Abstract
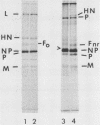
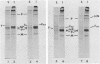
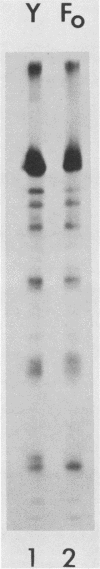
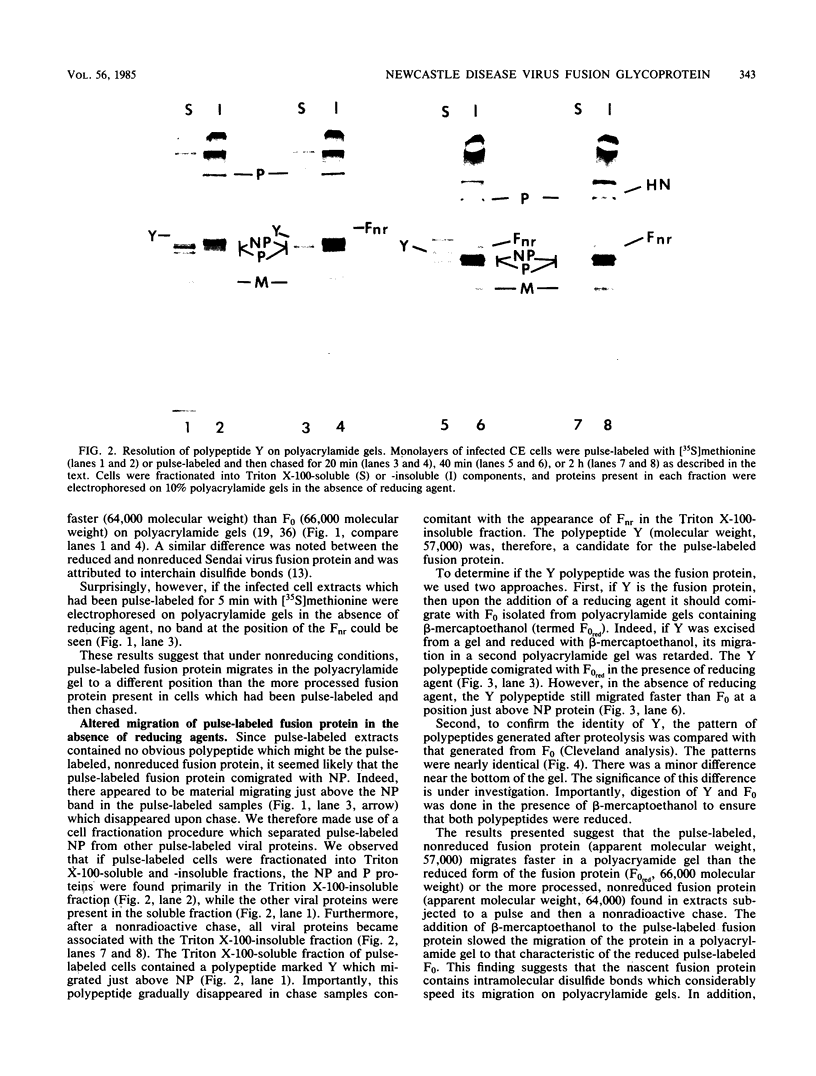
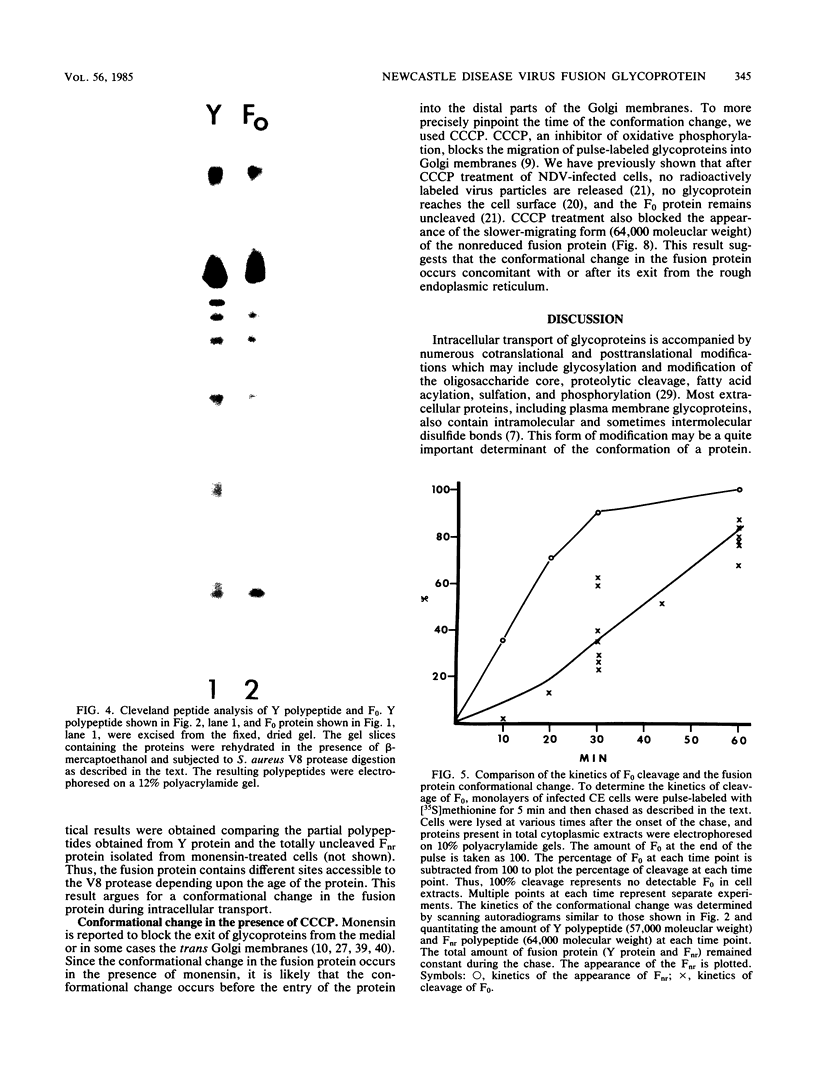
The migration on polyacrylamide gels of nascent (pulse-labeled) and more processed (pulse-labeled and then chased) forms of nonreduced Newcastle disease virus fusion glycoprotein were compared. Results are presented which demonstrate that pulse-labeled fusion protein, which has an apparent molecular weight of 66,000 under reducing conditions (Collins et al., J. Virol. 28: 324-336), migrated with an apparent molecular weight of 57,000 under nonreducing conditions. This form of the Newcastle disease virus fusion protein has not been previously detected. This result suggests that the nascent fusion protein has extensive intramolecular disulfide bonds which, if intact, significantly alter the migration of the protein on gels. Furthermore, upon a nonradioactive chase, the migration of the fusion protein in polyacrylamide gels changed from the 57,000-molecular-weight species to the previously characterized nonreduced form of the fusion protein (molecular weight, 64,000). Evidence is presented that this change in migration on polyacrylamide gels is due to a conformational change in the molecule which is likely due to the disruption of some intramolecular disulfide bonds: Cleveland peptide analysis of the pulse-labeled nonreduced fusion protein (molecular weight, 57,000) yielded a pattern of polypeptides quite different from that obtained from the more processed form of the fusion protein (molecular weight, 64,000). However, the pattern of polypeptides obtained from the nonreduced 64,000-molecular-weight species was quite similar to that obtained from the fully reduced nascent protein (molecular weight, 66,000). This conformational change occurred before cleavage of the molecule. To determine the cell compartment in which the conformational change occurs, use was made of inhibitors which block glycoprotein migration at specific points. Monensin allowed the appearance of the 64,000-molecular-weight form of the fusion protein, whereas carboxyl cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazine blocked the appearance of the 64,000-molecular-weight form of the fusion protein. Thus, the fusion protein undergoes a conformational change as it moves between the rough endoplasmic reticulum and the medial Golgi membranes.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergman L. W., Kuehl W. M. Formation of an intrachain disulfide bond on nascent immunoglobulin light chains. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):8869–8876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatis P. A., Morrison T. G. Fatty acid modification of Newcastle disease virus glycoproteins. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):342–347. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.342-347.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins P. L., Hightower L. E., Ball L. A. Transcription and translation of Newcastle disease virus mRNA's in vitro. J Virol. 1978 Oct;28(1):324–336. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.1.324-336.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fries E., Rothman J. E. Transport of vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein in a cell-free extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3870–3874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G., Quinn P., Warren G. Dissection of the Golgi complex. I. Monensin inhibits the transport of viral membrane proteins from medial to trans Golgi cisternae in baby hamster kidney cells infected with Semliki Forest virus. J Cell Biol. 1983 Mar;96(3):835–850. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.3.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamaguchi M., Yoshida T., Nishikawa K., Naruse H., Nagai Y. Transcriptive complex of Newcastle disease virus. I. Both L and P proteins are required to constitute an active complex. Virology. 1983 Jul 15;128(1):105–117. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90322-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hightower L. E., Bratt M. A. Protein metabolism during the steady state of Newcastle disease virus infection. I. Kinetics of amino acid and protein accumulation. J Virol. 1975 Apr;15(4):696–706. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.4.696-706.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu M., Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Activation of the Sendai virus fusion protein (f) involves a conformational change with exposure of a new hydrophobic region. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3557–3563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. C., Schlesinger M. J. Vesicular stomatitis virus and sindbis virus glycoprotein transport to the cell surface is inhibited by ionophores. Virology. 1980 Jun;103(2):407–424. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90200-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsbury D. W., Darlington R. W. Isolation and properties of Newcastle disease virus nucleocapsid. J Virol. 1968 Mar;2(3):248–255. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.3.248-255.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb R. A., Mahy B. W., Choppin P. W. The synthesis of sendai virus polypeptides in infected cells. Virology. 1976 Jan;69(1):116–131. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90199-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenk R., Ransom L., Kaufmann Y., Penman S. A cytoskeletal structure with associated polyribosomes obtained from HeLa cells. Cell. 1977 Jan;10(1):67–78. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90141-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQueen N. L., Nayak D. P., Jones L. V., Compans R. W. Chimeric influenza virus hemagglutinin containing either the NH2 terminus or the COOH terminus of G protein of vesicular stomatitis virus is defective in transport to the cell surface. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):395–399. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison T. G., Simpson D. Synthesis, stability, and cleavage of Newcastle disease virus glycoproteins in the absence of glycosylation. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):171–180. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.171-180.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison T. G., Ward L. J. Intracellular processing of the vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein and the Newcastle disease virus hemagglutinin-neuraminidase glycoprotein. Virus Res. 1984;1(3):225–239. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(84)90041-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison T., Ward L. J., Semerjian A. Intracellular processing of the Newcastle disease virus fusion glycoprotein. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):851–857. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.851-857.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mountcastle W. E., Compans R. W., Choppin P. W. Proteins and glycoproteins of paramyxoviruses: a comparison of simian virus 5, Newcastle disease virus, and Sendai virus. J Virol. 1971 Jan;7(1):47–52. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.1.47-52.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai Y., Klenk H. D., Rott R. Proteolytic cleavage of the viral glycoproteins and its significance for the virulence of Newcastle disease virus. Virology. 1976 Jul 15;72(2):494–508. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90178-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai Y., Ogura H., Klenk H. Studies on the assembly of the envelope of Newcastle disease virus. Virology. 1976 Feb;69(2):523–538. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90482-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M., Weber K. The detertent-resistant cytoskeleton of tissue culture cells includes the nucleus and the microfilament bundles. Exp Cell Res. 1977 May;106(2):339–349. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90179-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeples M. E., Bratt M. A. UV irradiation analysis of complementation between, and replication of, RNA-negative temperature-sensitive mutants of Newcastle disease virus. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):965–973. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.965-973.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesonen M., Käriäinen L. Incomplete complex oligosaccharides in semliki forest virus envelope proteins arrested within the cell in the presence of monensin. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jun 25;158(2):213–230. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90430-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters T., Jr, Davidson L. K. The biosynthesis of rat serum albumin. In vivo studies on the formation of the disulfide bonds. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8847–8853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E. The golgi apparatus: two organelles in tandem. Science. 1981 Sep 11;213(4513):1212–1219. doi: 10.1126/science.7268428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samson A. C., Fox C. F. Precursor protein for Newcastle disease virus. J Virol. 1973 Sep;12(3):579–587. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.3.579-587.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Identification of biological activities of paramyxovirus glycoproteins. Activation of cell fusion, hemolysis, and infectivity of proteolytic cleavage of an inactive precursor protein of Sendai virus. Virology. 1974 Feb;57(2):475–490. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90187-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Two disulfide-linked polypeptide chains constitute the active F protein of paramyxoviruses. Virology. 1977 Jul 1;80(1):54–66. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90380-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. F., Schlesinger M. J. Fatty acid binding to vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein: a new type of post-translational modification of the viral glycoprotein. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):813–819. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90321-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwalbe J. C., Hightower L. E. Maturation of the envelope glycoproteins of Newcastle disease virus on cellular membranes. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):947–957. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.947-957.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto J. T., Garten W., Rott R. The site of cleavage in infected cells and polypeptides of representative paramyxoviruses grown in cultured cells of the chorioallantoic membrane. Arch Virol. 1981;67(1):19–30. doi: 10.1007/BF01314598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartakoff A. M. Perturbation of vesicular traffic with the carboxylic ionophore monensin. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1026–1028. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90286-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartakoff A. M., Vassalli P. Plasma cell immunoglobulin secretion: arrest is accompanied by alterations of the golgi complex. J Exp Med. 1977 Nov 1;146(5):1332–1345. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.5.1332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]