Abstract
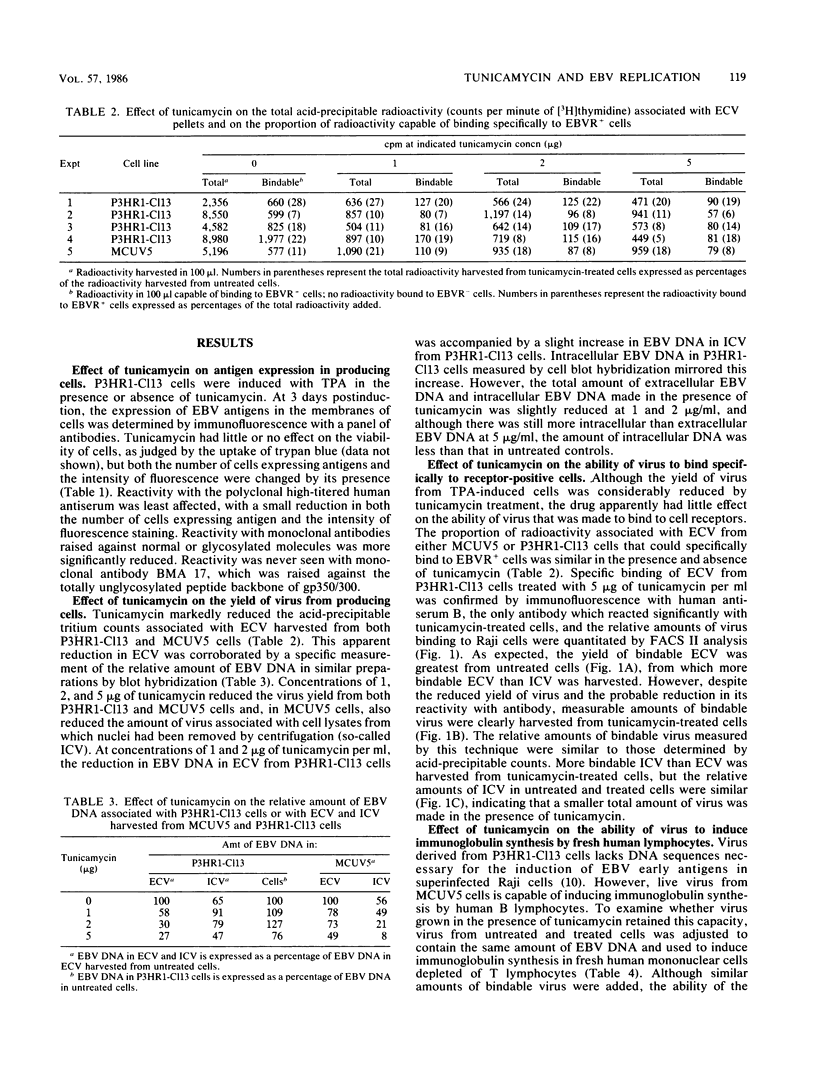
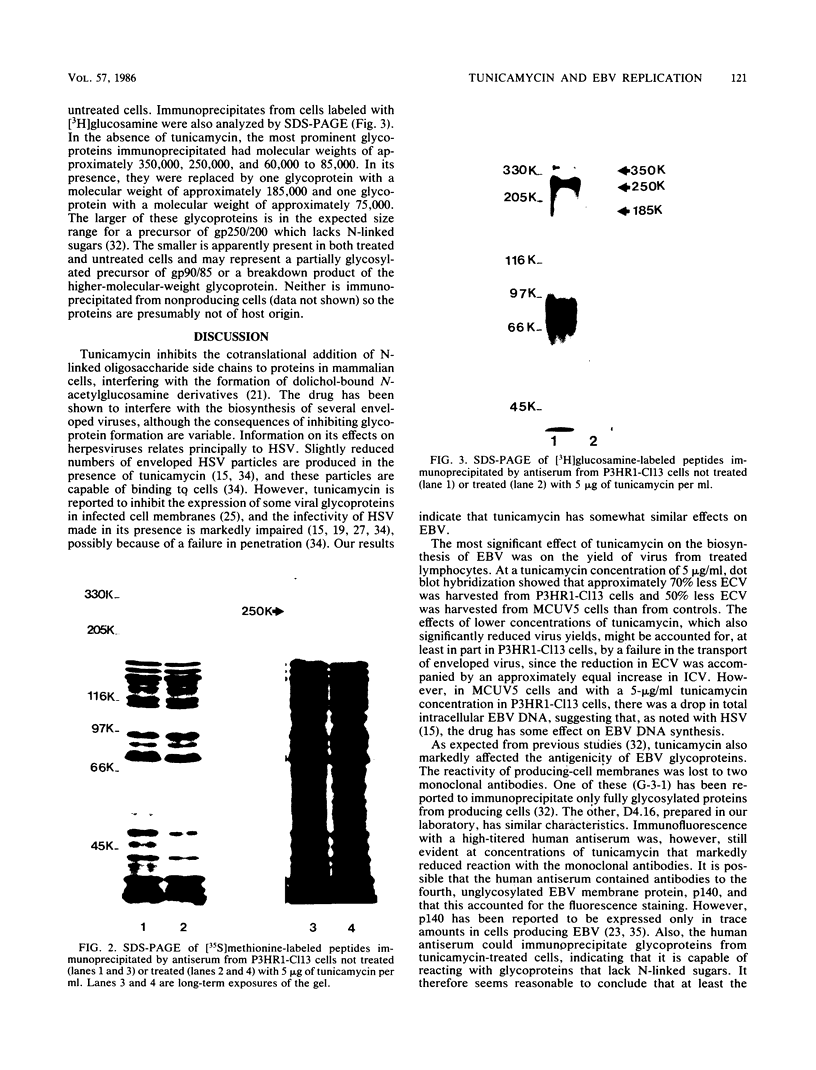
The effect of tunicamycin, which inhibits N-linked glycosylation, on the replication of Epstein-Barr virus was examined. Tunicamycin markedly reduced the yield of virus from producing cells. At concentrations of 1 to 2 micrograms of tunicamycin per ml, there was a buildup of intracellular virus in P3HR1-Cl13 cells but not in MCUV5 cells; at a concentration of 5 micrograms of tunicamycin per ml in P3HR1-Cl13 cells, viral DNA synthesis was inhibited as well. Viral glycoproteins lacking N-linked sugars were apparently inserted into the cell membrane, and the small amount of virus made in the presence of drug was able to bind specifically to its receptor on B cells. However, the ability of the virus to induce immunoglobulin secretion by fresh human lymphocytes was impaired. This implies a role for viral glycoproteins in the penetration as well as the attachment of virus.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baer R., Bankier A. T., Biggin M. D., Deininger P. L., Farrell P. J., Gibson T. J., Hatfull G., Hudson G. S., Satchwell S. C., Séguin C. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):207–211. doi: 10.1038/310207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balachandran N., Harnish D., Rawls W. E., Bacchetti S. Glycoproteins of herpes simplex virus type 2 as defined by monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):344–355. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.344-355.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. G., Britton S. A new approach to the study of human B lymphocyte function using an indirect plaque assay and a direct B cell activator. Immunol Rev. 1979;45:41–67. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00272.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandsma J., Miller G. Nucleic acid spot hybridization: rapid quantitative screening of lymphoid cell lines for Epstein-Barr viral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6851–6855. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dambaugh T., Beisel C., Hummel M., King W., Fennewald S., Cheung A., Heller M., Raab-Traub N., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus (B95-8) DNA VII: molecular cloning and detailed mapping. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2999–3003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edson C. M., Thorley-Lawson D. A. Synthesis and processing of the three major envelope glycoproteins of Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):547–556. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.547-556.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heston L., Rabson M., Brown N., Miller G. New Epstein-Barr virus variants from cellular subclones of P3J-HR-1 Burkitt lymphoma. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):160–163. doi: 10.1038/295160a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman G. J., Lazarowitz S. G., Hayward S. D. Monoclonal antibody against a 250,000-dalton glycoprotein of Epstein-Barr virus identifies a membrane antigen and a neutralizing antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2979–2983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hummel M., Thorley-Lawson D., Kieff E. An Epstein-Barr virus DNA fragment encodes messages for the two major envelope glycoproteins (gp350/300 and gp220/200). J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):413–417. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.413-417.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutt-Fletcher L. M., Balachandran N., Elkins M. H. B cell activation by cytomegalovirus. J Exp Med. 1983 Dec 1;158(6):2171–2176. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.6.2171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafatos F. C., Jones C. W., Efstratiadis A. Determination of nucleic acid sequence homologies and relative concentrations by a dot hybridization procedure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1541–1552. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz E., Margalith E., Duksin D. Antiviral activity of tunicamycin on herpes simplex virus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jun;17(6):1014–1022. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.6.1014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishishita M., Luka J., Vroman B., Poduslo J. F., Pearson G. R. Production of monoclonal antibody to a late intracellular Epstein-Barr virus-induced antigen. Virology. 1984 Mar;133(2):363–375. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90402-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein E., Klein G., Nadkarni J. S., Nadkarni J. J., Wigzell H., Clifford P. Surface IgM-kappa specificity on a Burkitt lymphoma cell in vivo and in derived culture lines. Cancer Res. 1968 Jul;28(7):1300–1310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenk H. D., Schwarz R. T. Viral glycoprotein metabolism as a target for antiviral substances. Antiviral Res. 1982 Sep;2(4):177–190. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(82)90041-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kousoulas K. G., Bzik D. J., DeLuca N., Person S. The effect of ammonium chloride and tunicamycin on the glycoprotein content and infectivity of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1983 Mar;125(2):468–474. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90217-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehle L., Tanner W. The specific site of tunicamycin inhibition in the formation of dolichol-bound N-acetylglucosamine derivatives. FEBS Lett. 1976 Nov 15;72(1):167–170. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80922-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan A. J., Smith A. R., Barker R. N., Epstein M. A. A structural investigation of the Epstein-Barr (EB) virus membrane antigen glycoprotein, gp340. J Gen Virol. 1984 Feb;65(Pt 2):397–404. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-2-397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller-Lantzsch N., Georg-Fries B., Herbst H., zur Hausen H., Braun D. G. Epstein-Barr virus strain- and group-specific antigenic determinants detected by monoclonal antibodies. Int J Cancer. 1981 Sep 15;28(3):321–327. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910280311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemerow G. R., Cooper N. R. Early events in the infection of human B lymphocytes by Epstein-Barr virus: the internalization process. Virology. 1984 Jan 15;132(1):186–198. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90102-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrild B., Pedersen B. Effect of tunicamycin on the synthesis of herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoproteins and their expression on the cell surface. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):395–402. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.395-402.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PULVERTAFT J. V. CYTOLOGY OF BURKITT'S TUMOUR (AFRICAN LYMPHOMA). Lancet. 1964 Feb 1;1(7327):238–240. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)92345-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellett P. E., Kousoulas K. G., Pereira L., Roizman B. Anatomy of the herpes simplex virus 1 strain F glycoprotein B gene: primary sequence and predicted protein structure of the wild type and of monoclonal antibody-resistant mutants. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):243–253. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.243-253.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizer L. I., Cohen G. H., Eisenberg R. J. Effect of tunicamycin on herpes simplex virus glycoproteins and infectious virus production. J Virol. 1980 Apr;34(1):142–153. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.1.142-153.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarmiento M., Haffey M., Spear P. G. Membrane proteins specified by herpes simplex viruses. III. Role of glycoprotein VP7(B2) in virion infectivity. J Virol. 1979 Mar;29(3):1149–1158. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.3.1149-1158.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons J. G., Hutt-Fletcher L. M., Fowler E., Feighny R. J. Studies of the Epstein-Barr virus receptor found on Raji cells. I. Extraction of receptor and preparation of anti-receptor antibody. J Immunol. 1983 Mar;130(3):1303–1308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strnad B. C., Adams M. R., Rabin H. Glycosylation pathways of two major Epstein-Barr virus membrane antigens. Virology. 1983 May;127(1):168–176. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90381-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strnad B. C., Schuster T., Klein R., Hopkins R. F., 3rd, Witmer T., Neubauer R. H., Rabin H. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies against the Epstein-Barr virus membrane antigen. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):258–264. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.258-264.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svennerholm B., Olofsson S., Lundén R., Vahlne A., Lycke E. Adsorption and penetration of enveloped herpes simplex virus particles modified by tunicamycin or 2-deoxy-D-glucose. J Gen Virol. 1982 Dec;63(2):343–349. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-63-2-343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorley-Lawson D. A., Edson C. M., Geilinger K. Epstein-Barr virus antigens-a challenge to modern biochemistry. Adv Cancer Res. 1982;36:295–348. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60428-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorley-Lawson D. A., Geilinger K. Monoclonal antibodies against the major glycoprotein (gp350/220) of Epstein-Barr virus neutralize infectivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5307–5311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells A., Koide N., Klein G. Two large virion envelope glycoproteins mediate Epstein-Barr virus binding to receptor-positive cells. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):286–297. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.286-297.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




