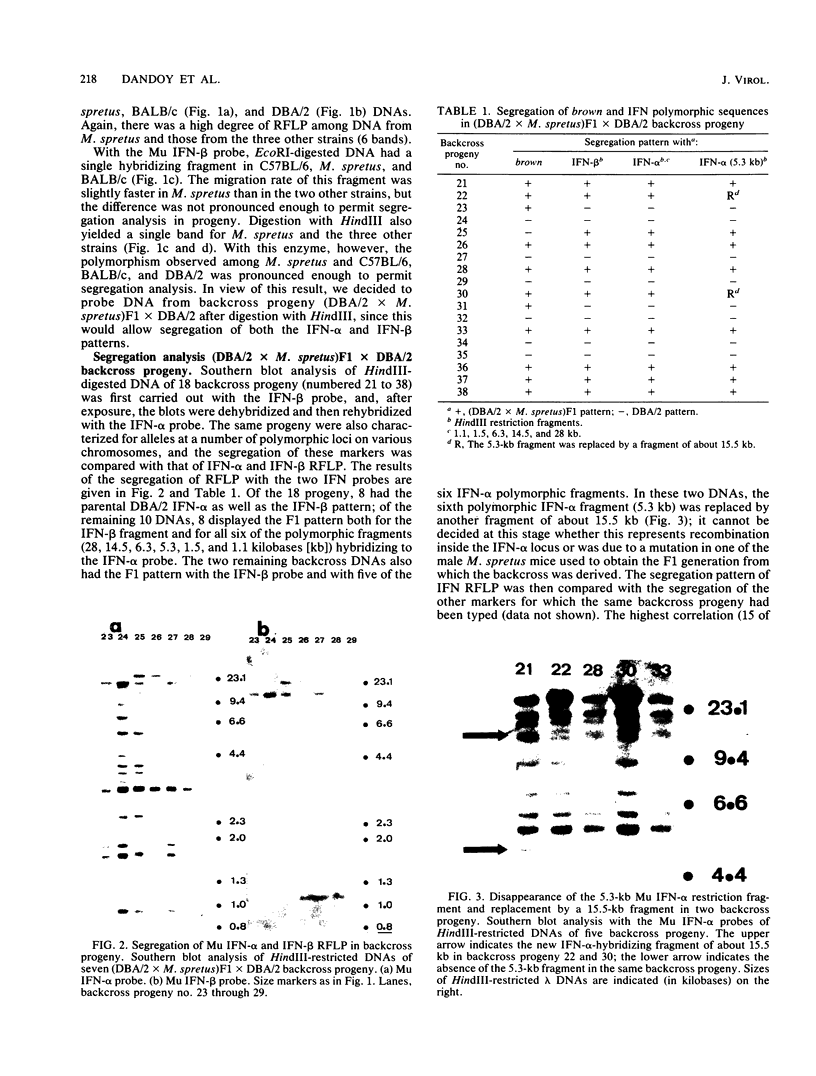
Abstract
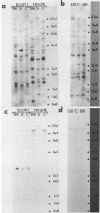
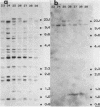
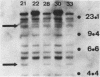
Southern blot analysis with murine (Mu) interferon (IFN)-alpha cDNA of restricted genomic DNA of three inbred strains of mice belonging to the species Mus musculus domesticus (BALB/c, C57BL/6, and DBA/2) revealed only a limited degree of polymorphism. For example, with HindIII there were only two polymorphic bands out of 14 hybridizing fragments. With Mu IFN-beta cDNA there was no polymorphism at all between BALB/c and C57BL/6 in DNA restricted with seven different enzymes. In contrast, HindIII-restricted DNA of an inbred strain of wild mice (M. spretus Lataste) hybridized with the IFN-alpha probe displayed a high degree of polymorphism compared with the three strains of laboratory mice and was also polymorphic when probed with IFN-beta cDNA. Although M. musculus domesticus and M. spretus Lataste represent different species, certain interspecies crosses are possible in the laboratory. This enabled us to follow segregation of restriction fragment length polymorphism in HindIII-restricted DNA obtained from 18 backcross progeny of a (DBA/2 X M. spretus)F1 X DBA/2 interspecies cross. There was complete coincidence between the segregation of parental (DBA/2) and (DBA/2 X M. spretus)F1-type IFN-beta and IFN-alpha restriction fragment length polymorphism, indicating tight linkage of the IFN-beta and IFN-alpha genes. In addition, in 15 of 18 progeny the segregation coincided with that of the brown locus on chromosome 4, in accord with previous results obtained with the IFN-alpha probe in strains derived from crosses between BALB/c and C57BL/6 mice. Thus, the Mu IFN-beta gene is tightly linked to the Mu IFN-alpha gene cluster on chromosome 4 near the brown locus.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonhomme F., Catalan J., Britton-Davidian J., Chapman V. M., Moriwaki K., Nevo E., Thaler L. Biochemical diversity and evolution in the genus Mus. Biochem Genet. 1984 Apr;22(3-4):275–303. doi: 10.1007/BF00484229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonhomme F., Martin S., Thaler L. Hybridation en laboratoire de Mus musculus L. et Mus spretus Lataste. Experientia. 1978 Sep 15;34(9):1140–1141. doi: 10.1007/BF01922917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britton J., Thaler L. Evidence for the presence of two sympatric species of mice (genus Mus L.) in southern France based on biochemical genetics. Biochem Genet. 1978 Apr;16(3-4):213–225. doi: 10.1007/BF00484079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dandoy F., Kelley K. A., DeMaeyer-Guignard J., DeMaeyer E., Pitha P. M. Linkage analysis of the murine interferon-alpha locus on chromosome 4. J Exp Med. 1984 Jul 1;160(1):294–302. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.1.294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daugherty B., Martin-Zanca D., Kelder B., Collier K., Seamans T. C., Hotta K., Pestka S. Isolation and bacterial expression of a murine alpha leukocyte interferon gene. J Interferon Res. 1984 Fall;4(4):635–643. doi: 10.1089/jir.1984.4.635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferris S. D., Sage R. D., Wilson A. C. Evidence from mtDNA sequences that common laboratory strains of inbred mice are descended from a single female. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):163–165. doi: 10.1038/295163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi Y., Sokawa Y., Watanabe Y., Kawade Y., Ohno S., Takaoka C., Taniguchi T. Structure and expression of a cloned cDNA for mouse interferon-beta. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9522–9529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley K. A., Kozak C. A., Dandoy F., Sor F., Skup D., Windass J. D., DeMaeyer-Guignard J., Pitha P. M., DeMaeyer E. Mapping of murine interferon-alpha genes to chromosome 4. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(2-3):181–188. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90188-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley K. A., Pitha P. M. Characterization of a mouse interferon gene locus I. Isolation of a cluster of four alpha interferon genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 11;13(3):805–823. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.3.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett M., Cox D. R., Yee D., Boll W., Weissmann C., Epstein C. J., Epstein L. B. The chromosomal location of mouse interferon alpha genes. EMBO J. 1984 Jul;3(7):1643–1646. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02023.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naylor S. L., Gray P. W., Lalley P. A. Mouse immune interferon (IFN-gamma) gene is on chromosome 10. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1984 Sep;10(5):531–534. doi: 10.1007/BF01534857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naylor S. L., Sakaguchi A. Y., Shows T. B., Law M. L., Goeddel D. V., Gray P. W. Human immune interferon gene is located on chromosome 12. J Exp Med. 1983 Mar 1;157(3):1020–1027. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.3.1020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owerbach D., Rutter W. J., Shows T. B., Gray P., Goeddel D. V., Lawn R. M. Leukocyte and fibroblast interferon genes are located on human chromosome 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3123–3127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G. D., Boll W., Taira H., Mantei N., Lengyel P., Weissmann C. Structure and expression of cloned murine IFN-alpha genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Feb 11;11(3):555–573. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.3.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shows T. B., Sakaguchi A. Y., Naylor S. L., Goedell D. V., Lawn R. M. Clustering of leukocyte and fibroblast interferon genes of human chromosome 9. Science. 1982 Oct 22;218(4570):373–374. doi: 10.1126/science.6181564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trent J. M., Olson S., Lawn R. M. Chromosomal localization of human leukocyte, fibroblast, and immune interferon genes by means of in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7809–7813. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann C., Nagata S., Boll W., Fountoulakis M., Fujisawa A., Fujisawa J. I., Haynes J., Henco K., Mantei N., Ragg H. Structure and expression of human IFN-alpha genes. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Sep 24;299(1094):7–28. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1982.0102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwarthoff E. C., Mooren A. T., Trapman J. Organization, structure and expression of murine interferon alpha genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 11;13(3):791–804. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.3.791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Korput J. A., Hilkens J., Kroezen V., Zwarthoff E. C., Trapman J. Mouse interferon alpha and beta genes are linked at the centromere proximal region of chromosome 4. J Gen Virol. 1985 Mar;66(Pt 3):493–502. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-3-493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]