Abstract
The toxicity of Clostridium perfringens was determined in mice utilizing three different routes of inoculation. There was marked variation in the minimum lethal dose with the different routes; the largest amount was required for the intracutaneous route, less for the intravenous route, and least with the intraperitoneal route. The relationship of toxicity to the lecithinase content of different toxin preparations was assayed. It was found that the toxicity of toxin preparations in different states of purification was not correlated with their lecithinase content.
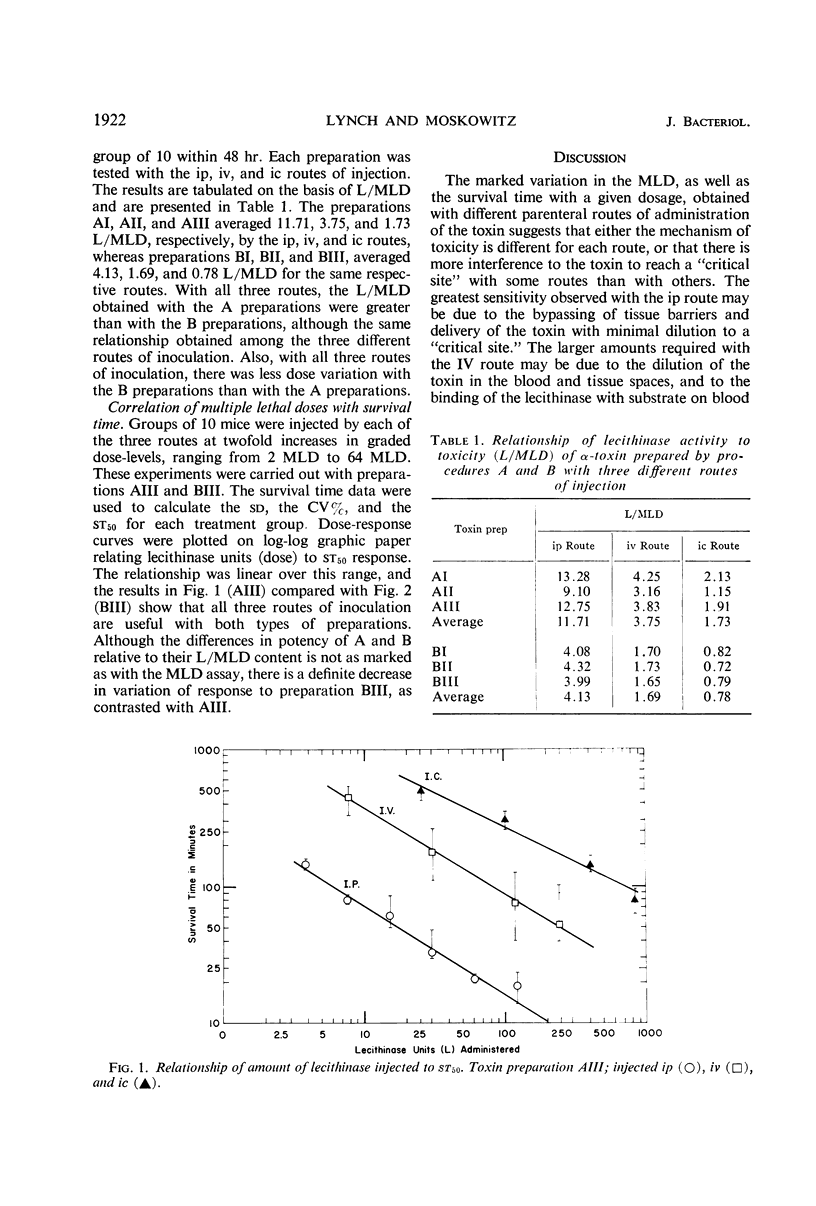
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DOLBY D. E., MACFARLANE M. G. Variation in the toxicity of lecithinases (alpha-toxin) from different strains of Clostridium welchii. Br J Exp Pathol. 1956 Aug;37(4):324–332. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macfarlane M. G., Knight B. C. The biochemistry of bacterial toxins: The lecithinase activity of Cl. welchii toxins. Biochem J. 1941 Sep;35(8-9):884–902. doi: 10.1042/bj0350884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTH F. B., PILLEMER L. The separation of alpha toxin (lecithinase) from filtrates of Clostridium welchii. J Immunol. 1953 Jun;70(6):533–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHELDON D. R., MOSKOWITZ M., DEVERELL M. W. Agar diffusion procedures for the assay of lecithinase from Clostridium perfringens. J Bacteriol. 1959 Apr;77(4):375–382. doi: 10.1128/jb.77.4.375-382.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VANHEYNINGEN W. E., ARSECULERATNE S. N. EXOTOXINS. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1964;18:195–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.18.100164.001211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


