Abstract
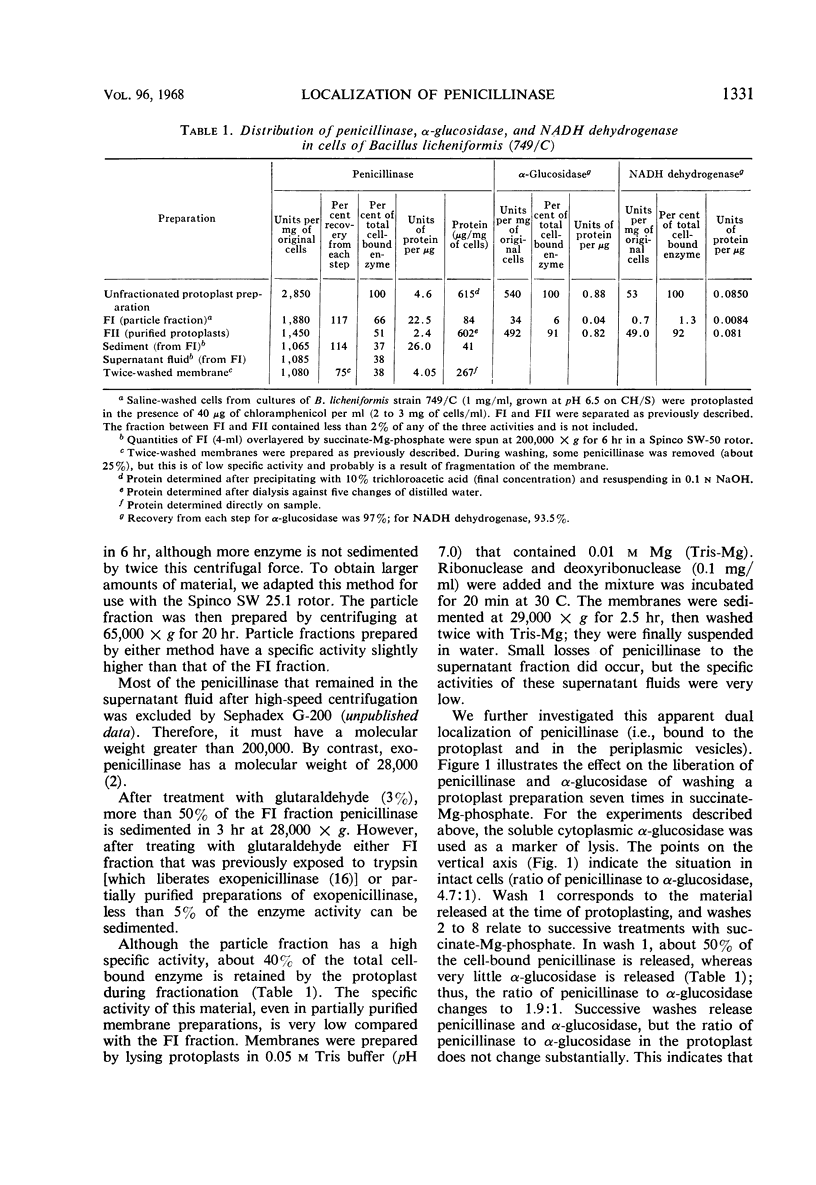
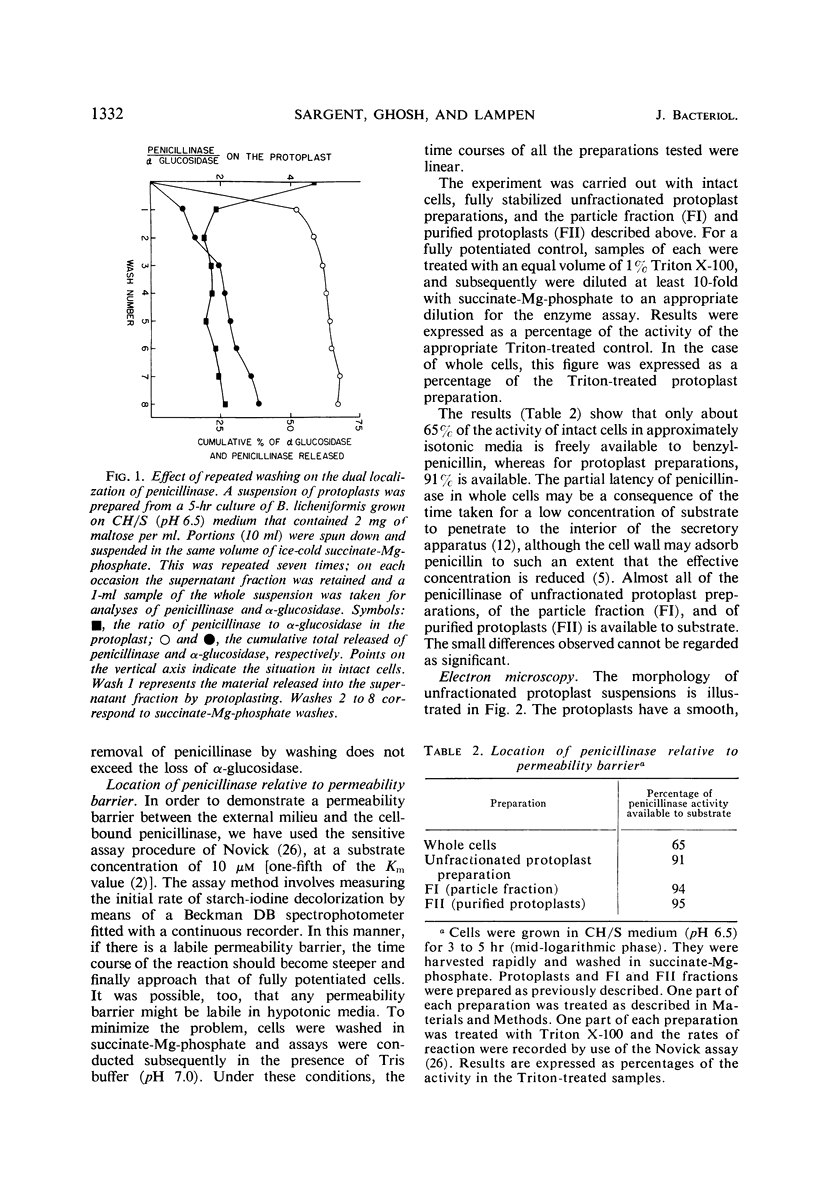
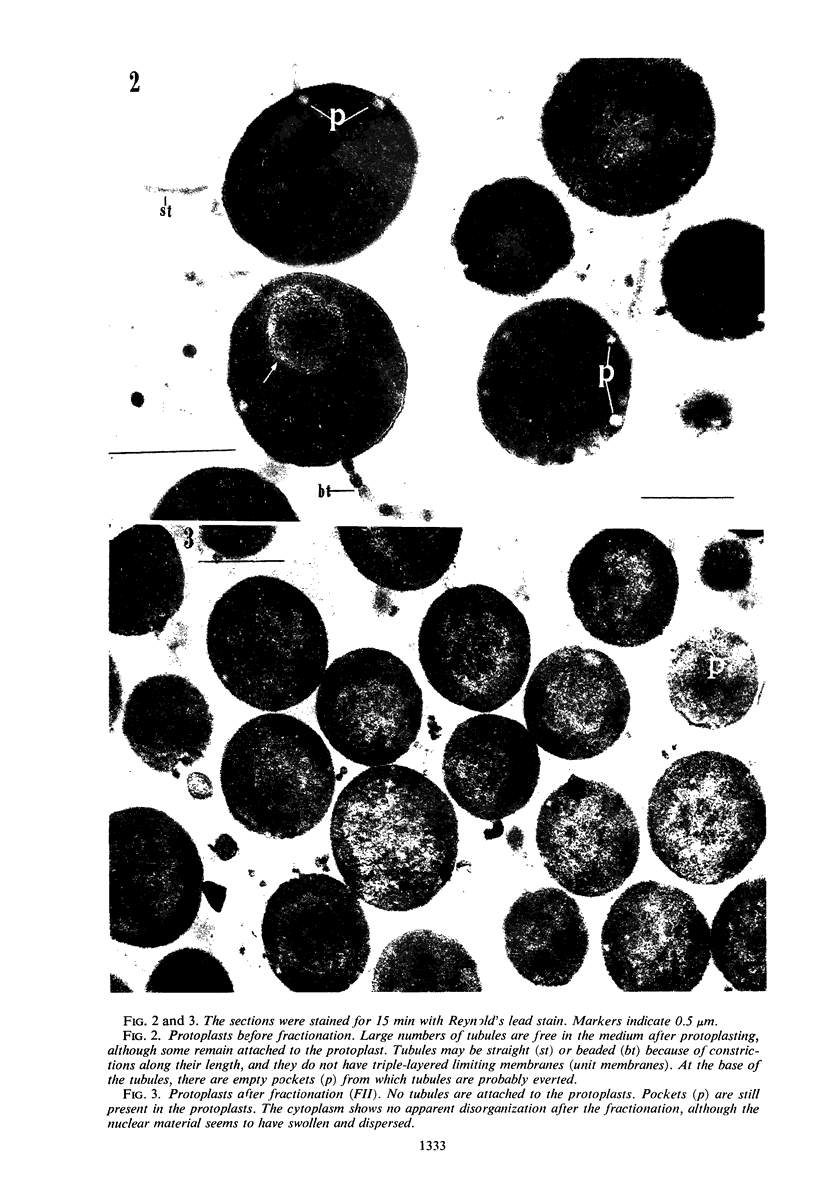
When protoplasts are prepared from Bacillus licheniformis (strain 749/C, constitutive for penicillinase), approximately 60% of the cell-bound penicillinase is released. The remainder is retained by the protoplast and cannot be removed by washing. This release is specific, in that less than 7% of the cellular reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) dehydrogenase and α-glucosidase is liberated by the treatment. The freed penicillinase is excluded from G-200 Sephadex, and it is partially sedimented with a force of 65,000 × g for 20 hr. It is probably attached to characteristic tubular and vesicular structures with single-layered membranes that are comparable to structures previously described in intact penicillinase-forming cells. The specific activity of the organelle is more than six times that of twice washed peripheral membrane; furthermore, about 8% of the protein of the structure is penicillinase. At substrate concentrations (benzylpenicillin) of about one-fifth the Km value, whole cells show a slight permeability restriction, although this does not occur in isolated particles and protoplasts.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C. Cellular site in Bacillus subtilis of a nuclease which preferentially degrades single-stranded nucleic acids. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1004–1011. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1004-1011.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPER P. D. Site of action of radiopenicillin. Bacteriol Rev. 1956 Mar;20(1):28–48. doi: 10.1128/br.20.1.28-48.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citri N., Pollock M. R. The biochemistry and function of beta-lactamase (penicillinase). Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1966;28:237–323. doi: 10.1002/9780470122730.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coles N. W., Gross R. Influence of organic anions on the liberation of penicillinase from Staphylococcus aureus. Biochem J. 1967 Mar;102(3):748–752. doi: 10.1042/bj1020748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coles N. W., Gross R. Liberation of surface-located penicillinase from Staphylococcus aureus. Biochem J. 1967 Mar;102(3):742–747. doi: 10.1042/bj1020742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEMIS D. J., ROTHSTEIN A., MEIER R. The relationship of the cell surface to metabolism. X. The location and function of invertase in the yeast cell. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1954 Jan;48(1):55–62. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(54)90305-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FITZ-JAMES P. FATE OF THE MESOSOMES OF BACILLUS MEGATERIUM DURING PROTOPLASTING. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jun;87:1483–1491. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.6.1483-1491.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIIS J., OTTOLENGHI P. Localization of invertase in a strain of veast. C R Trav Lab Carlsberg. 1959;31:259–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIIS J., OTTOLENGHI P. Localization of melibiase in a strain of veast. C R Trav Lab Carlsberg. 1959;31:272–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh B. K., Murray R. G. Fine structure of Listeria monocytogenes in relation to protoplast formation. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):411–426. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.1.411-426.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh B. K., Sargent M. G., Lampen J. O. Morphological phenomena associated with penicillinase induction and secretion in Bacillus licheniformis. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):1314–1328. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.1314-1328.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heppel L. A. Selective release of enzymes from bacteria. Science. 1967 Jun 16;156(3781):1451–1455. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3781.1451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUSHNER D. J., POLLOCK M. R. The location of cell-bound penicillinase in Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Oct;26:255–265. doi: 10.1099/00221287-26-2-255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampen J. O. Cell-bound penicillinase of Bacillus licheniformis; properties and purification. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Aug;48(2):249–259. doi: 10.1099/00221287-48-2-249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampen J. O. Release of penicillinase by Bacillus licheniformis. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Aug;48(2):261–268. doi: 10.1099/00221287-48-2-261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALAMY M. H., HORECKER B. L. RELEASE OF ALKALINE PHOSPHATASE FROM CELLS OF ESCHERICHIA COLI UPON LYSOZYME SPHEROPLAST FORMATION. Biochemistry. 1964 Dec;3:1889–1893. doi: 10.1021/bi00900a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALAMY M., HORECKER B. L. The localization of alkaline phosphatase in E. coli K12. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1961 Jun 2;5:104–108. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(61)90020-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOVICK R. P. Micro-iodometric assay for penicillinase. Biochem J. 1962 May;83:236–240. doi: 10.1042/bj0830236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLLOCK M. R. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF PENICILLINASES FROM TWO STRAINS OF BACILLUS LICHENIFORMIS: A CHEMICAL, PHYSICOCHEMICAL AND PHYSIOLOGICAL COMPARISON. Biochem J. 1965 Mar;94:666–675. doi: 10.1042/bj0940666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLLOCK M. R. The measurement of the liberation of penicillinase from Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Oct;26:239–253. doi: 10.1099/00221287-26-2-239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POMERANZ V. INACTIVATION OF ALPHA-AMYLASES BY COBALT COMPLEXES. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Nov 8;77:451–454. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90520-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYTER A., JACOB F. ETUDE AU MICROSCOPE 'ELECTRONIQUE DE LA LIAISON ENTRE NOYAU ET M'ESOSOME CHEZ BACILLUS SUBTILIS. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1964 Sep;107:384–400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYTER A., LANDMAN O. E. ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY OF THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN MESOSOME LOSS AND THE STABLE L STATE (OR PROTOPLAST STATE) IN BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Aug;88:457–467. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.2.457-467.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaveley D. A. The isolation and characterisation of cytoplasmic membranes and mesosomes of Bacillus licheniformis 6346. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Mar 27;30(6):649–655. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90562-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryter A. Association of the nucleus and the membrane of bacteria: a morphological study. Bacteriol Rev. 1968 Mar;32(1):39–54. doi: 10.1128/br.32.1.39-54.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryter A., Frehel C., Ferrandes B. Comportement des mésosomes lors de l'attaque de Bacillus subtilis par le lysozyme en milieu hyper- ou hypotonique. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1967 Oct 23;265(17):1259–1262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryter A., Jacob F. Etude morphologique de la liaison du noyau à la membrane chez E. coli et chez les protoplastes de B. subtilis. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1966 Jun;110(6):801–812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEININ R. The localizatio of the cell-bound penicillinase of Bacillus cereus in protoplasts. J Gen Microbiol. 1959 Aug;21:124–134. doi: 10.1099/00221287-21-1-124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUTTON D. D., LAMPEN J. O. Localization of sucrose and maltose fermenting systems in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jan 29;56:303–312. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90567-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent M. G. Rapid fixed-time assay for penicillinase. J Bacteriol. 1968 Apr;95(4):1493–1494. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.4.1493-1494.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weimberg R., Orton W. L. Elution of Acid Phosphatase from the Cell Surface of Saccharomyces mellis by Potassium Chloride. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jul;90(1):82–94. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.1.82-94.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weimberg R., Orton W. L. Elution of exocellular enzymes from Saccharomyces fragilis and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):1–13. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.1.1-13.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




