Abstract
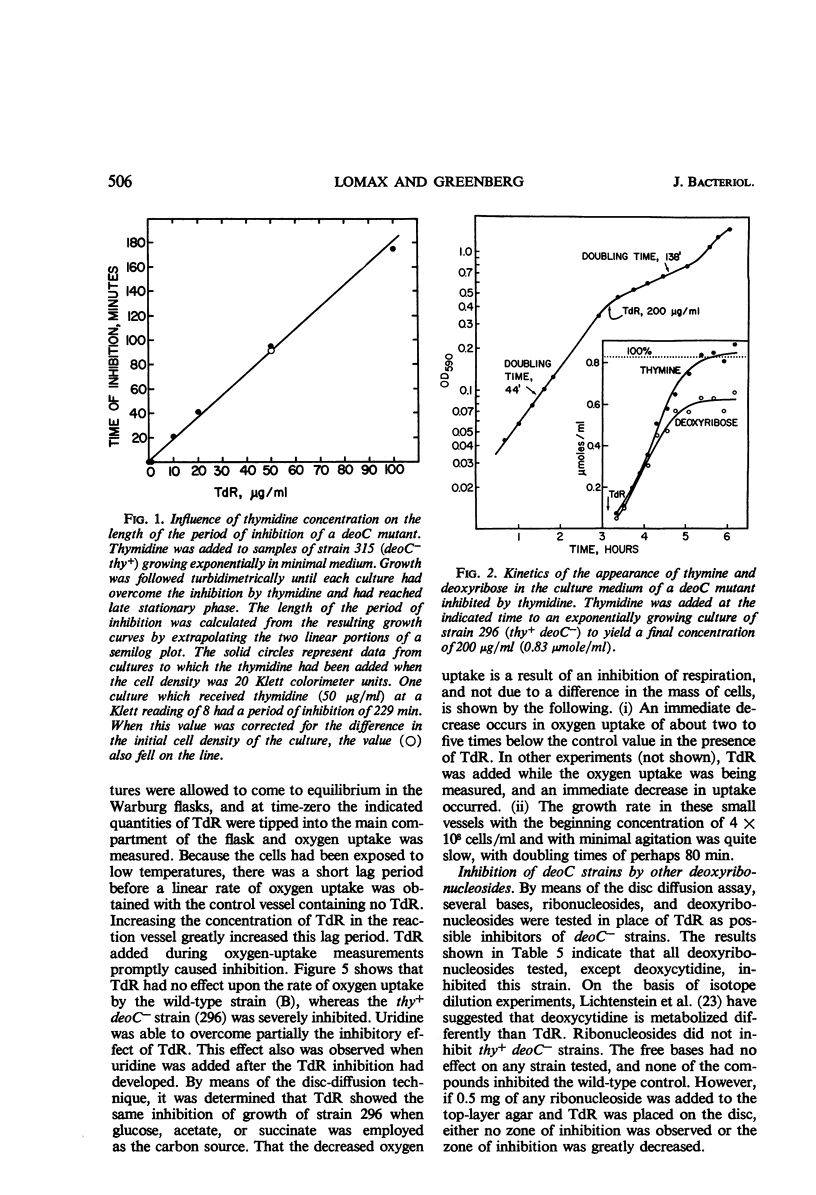
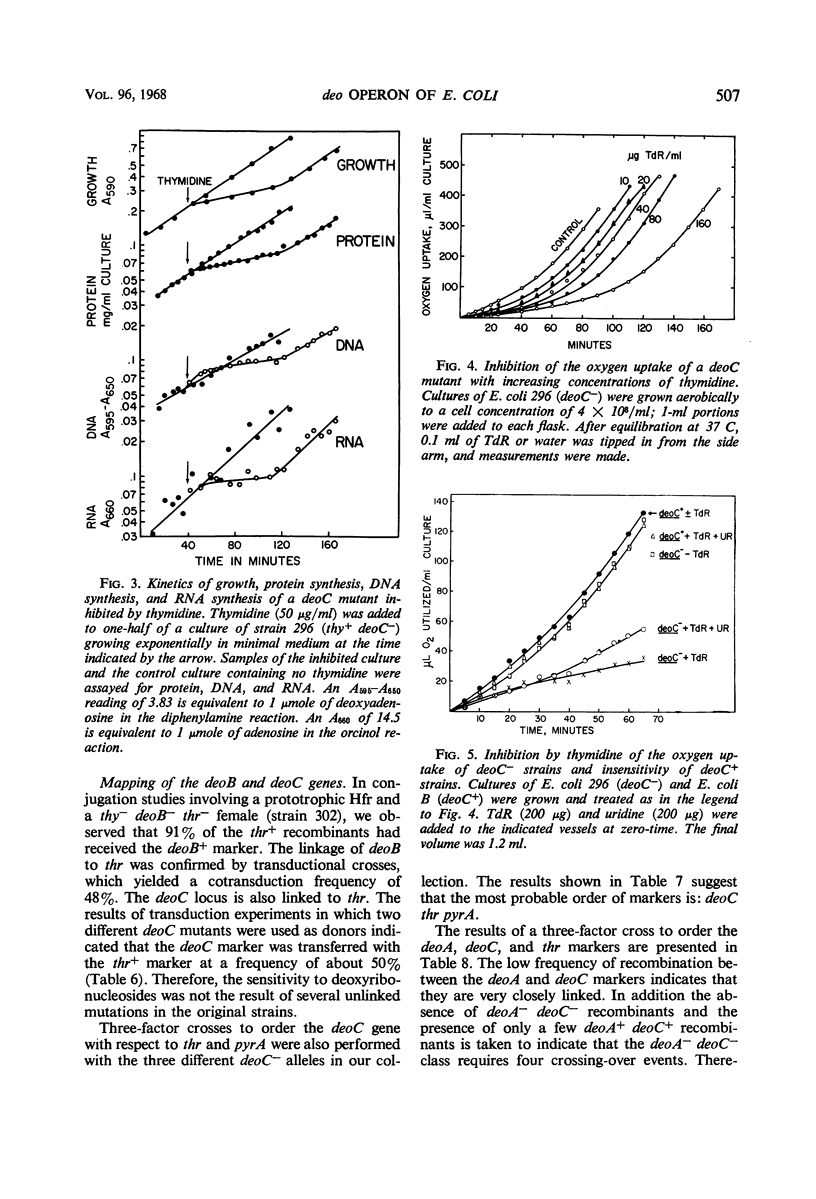
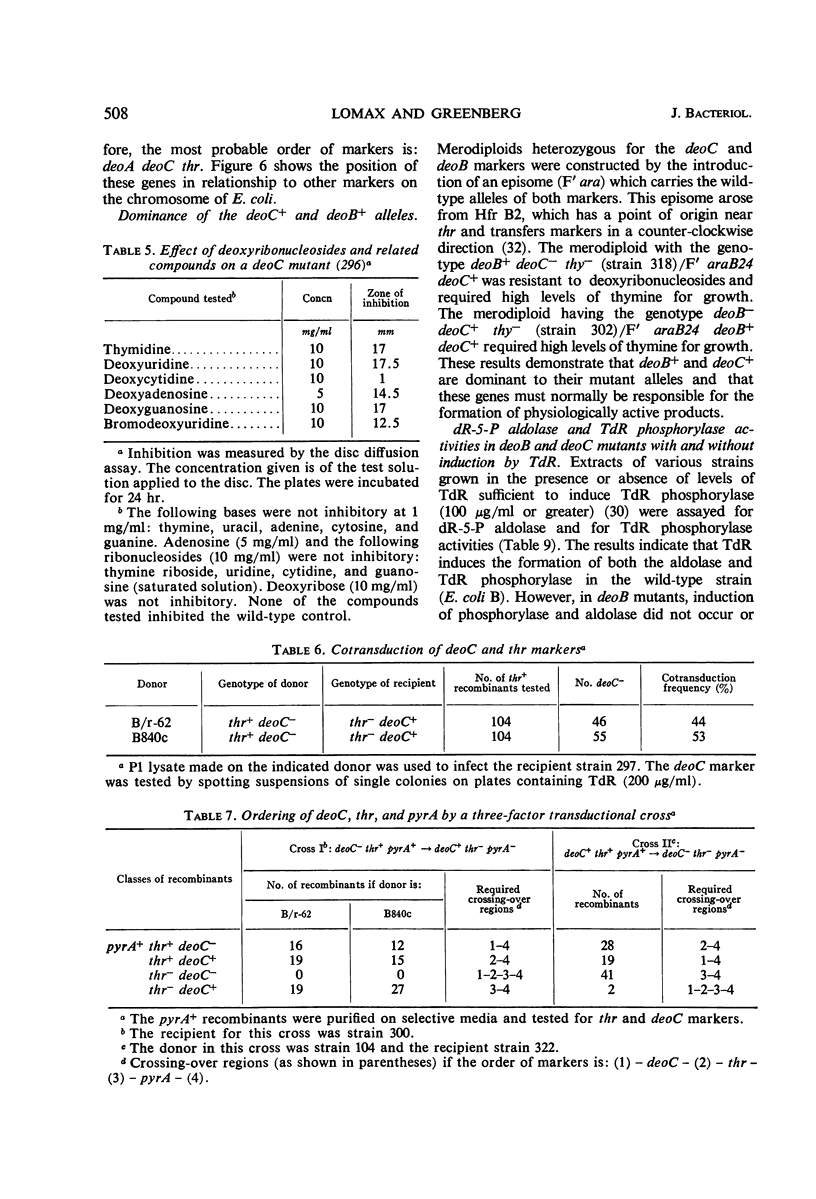
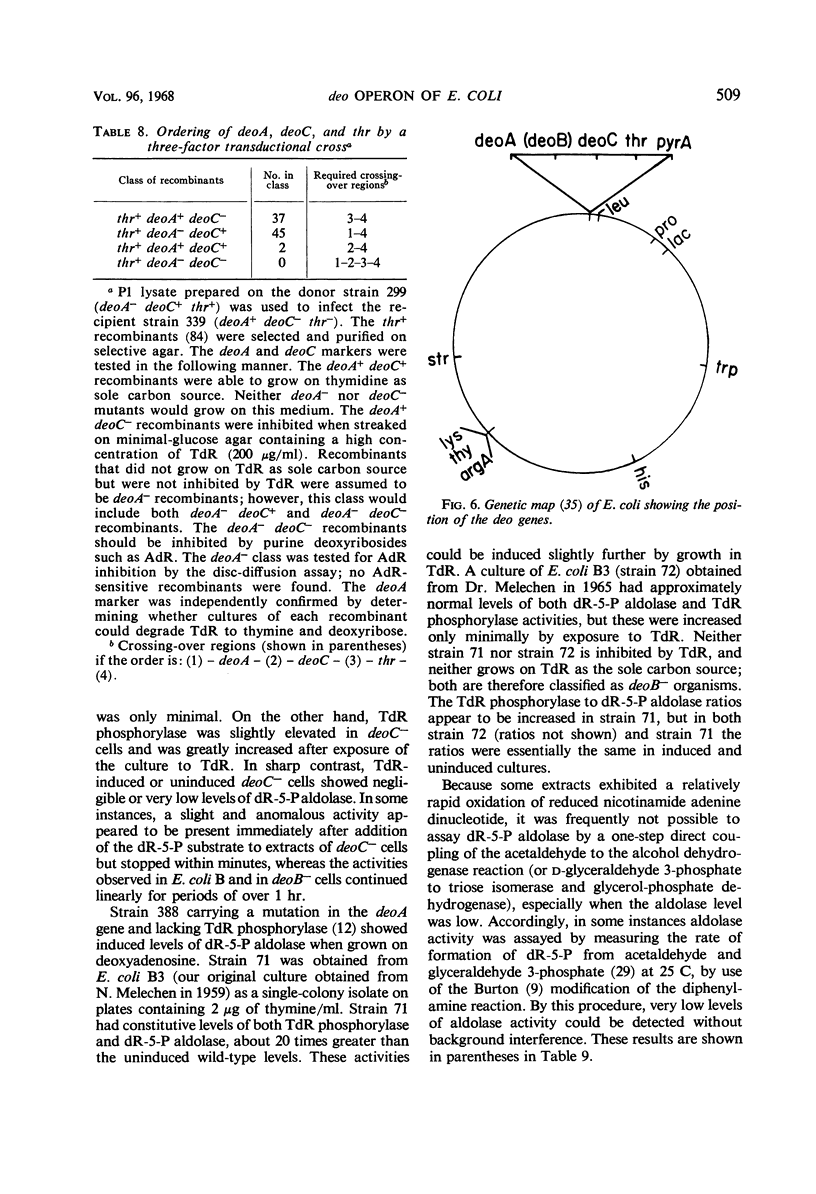
Inability to grow on deoxyribonucleosides as the sole carbon source is characteristic of deo mutants of Escherichia coli. Growth of deoC mutants, which lack deoxyribose 5-phosphate aldolase, is reversibly inhibited by deoxyribonucleosides through inhibition of respiration. By contrast, deoB mutants are not sensitive to deoxyribonucleosides, and deoxyribose 5-phosphate aldolase and thymidine phosphorylase are present at normal levels but are not inducible by thymidine. Organisms with the genotype deoB−thy− or deoC−thy− are able to grow on low levels of thymine, whereas deoB+thy− or deoC+thy− strains require high levels of thymine for growth. The deoB and deoC mutations are transducible with and map on the counterclockwise side of the threonine marker. They are closely linked to deoA, a gene determining thymidine phosphorylase. Merodiploids heterozygous for either the deoB or deoC genes are resistant to deoxyribonucleosides and, in combination with the thy mutation, require high levels of thymine for growth. Cultures of thy+deoC− mutants are inhibited by thymidine until this compound has been completely degraded and excreted as deoxyribose and thymine, whereupon growth promptly resumes at a normal rate. The inhibition of respiration in deoC strains and the induction of thymidine phosphorylase and deoxyribose 5-phosphate aldolase in the wild-type organism are considered to result from the accumulation of deoxyribose 5-phosphate.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLEN M. K., YANOFSKY C. A BIOCHEMICAL AND GENETIC STUDY OF REVERSION WITH THE A-GENE A-PROTEIN SYSTEM OF ESCHERICHIA COLI TRYPTOPHAN SYNTHETASE. Genetics. 1963 Aug;48:1065–1083. doi: 10.1093/genetics/48.8.1065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alikhanian S. I., Iljina T. S., Kaliaeva E. S., Kameneva S. V., Sukhodolec V. V. A genetical study of thymineless mutants of E. coli K12. Genet Res. 1966 Aug;8(1):83–100. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300009939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitman T. R., Bradford R. M. Inability of low thymine-requiring mutants of Escherichia coli lacking phosphodeoxyribomutase to be induced for deoxythymidine phosphorylase and deoxyriboaldolase. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2434–2435. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2434-2435.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitman T. R., Bradford R. M. Metabolism of thymineless mutants of Escherichia coli. I. Absence of thymidylate synthetase activity and growth characteristics of two sequential thymineless mutants. J Bacteriol. 1967 Mar;93(3):845–852. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.3.845-852.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitman T. R., Bradford R. M. The absence of deoxyriboaldolase activity in a thymineless mutant of Escherichia coli strain 15: a possible explanation for the low thymine requirement of some thymineless strains. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Mar 29;138(1):217–220. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90610-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budman D. R., Pardee A. B. Thymidine and thymine incorporation into deoxyribonucleic acid: inhibition and repression by uridine of thymidine phosphorylase of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1546–1550. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1546-1550.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale B., Greenberg G. R. Genetic mapping of a mutation in Escherichia coli showing reduced activity of thymidine phosphorylase. J Bacteriol. 1967 Sep;94(3):778–779. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.3.778-779.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDKIN M., ROBERTS D. The enzymatic synthesis of nucleosides. I. Thymidine phosphorylase in mammalian tissue. J Biol Chem. 1954 Mar;207(1):245–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fangman W. L., Novick A. Mutant bacteria showing efficient utilization of thymidine. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jun;91(6):2390–2391. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.6.2390-2391.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORINI L., KAUFMAN H. Selecting bacterial mutants by the penicillin method. Science. 1960 Feb 26;131(3400):604–605. doi: 10.1126/science.131.3400.604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS J., ENGLESBERG E. Determination of the order of mutational sites governing L-arabinose utilization in Escherichia coli B/r bv transduction with phage Plbt. Virology. 1959 Nov;9:314–331. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(59)90125-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFFMANN C. E., LAMPEN J. O. Products of desoxyribose degradation by Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1952 Oct;198(2):885–893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison A. P., Jr Thymine incorporation and metabolism by various classes of thymine-less bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Dec;41(3):321–333. doi: 10.1099/00221287-41-3-321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffee P. A. 2-deoxyribose gene-enzyme complex in Salmonella typhimurium. I. Isolation and enzymatic characterization of 2-deoxyribose-negative mutants. J Bacteriol. 1968 Feb;95(2):449–457. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.2.449-457.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAUDEWITZ F. Production of bacterial mutants with nitrous acid. Nature. 1959 Jun 27;183:1829–1830. doi: 10.1038/1831829a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LENNOX E. S. Transduction of linked genetic characters of the host by bacteriophage P1. Virology. 1955 Jul;1(2):190–206. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(55)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LICHTENSTEIN J., BARNER H. D., COHEN S. S. The metabolism of exogenously supplied nucleotides by Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1960 Feb;235:457–465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OKADA T., YANAGISAWA K., RYAN F. J. A method for securing thymineless mutants from strains of E. coli. Z Vererbungsl. 1961;92:403–412. doi: 10.1007/BF00890061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada T. Mutational Site of the Gene Controlling Quantitative Thymine Requirement in ESCHERICHIA COLI K-12. Genetics. 1966 Dec;54(6):1329–1336. doi: 10.1093/genetics/54.6.1329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piérard A., Glansdorff N., Mergeay M., Wiame J. M. Control of the biosynthesis of carbamoyl phosphate in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1965 Nov;14(1):23–36. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80226-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RACHMELER M., GERHART J., ROSNER J. Limited thymidine uptake in Escherichia coli due to an inducible thymidine phosphorylase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Apr 29;49:222–225. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90888-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RACKER E. Enzymatic synthesis and breakdown of desoxyribose phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1952 May;196(1):347–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAZZELL W. E., CASSHYAP P. SUBSTRATE SPECIFICITY AND INDUCTION OF THYMIDINE PHOSPHORYLASE IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jun;239:1789–1793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAPIRO D. M., EIGNER J., GREENBERG G. R. INABILITY OF THYMINE-DEPENDENT MUTANTS OF BACTERIOPHAGE T4 TO INDUCE THYMIDYLATE SYNTHETASE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Apr;53:874–881. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.4.874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH C. G., BERNSTEIN I. A. Studies on phosphodeoxyribomutase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Sep 2;52:184–193. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90916-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STACEY K. A., SIMSON E. IMPROVED METHOD FOR THE ISOLATION OF THYMINE-REQUIRING MUTANTS OF ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Bacteriol. 1965 Aug;90:554–555. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.2.554-555.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard D., Englesberg E. Positive control in the L-arabinose gene-enzyme complex of Escherichia coli B/r exhibited with stable merodiploids. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1966;31:345–347. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1966.031.01.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A. L., Trotter C. D. Revised linkage map of Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1967 Dec;31(4):332–353. doi: 10.1128/br.31.4.332-353.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


