Abstract
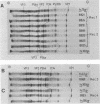
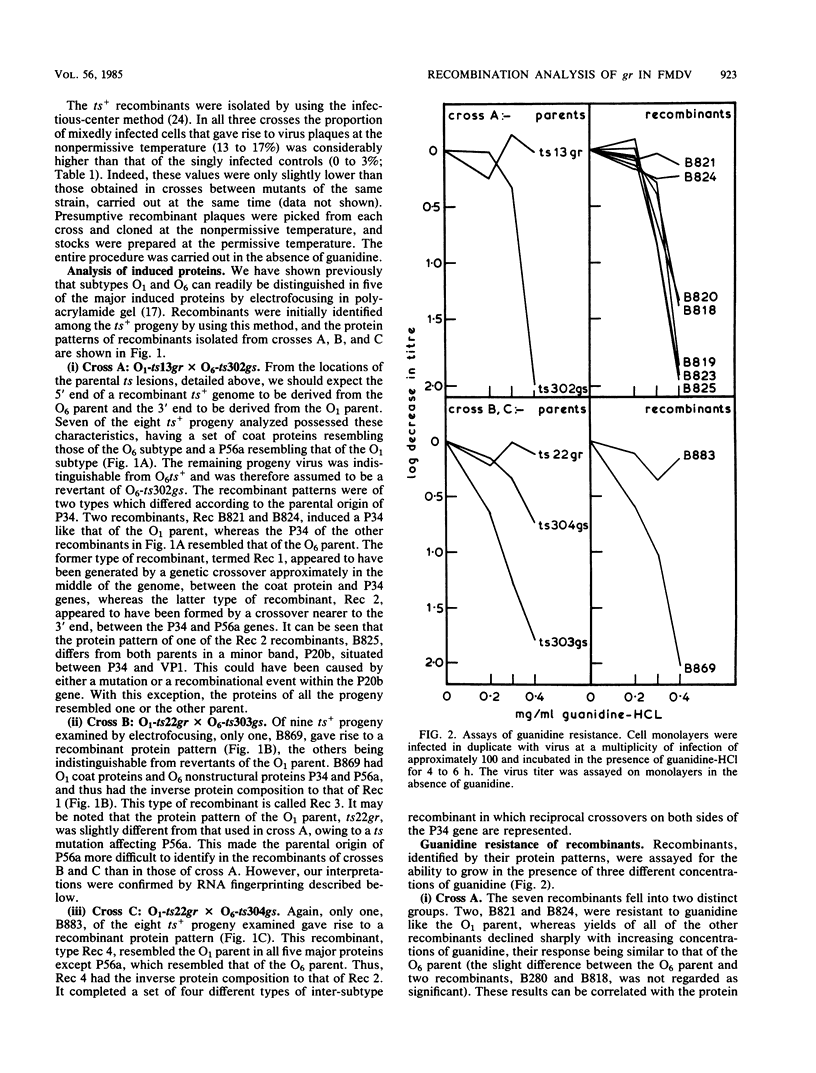
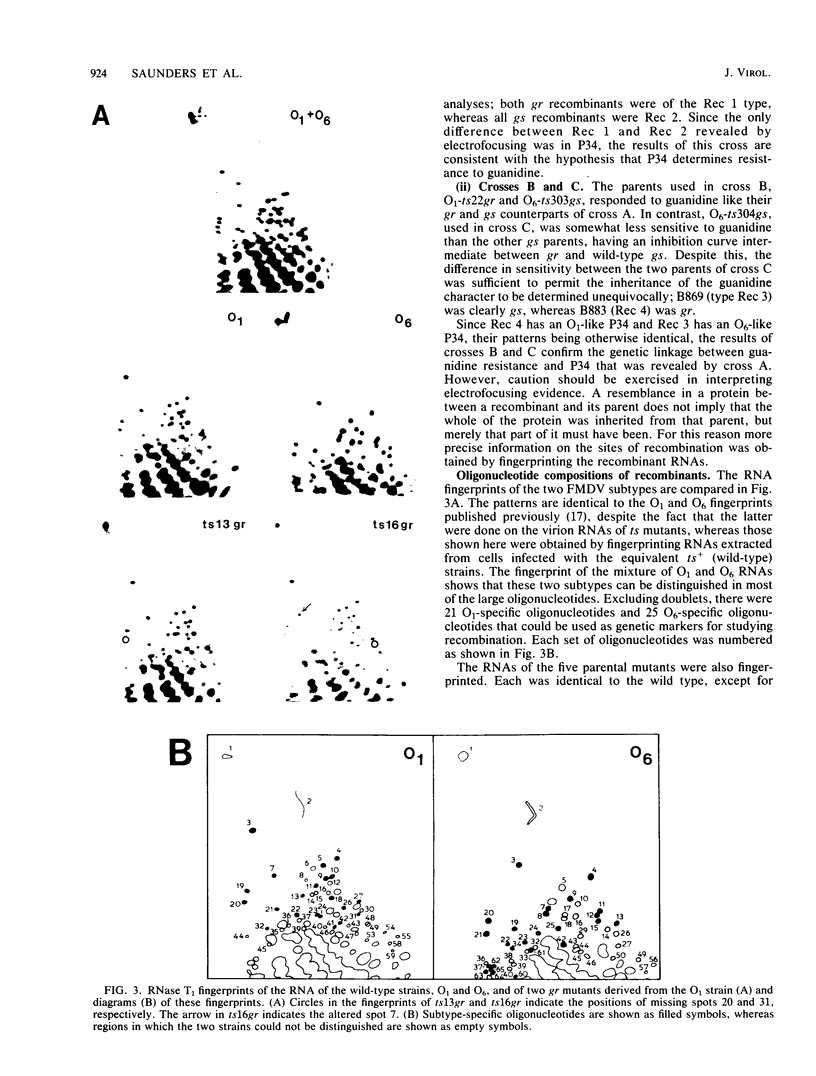
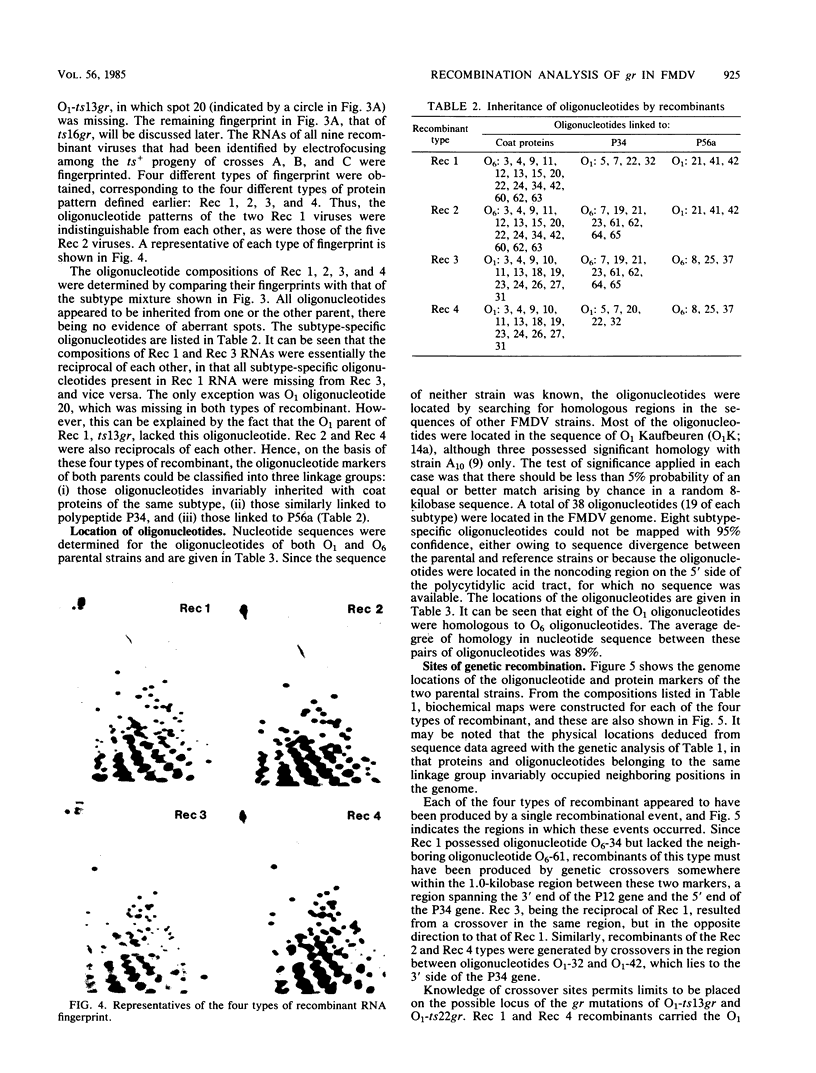
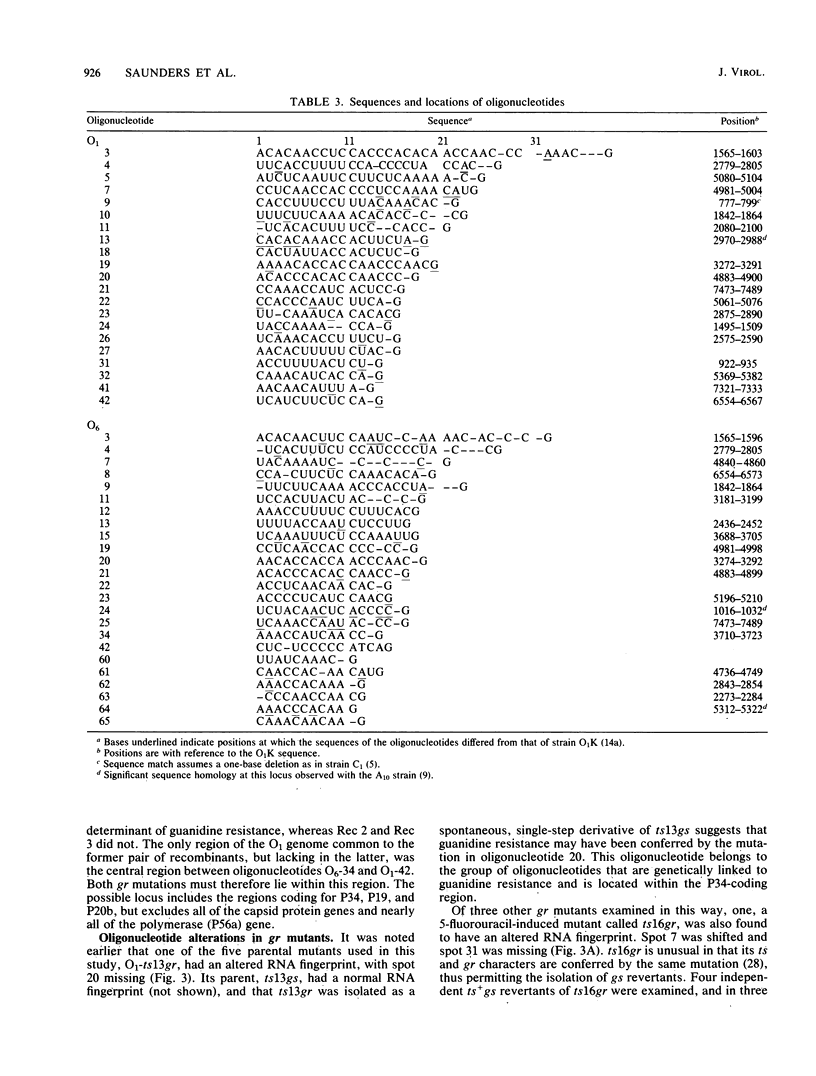
Guanidine resistance (gr) mutations of foot-and-mouth disease virus were mapped by recombining pairs of temperature-sensitive mutants belonging to different subtypes. In each cross, one parent possessed a gr mutation. Recombinants were isolated by selection at the nonpermissive temperature and assayed for the ability to grow in the presence of guanidine. From the progeny of three crosses, four different types of recombinant were distinguished on the basis of protein composition and RNA fingerprint. The sequences of the RNase T1-resistant oligonucleotides were determined and located in the full-length sequence of foot-and-mouth disease virus. The resulting maps show that (i) each recombinant was generated by a single genetic crossover, and (ii) both of the gr mutations studied were located within an internal 2.9-kilobase region which spans the P34 gene. This supports our hypothesis that guanidine inhibits the growth of foot-and-mouth disease virus by acting on nonstructural polypeptide P34. Additional evidence was provided by RNA fingerprinting gr mutants. In two of four cases the gr mutation was associated with a change in an oligonucleotide located near the 3' end of the P34 gene; in one of these the nucleotide substitution was identified.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agol V. I., Grachev V. P., Drozdov S. G., Kolesnikova M. S., Kozlov V. G., Ralph N. M., Romanova L. I., Tolskaya E. A., Tyufanov A. V., Viktorova E. G. Construction and properties of intertypic poliovirus recombinants: first approximation mapping of the major determinants of neurovirulence. Virology. 1984 Jul 15;136(1):41–55. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90246-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson-Sillman K., Bartal S., Tershak D. R. Guanidine-resistant poliovirus mutants produce modified 37-kilodalton proteins. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):922–928. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.922-928.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALTIMORE D., EGGERS H. J., FRANKLIN R. M., TAMM I. Poliovirus-induced RNA polymerase and the effects of virus-specific inhibitors on its production. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Jun;49:843–849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.6.843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck E., Forss S., Strebel K., Cattaneo R., Feil G. Structure of the FMDV translation initiation site and of the structural proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 25;11(22):7873–7885. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.22.7873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black D. N., Brown F. Effect of actinomycin D and guanidine on the formation of a ribonucleic acid polymerase induced by foot-and mouth-disease virus and on the replication of virus and viral ribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1969 Apr;112(3):317–323. doi: 10.1042/bj1120317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth B. E., Shimshick E. J., Yin F. H. Association of the polioviral RNA polymerase complex with phospholipid membranes. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):457–466. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.457-466.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caliguiri L. A., Tamm I. Action of guanidine on the replication of poliovirus RNA. Virology. 1968 Jul;35(3):408–417. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90219-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll A. R., Rowlands D. J., Clarke B. E. The complete nucleotide sequence of the RNA coding for the primary translation product of foot and mouth disease virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 12;12(5):2461–2472. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.5.2461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper P. D. A genetic map of poliovirus temperature-sensitive mutants. Virology. 1968 Aug;35(4):584–596. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90287-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper P. D., Wentworth B. B., McCahon D. Guanidine inhibition of poliovirus: a dependence of viral RNA synthesis on the configuration of structural protein. Virology. 1970 Mar;40(3):480–493. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90191-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford N. M., Baltimore D. Genome-linked protein VPg of poliovirus is present as free VPg and VPg-pUpU in poliovirus-infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7452–7455. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emini E. A., Leibowitz J., Diamond D. C., Bonin J., Wimmer E. Recombinants of Mahoney and Sabin strain poliovirus type 1: analysis of in vitro phenotypic markers and evidence that resistance to guanidine maps in the nonstructural proteins. Virology. 1984 Aug;137(1):74–85. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etchison D., Ehrenfeld E. Comparison of replication complexes synthesizing poliovirus RNA. Virology. 1981 May;111(1):33–46. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90651-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forss S., Strebel K., Beck E., Schaller H. Nucleotide sequence and genome organization of foot-and-mouth disease virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 24;12(16):6587–6601. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.16.6587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris T. J., Robson K. H., Brown F. A study of the level of nucleotide sequence conservation between the RNAs of two types serotypes of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Gen Virol. 1980 Oct;50(2):403–418. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-50-2-403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris T. J. The nucleotide sequence at the 5' end of foot and mouth disease virus RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 11;7(7):1765–1785. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.7.1765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A. M., McCahon D., Slade W. R., Newman J. W. Recombination in RNA. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):921–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90454-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A. M., Newman J. W. Temperature-sensitive mutants of foot-and-mouth disease virus with altered structural polypeptides. I. Identification by electrofocusing. J Virol. 1980 Apr;34(1):59–66. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.1.59-66.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A. M., Slade W. R., Newman J. W., McCahon D. Temperature-sensitive mutants of foot-and-mouth disease virus with altered structural polypeptides. II. Comparison of recombination and biochemical maps. J Virol. 1980 Apr;34(1):67–72. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.1.67-72.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korant B. D. Poliovirus coat protein as the site of guanidine action. Virology. 1977 Aug;81(1):25–36. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90055-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Torre J. L., Underwood B. O., Lebendiker M., Gorman B. M., Brown F. Application of RNase T1 one- and two-dimensional analyses to the rapid identification of foot-and-mouth disease viruses. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):142–147. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.142-147.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake J. R., Priston A. J., Slade W. R. A genetic recombination map of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Gen Virol. 1975 Jun;27(3):355–367. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-27-3-355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe P. A., King A. M., McCahon D., Brown F., Newman J. W. Temperature-sensitive RNA polymerase mutants of a picornavirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4448–4452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCahon D., Slade W. R. A sensitive method for the detection and isolation of recombinants of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Gen Virol. 1981 Apr;53(Pt 2):333–342. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-53-2-333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCahon D., Slade W. R., Priston R. A., Lake J. R. An extended genetic recombination map for foot-and-mouth diseases virus. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jun;35(3):555–565. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-35-3-555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards O. C., Martin S. C., Jense H. G., Ehrenfeld E. Structure of poliovirus replicative intermediate RNA. Electron microscope analysis of RNA cross-linked in vivo with psoralen derivative. J Mol Biol. 1984 Mar 5;173(3):325–340. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90124-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rueckert R. R., Wimmer E. Systematic nomenclature of picornavirus proteins. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):957–959. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.957-959.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders K., King A. M. Guanidine-resistant mutants of aphthovirus induce the synthesis of an altered nonstructural polypeptide, P34. J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):389–394. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.389-394.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takegami T., Kuhn R. J., Anderson C. W., Wimmer E. Membrane-dependent uridylylation of the genome-linked protein VPg of poliovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7447–7451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tershak D. R. Guanidine-resistant defective interfering particles of poliovirus. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):615–625. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.615-625.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tershak D. R. Inhibition of poliovirus polymerase by guanidine in vitro. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):313–318. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.313-318.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]