Abstract
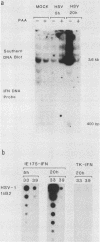
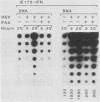
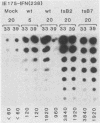
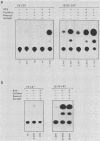
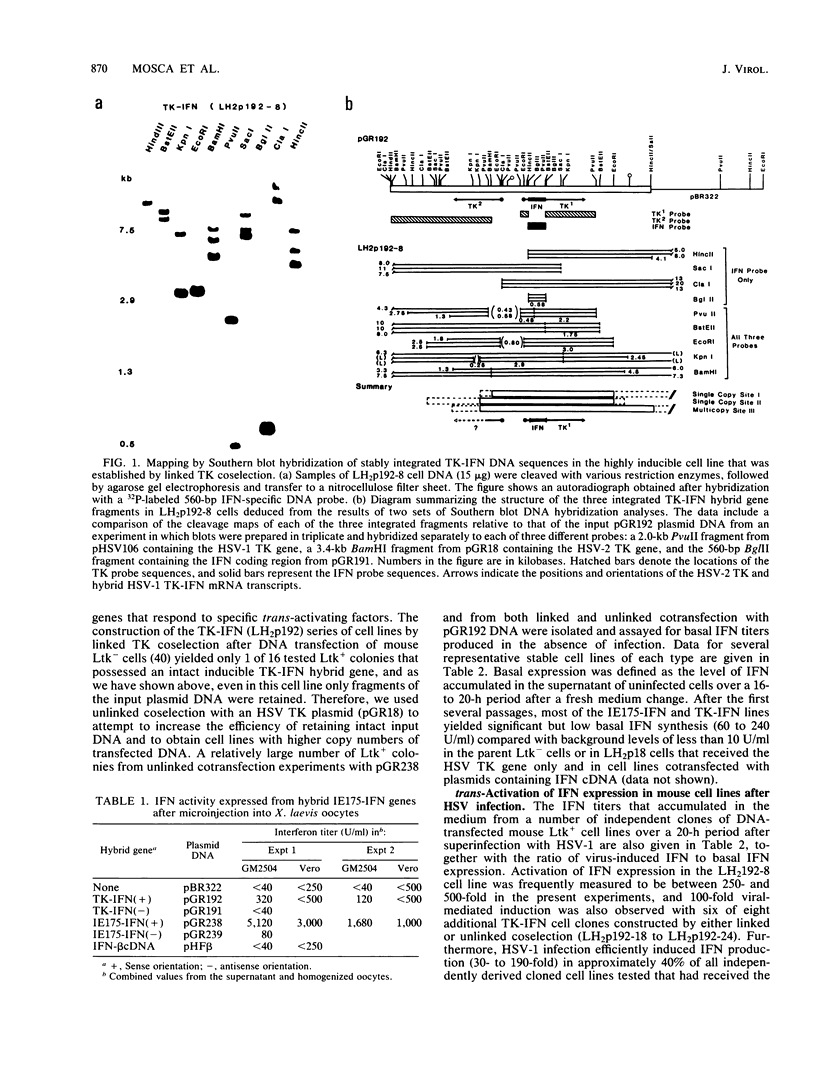
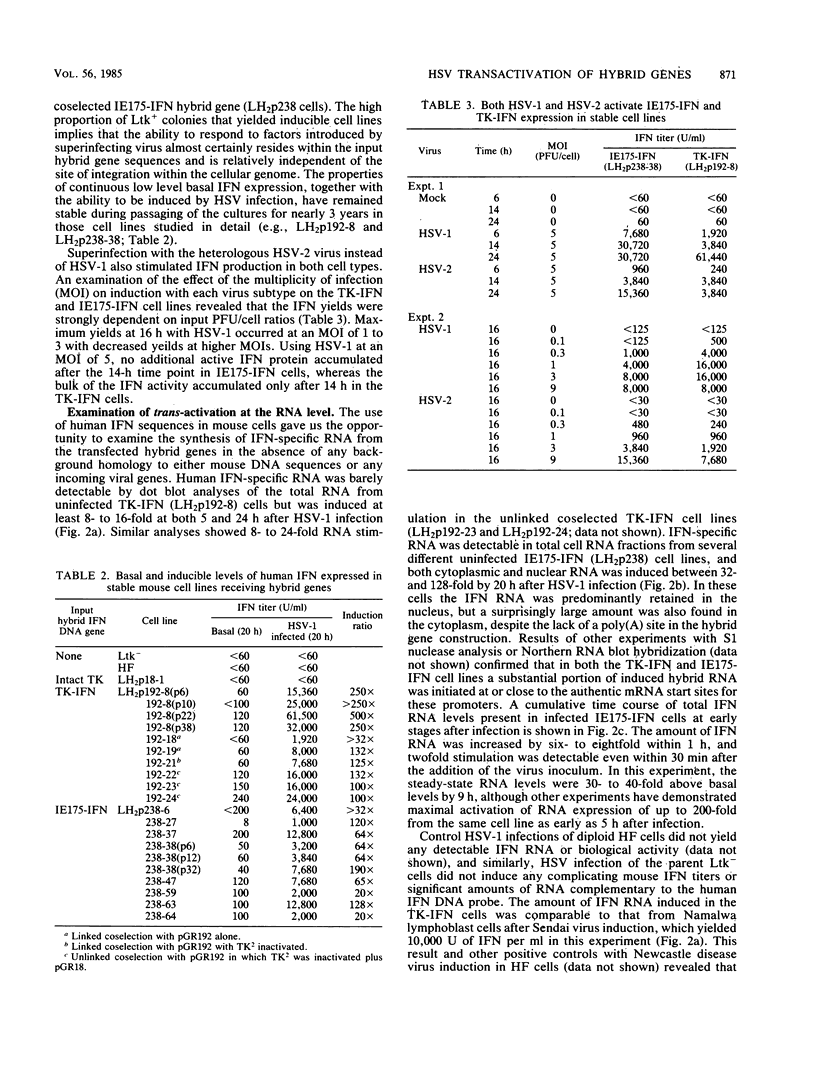
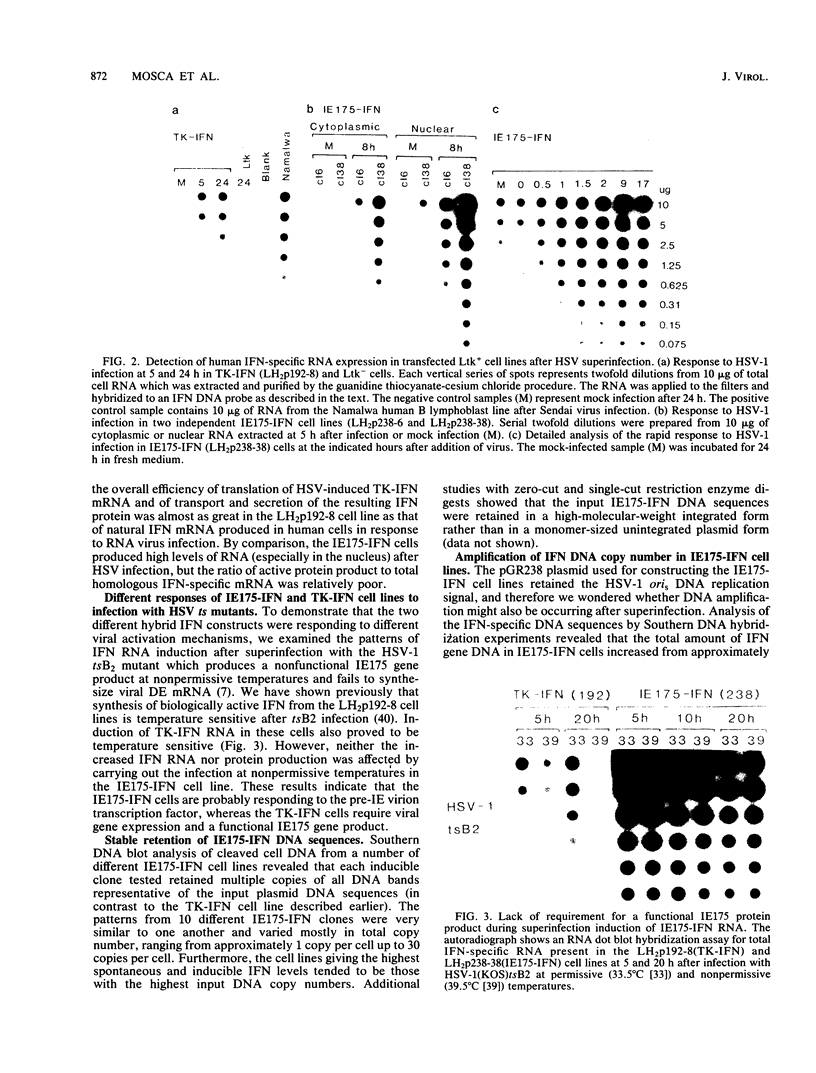
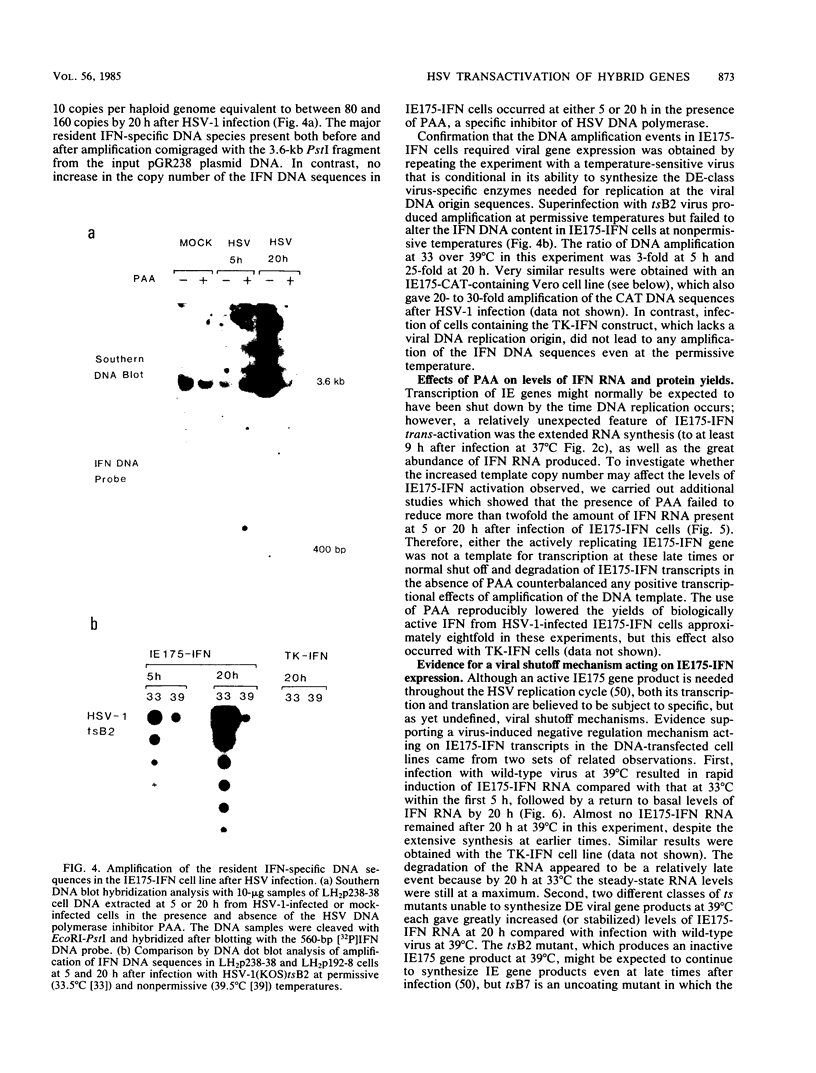
We compared the levels of gene expression obtained after herpes simplex virus (HSV) superinfection of cell lines containing integrated human beta-interferon (IFN) or chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) genes under the control of HSV immediate-early (IE) or delayed-early class promoters. DNA-transfected mouse Ltk+ cell lines harboring coselected IE175-IFN or thymidine kinase (TK)-IFN hybrid genes gave only low basal expression of human IFN. However, infection of both cell types with HSV type 1 or HSV type 2 produced abundant synthesis of IFN-specific RNA and biologically active IFN protein product. The IE175-IFN cell lines consistently gave 20- to 150-fold increases in IFN titers, and several TK-IFN cell lines yielded 100- to 500-fold induction. In the IE175-IFN cells, expression of IFN RNA also increased up to 200-fold and was detectable within 30 to 60 min after virus infection. Qualitatively similar results were obtained with hybrid G418-resistant Ltk- or Vero cell lines containing coselected IE175-CAT and TK-CAT constructs, except that there was relatively high basal expression of IE175-CAT. All three sets of IE cell lines (but not the delayed-early cell lines) responded to virus infection both in the presence of cycloheximide and with mutants defective in IE gene expression, demonstrating specific trans-activation by the pre-IE virion factor. In contrast, activation in the TK hybrid cell types required viral gene expression and the presence of a functional IE175 gene product. Up to 30-fold amplification in the copy number of the resident IFN or CAT DNA sequences also occurred within 20 h after HSV infection in IE175 hybrid cells but not in TK hybrid cells. Amplification was abolished either by treatment with phosphonacetate or by superinfection with a ts mutant unable to synthesize viral DNA, demonstrating specific HSV activation of the viral DNA replication origin (oriS) present in the IE hybrid constructs.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Batterson W., Furlong D., Roizman B. Molecular genetics of herpes simplex virus. VIII. further characterization of a temperature-sensitive mutant defective in release of viral DNA and in other stages of the viral reproductive cycle. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):397–407. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.397-407.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batterson W., Roizman B. Characterization of the herpes simplex virion-associated factor responsible for the induction of alpha genes. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):371–377. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.371-377.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. B., Watson R. J., Wilkie N. M. Temporal regulation of herpes simplex virus type 1 transcription: location of transcripts on the viral genome. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):275–285. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90205-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordingley M. G., Campbell M. E., Preston C. M. Functional analysis of a herpes simplex virus type 1 promoter: identification of far-upstream regulatory sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2347–2365. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A., Schaffer P. A. Fine-structure mapping and functional analysis of temperature-sensitive mutants in the gene encoding the herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate early protein VP175. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):189–203. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.189-203.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El Kareh A., Silverstein S., Smiley J. Control of expression of the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene in biochemically transformed cells. J Gen Virol. 1984 Jan;65(Pt 1):19–36. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-1-19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. A detailed analysis of an HSV-1 early promoter: sequences involved in trans-activation by viral immediate-early gene products are not early-gene specific. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 11;12(7):3037–3056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.7.3037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick M. L., Clark J. Expression of early viral genes: a possible pre-alpha protein in cells infected with herpes simplex virus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Oct 29;108(4):1454–1459. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(82)80070-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick M. L., Walker M. J. Suppression of the synthesis of cellular macromolecules by herpes simplex virus. J Gen Virol. 1978 Oct;41(1):37–51. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-41-1-37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herz C., Roizman B. The alpha promoter regulator-ovalbumin chimeric gene resident in human cells is regulated like the authentic alpha 4 gene after infection with herpes simplex virus 1 mutants in alpha 4 gene. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):145–151. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90343-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. M., Sinden R. R., Sadler J. R. Herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 induce shutoff of host protein synthesis by different mechanisms in Friend erythroleukemia cells. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):241–250. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.241-250.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis: sequential transition of polypeptide synthesis requires functional viral polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1276–1280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imperiale M. J., Feldman L. T., Nevins J. R. Activation of gene expression by adenovirus and herpesvirus regulatory genes acting in trans and by a cis-acting adenovirus enhancer element. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):127–136. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90215-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. C., Hayward G. S., Roizman B. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus DNA VII. alpha-RNA is homologous to noncontiguous sites in both the L and S components of viral DNA. J Virol. 1977 Jan;21(1):268–276. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.1.268-276.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston R. E., Kaufman R. J., Sharp P. A. Regulation of transcription of the adenovirus EII promoter by EIa gene products: absence of sequence specificity. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):1970–1977. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang J. C., Spandidos D. A., Wilkie N. M. Transcriptional regulation of a herpes simplex virus immediate early gene is mediated through an enhancer-type sequence. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):389–395. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01817.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiden J. M., Buttyan R., Spear P. G. Herpes simplex virus gene expression in transformed cells. I. Regulation of the viral thymidine kinase gene in transformed L cells by products of superinfecting virus. J Virol. 1976 Nov;20(2):413–424. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.2.413-424.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung W. C., Dimock K., Smiley J. R., Bacchetti S. Herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase transcripts are absent from both nucleus and cytoplasm during infection in the presence of cycloheximide. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):361–365. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.361-365.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackem S., Roizman B. Differentiation between alpha promoter and regulator regions of herpes simplex virus 1: the functional domains and sequence of a movable alpha regulator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4917–4921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackem S., Roizman B. Structural features of the herpes simplex virus alpha gene 4, 0, and 27 promoter-regulatory sequences which confer alpha regulation on chimeric thymidine kinase genes. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):939–949. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.939-949.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Gavis E. R. Expression of the herpes thymidine kinase gene in Xenopus laevis oocytes: an assay for the study of deletion mutants constructed in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):5931–5948. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.5931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Gavis E. R., Kingsbury R., Axel R. Analysis of transcriptional regulatory signals of the HSV thymidine kinase gene: identification of an upstream control region. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):385–398. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middleton M. H., Reyes G. R., Ciufo D. M., Buchan A., Macnab J. C., Hayward G. S. Expression of cloned herpesvirus genes. I. Detection of nuclear antigens from herpes simplex virus type 2 inverted repeat regions in transfected mouse cells. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):1091–1101. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.1091-1101.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minson A. C., Wildy P., Buchan A., Darby G. Introduction of the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene into mouse cells using virus DNA or transformed cell DNA. Cell. 1978 Mar;13(3):581–587. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90331-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocarski E. S., Roizman B. Herpesvirus-dependent amplification and inversion of cell-associated viral thymidine kinase gene flanked by viral a sequences and linked to an origin of viral DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5626–5630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murchie M. J., McGeoch D. J. DNA sequence analysis of an immediate-early gene region of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome (map coordinates 0.950 to 0.978). J Gen Virol. 1982 Sep;62(Pt 1):1–15. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-62-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka Y., Silverstein S. Requirement of protein synthesis for the degradation of host mRNA in Friend erythroleukemia cells infected wtih herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1978 Sep;27(3):619–627. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.3.619-627.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Hayward G. S. Evidence for a direct role for both the 175,000- and 110,000-molecular-weight immediate-early proteins of herpes simplex virus in the transactivation of delayed-early promoters. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):751–760. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.751-760.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Hayward G. S. Expression of recombinant genes containing herpes simplex virus delayed-early and immediate-early regulatory regions and trans activation by herpesvirus infection. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):522–531. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.522-531.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitha P. M., Ciufo D. M., Kellum M., Raj N. B., Reyes G. R., Hayward G. S. Induction of human beta-interferon synthesis with poly(rI . rC) in mouse cells transfected with cloned cDNA plasmids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4337–4341. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post L. E., Mackem S., Roizman B. Regulation of alpha genes of herpes simplex virus: expression of chimeric genes produced by fusion of thymidine kinase with alpha gene promoters. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):555–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90346-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M. Control of herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNA synthesis in cells infected with wild-type virus or the temperature-sensitive mutant tsK. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):275–284. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.275-284.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raj N. B., Pitha P. M. Analysis of interferon mRNA in human fibroblast cells induced to produce interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7426–7430. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read G. S., Frenkel N. Herpes simplex virus mutants defective in the virion-associated shutoff of host polypeptide synthesis and exhibiting abnormal synthesis of alpha (immediate early) viral polypeptides. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):498–512. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.498-512.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes G. R., Gavis E. R., Buchan A., Raj N. B., Hayward G. S., Pitha P. M. Expression of human beta-interferon cDNA under the control of a thymidine kinase promoter from herpes simplex virus. Nature. 1982 Jun 17;297(5867):598–601. doi: 10.1038/297598a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes G. R., Jeang K. T., Hayward G. S. Transfection with the isolated herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase genes. I. Minimal size of the active fragments from HSV-1 and HSV-2. J Gen Virol. 1982 Oct;62(Pt 2):191–206. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-62-2-191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes G. R., McLane M. W., Hayward G. S. Transfection with the isolated herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase genes. II. Evidence for amplification of viral and adjacent cellular DNA sequences. J Gen Virol. 1982 Jun;60(Pt 2):209–224. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-60-2-209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggin C. H., Pitha P. M. Effect of interferon on the exogenous Friend murine leukemia virus infection. Virology. 1982 Apr 15;118(1):202–213. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90333-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J. E., Levinger L. F., Carter C. W., Jr Nucleosomal structure of Epstein-Barr virus DNA in transformed cell lines. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):657–665. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.657-665.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D. Localization of an origin of DNA replication within the TRS/IRS repeated region of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome. EMBO J. 1982;1(7):863–867. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01261.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., McMonagle E. C. Characterization of the TRS/IRS origin of DNA replication of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1983 Oct 30;130(2):427–438. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90097-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlazny D. A., Frenkel N. Replication of herpes simplex virus DNA: localization of replication recognition signals within defective virus genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):742–746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Clements J. B. A herpes simplex virus type 1 function continuously required for early and late virus RNA synthesis. Nature. 1980 May 29;285(5763):329–330. doi: 10.1038/285329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., DiMaio D., Maniatis T. Identification of two distinct regulatory regions adjacent to the human beta-interferon gene. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):865–879. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90544-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zipser D., Lipsich L., Kwoh J. Mapping functional domains in the promoter region of the herpes thymidine kinase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6276–6280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]