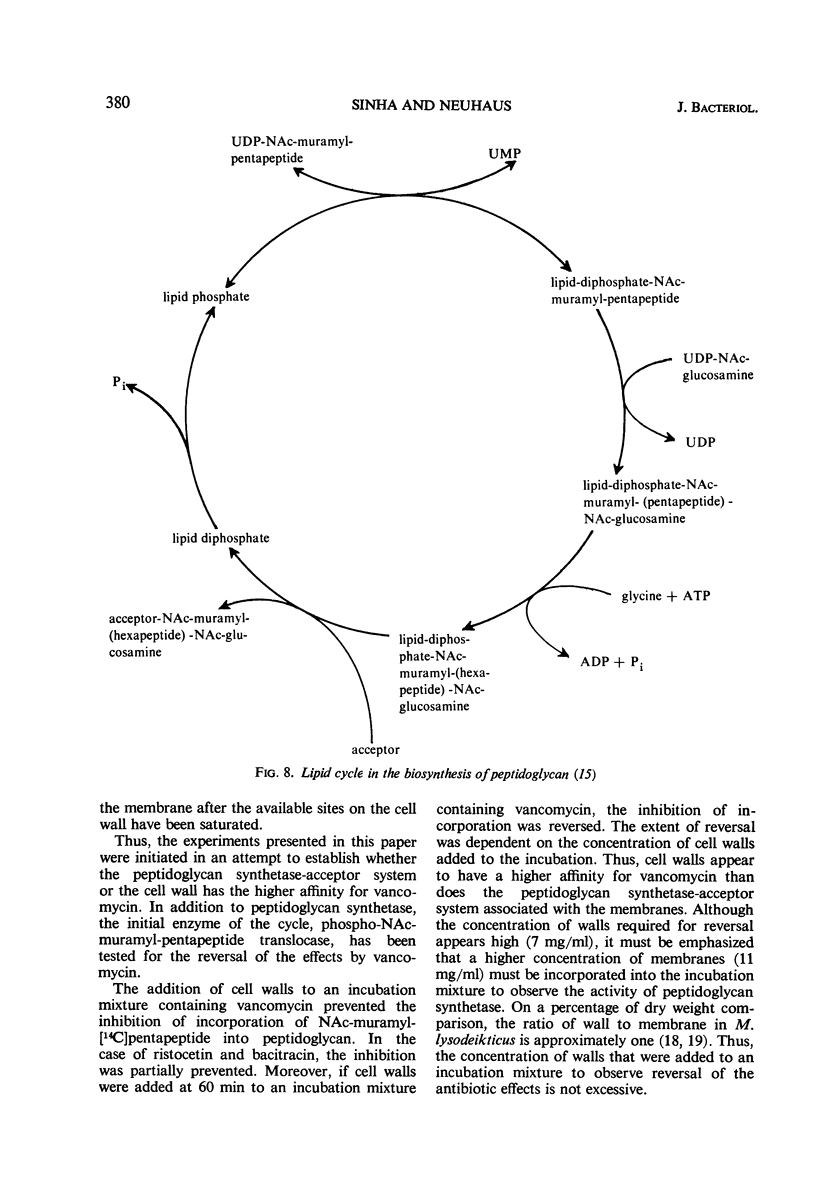
Addition of cell walls to the peptidoglycan synthetase-acceptor system containing vancomycin (50 μg/ml) prevented the inhibition by the antibiotic. In addition, the inhibition of incorporation of [14C]muramyl-pentapeptide into peptidoglycan in the presence of vancomycin was reversed by the addition of cell walls to the assay mixture at 60 min. Cell walls previously saturated with vancomycin lost their ability to reverse the inhibition by the antibiotic. The inhibition of peptidoglycan synthesis by ristocetin was partially reversed by the addition of cell walls. The initial stage in peptidoglycan synthesis is catalyzed by phospho-N-acetyl(NAc)muramyl-pentapeptide translocase (uridine 5′-phosphate) according to the reaction: UDP-NAc-muramyl-pentapeptide + acceptor ⇄ acceptor-phospho-NAc-muramyl-pentapeptide + UMP where acceptor is C55-isoprenoid alcohol phosphate. Vancomycin stimulates the transfer of phospho-NAc-muramyl-pentapeptide to the acceptor, and the addition of cell walls to this assay mixture prevented the stimulation of transfer. In addition to the transfer reaction, the enzyme catalyzes the exchange of [3H]uridine monophosphate (UMP) with UDP-NAc-muramyl-pentapeptide. The exchange reaction is effectively inhibited by vancomycin. For example, 60 μg of vancomycin per ml inhibited the rate of exchange by 50%. Addition of cell walls restored the exchange of UMP with the UMP moiety of UDP-NAc-muramyl-pentapeptide. Thus, cell walls appeared to have a higher affinity for vancomycin than did either the peptidoglycan synthetase-acceptor system or phospho-NAc-muramyl-pentapeptide translocase. These results provide support for the proposal made by Best and Durham that the effective binding of vancomycin to the cell wall could result in the inhibition of transfer of membrane-associated peptidoglycan chains to the growing wall.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. S., Matsuhashi M., Haskin M. A., Strominger J. L. Biosythesis of the peptidoglycan of bacterial cell walls. II. Phospholipid carriers in the reaction sequence. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jul 10;242(13):3180–3190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. S., Meadow P. M., Haskin M. A., Strominger J. L. Biosynthesis of the peptidoglycan of bacterial cell walls. I. Utilization of uridine diphosphate acetylmuramyl pentapeptide and uridine diphosphate acetylglucosamine for peptidoglycan synthesis by particulate enzymes from Staphylococcus aureus and Micrococcus lysodeikticus. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Sep 26;116(1):487–515. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90056-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEERS R. F., Jr Submerged culture of Micrococcus lysodeikticus for large-scale production of cells. Science. 1955 Nov 25;122(3178):1016–1016. doi: 10.1126/science.122.3178.1016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURGER M. M., GLASER L. THE SYNTHESIS OF TEICHOIC ACIDS. I. POLYGLYCEROPHOSPHATE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Oct;239:3168–3177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Best G. K., Durham N. N. Adsorption of the ristocetins to Bacillus subtilis cell walls. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1965;5:334–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Best G. K., Durham N. N. Vancomycin adsorption to Bacillus subtilis cell walls. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1965 Sep;111(3):685–691. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(65)90250-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CZERKAWSKI J. W., PERKINS H. R., ROGERS H. J. A study of the composition and structure of the cell-wall mucopeptide of micrococcus lysodeikticus. Biochem J. 1963 Mar;86:468–474. doi: 10.1042/bj0860468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee A. N., Perkins H. R. Compounds formed between nucleotides related to the biosynthesis of bacterial cell wall and vancomycin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Aug 12;24(3):489–494. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90188-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee A. N., Ward J. B., Perkins H. R. Synthesis of mucopeptide by L-form membranes. Nature. 1967 Jun 24;214(5095):1311–1314. doi: 10.1038/2141311a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GHUYSEN J. M., SALTON M. R. Acetylhexosamine compounds enzymically released from Micrococcus lysodeikticus cell walls. I. Isolation and composition of acetylhexosamine and acetylhexosamine-peptide complexes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Jun 3;40:462–472. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91387-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi Y., Strominger J. L., Sweeley C. C. Structure of a lipid intermediate in cell wall peptidoglycan synthesis: a derivative of a C55 isoprenoid alcohol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jun;57(6):1878–1884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.6.1878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JORDAN D. C. EFFECT OF VANCOMYCIN ON THE SYNTHESIS OF THE CELL WALL AND CYTOPLASMIC MEMBRANE OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. Can J Microbiol. 1965 Apr;11:390–393. doi: 10.1139/m65-050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz W., Matsuhashi M., Dietrich C. P., Strominger J. L. Biosynthesis of the peptidoglycan of bacterial cell walls. IV. Incorporation of glycine in Micrococcus lysodeikticus. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jul 10;242(13):3207–3217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEUHAUS F. C., STRUVE W. G. ENZYMATIC SYNTHESIS OF ANALOGS OF THE CELL-WALL PRECURSOR. I. KINETICS AND SPECIFICITY OF URIDINE DIPHOSPHO-N-ACETYLMURAMYL-L-ALANYL-D-GLUTAMYL-L-LYSINE:D-ALANYL-D-ALANINE LIGASE (ADENOSINE DIPHOSPHATE) FROM STREPTOCOCCUS FAECALIS R. Biochemistry. 1965 Jan;4:120–131. doi: 10.1021/bi00877a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS P. E. Studies on the mode of action of vancomycin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Sep 16;52:403–405. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90698-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALTON M. R., PAVLIK J. G. Studies of the bacterial cell wall. VI. Wall composition and sensitivity to lysozyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Apr 22;39:398–407. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90191-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRUVE W. G., NEUHAUS F. C. EVIDENCE FOR AN INITIAL ACCEPTOR OF UDP-NAC-MURAMYL-PENTAPEPTIDE IN THE SYNTHESIS OF BACTERIAL MUCOPEPTIDE. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Jan 4;18:6–12. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90873-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharon N., Osawa T., Flowers H. M., Jeanloz R. W. Isolation and study of the chemical structure of a disaccharide from Micrococcus lysodeikticus cell walls. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jan 10;241(1):223–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stickgold R. A., Neuhaus F. C. On the initial stage in peptidoglycan synthesis. Effect of 5-fluorouracil substitution on phospho-N-acetylmuramyl-pentapeptide translocase (uridine 5'-phosphate). J Biol Chem. 1967 Mar 25;242(6):1331–1337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struve W. G., Sinha R. K., Neuhaus F. C. On the initial stage in peptidoglycan synthesis. Phospho-N-acetylmuramyl-pentapeptide translocase (uridine monophosphate). Biochemistry. 1966 Jan;5(1):82–93. doi: 10.1021/bi00865a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALLAS C. H., STROMINGER J. L. Ristocetins, inhibitors of cell wall synthesis in Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jul;238:2264–2266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitney J. G., Grula E. A. Incorporation of D-serine into the cell wall mucopeptide of Micrococcus lysodeikticus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964;14:375–381. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(64)80013-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


