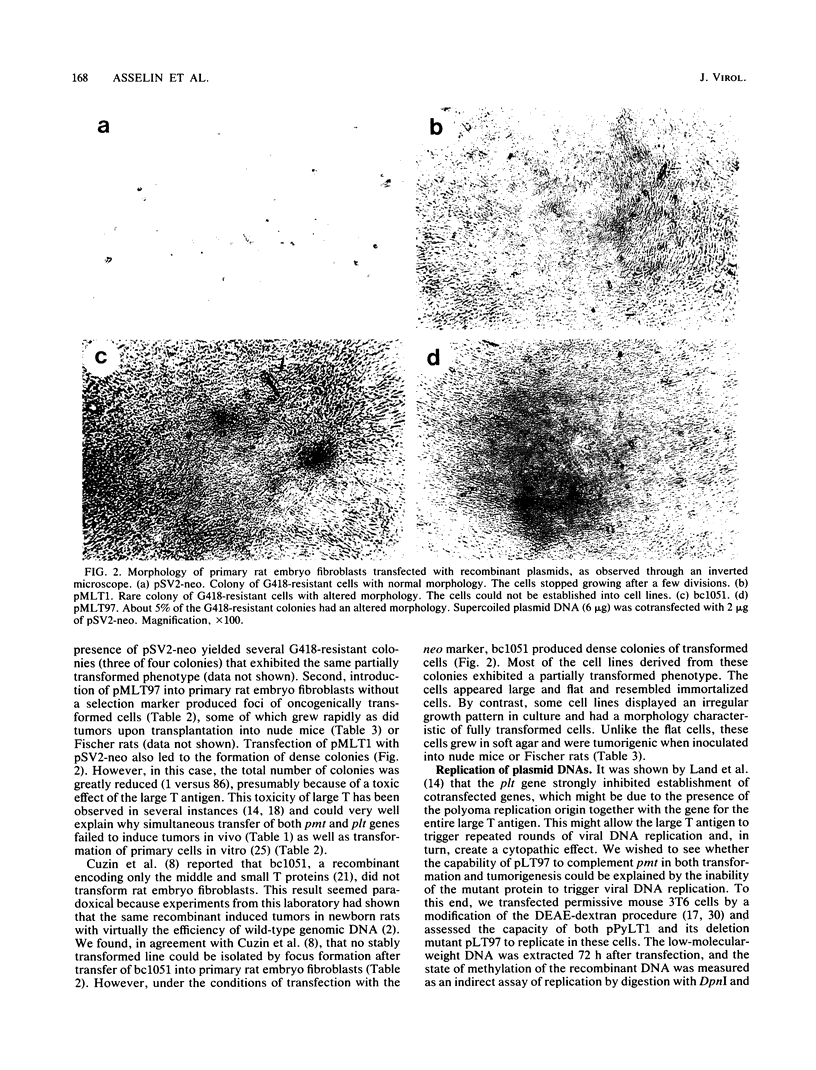
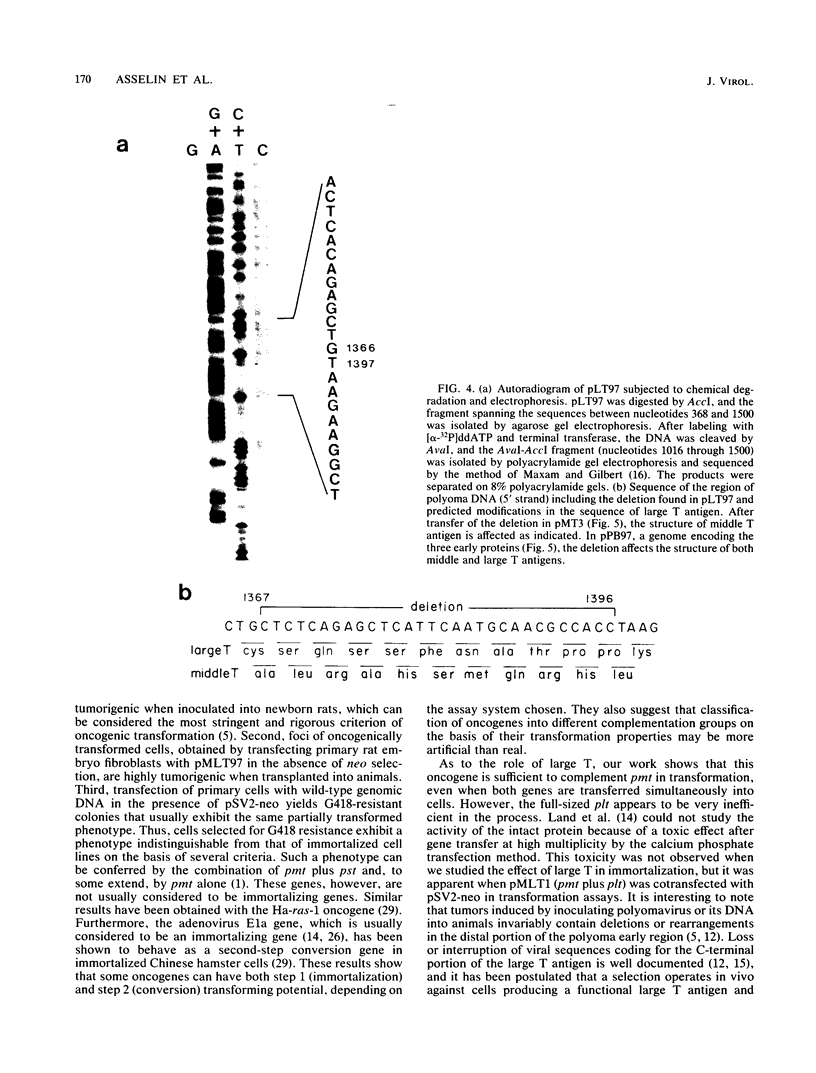
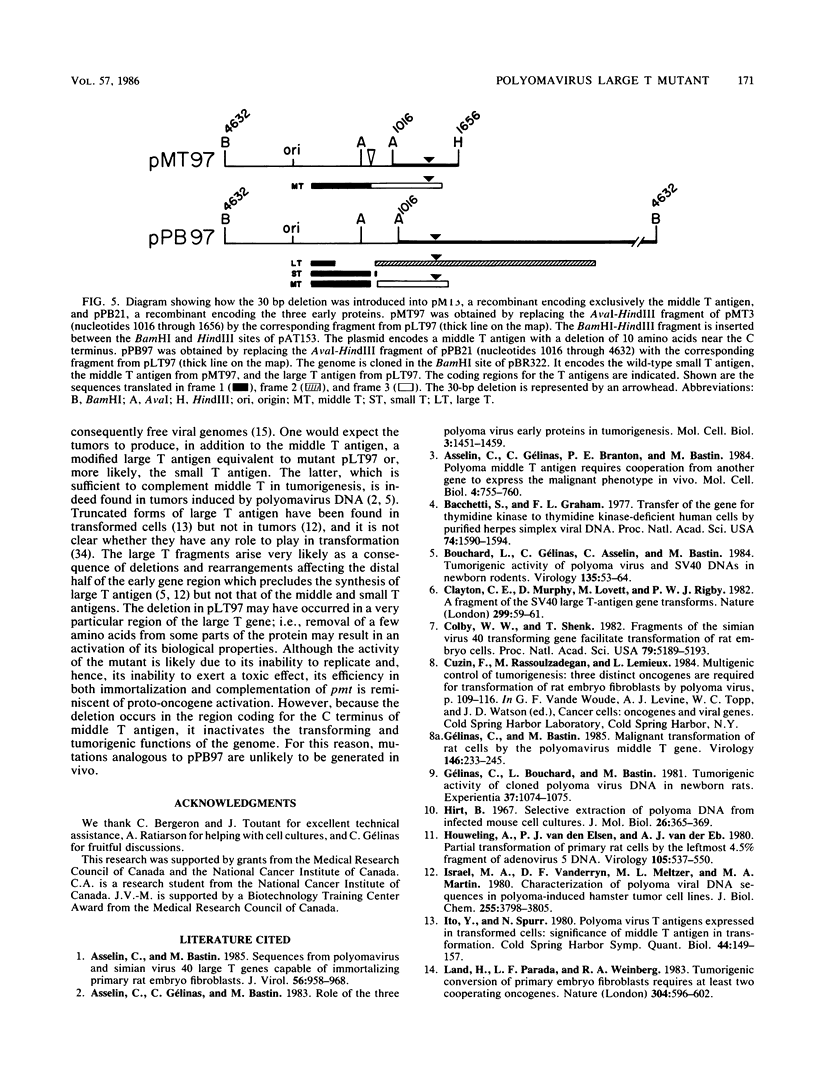
Abstract
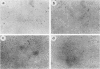
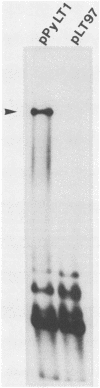
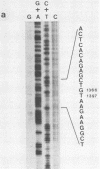
We have constructed a polyomavirus mutant genome which exhibits an increased immortalization potential when transfected into primary rat embryo fibroblasts. The mutation is a 30-base-pair deletion (nucleotides 1367 through 1396) that inactivates the transforming potential of middle T but activates some of the properties of large T associated with neoplastic transformation. Unlike the wild-type large T, the mutant large T can fully complement polyoma middle T in the tumorigenic process in vivo as well as in the transformation of primary cells in vitro. The activity of the mutant can be explained by its inability to replicate in cells and, hence, its inability to exert a cytopathic effect after gene transfer at high multiplicity. A recombinant which encodes the middle and small T antigens, but not the large T antigen, can also elicit a fully transformed phenotype when introduced into primary rat fibroblasts. These results confirm previous observations from this laboratory indicating that two, and not three, viral gene functions are required for polyomavirus-mediated oncogenic transformation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asselin C., Bastin M. Sequences from polyomavirus and simian virus 40 large T genes capable of immortalizing primary rat embryo fibroblasts. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):958–968. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.958-968.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asselin C., Gelinas C., Bastin M. Role of the three polyoma virus early proteins in tumorigenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;3(8):1451–1459. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.8.1451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asselin C., Gélinas C., Branton P. E., Bastin M. Polyoma middle T antigen requires cooperation from another gene to express the malignant phenotype in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;4(4):755–760. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.4.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacchetti S., Graham F. L. Transfer of the gene for thymidine kinase to thymidine kinase-deficient human cells by purified herpes simplex viral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1590–1594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouchard L., Gelinas C., Asselin C., Bastin M. Tumorigenic activity of polyoma virus and SV40 DNAs in newborn rodents. Virology. 1984 May;135(1):53–64. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90116-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton C. E., Murphy D., Lovett M., Rigby P. W. A fragment of the SV40 large T-antigen gene transforms. Nature. 1982 Sep 2;299(5878):59–61. doi: 10.1038/299059a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colby W. W., Shenk T. Fragments of the simian virus 40 transforming gene facilitate transformation of rat embryo cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5189–5193. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gélinas C., Bastin M. Malignant transformation of rat cells by the polyomavirus middle T gene. Virology. 1985 Oct 30;146(2):233–245. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gélinas C., Bouchard L., Bastin M. Tumorigenic activity of cloned polyoma virus DNA in newborn rats. Experientia. 1981 Oct 15;37(10):1074–1075. doi: 10.1007/BF02085017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houweling A., van den Elsen P. J., van der Eb A. J. Partial transformation of primary rat cells by the leftmost 4.5% fragment of adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1980 Sep;105(2):537–550. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90054-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel M. A., Vanderryn D. F., Meltzer M. L., Martin M. A. Characterization of polyoma viral DNA sequences in polyoma-induced hamster tumor cell lines. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 25;255(8):3798–3805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Spurr N. Polyoma virus T antigens expressed in transformed cells: significance of middle T antigen in transformation. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 1):149–157. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Parada L. F., Weinberg R. A. Tumorigenic conversion of primary embryo fibroblasts requires at least two cooperating oncogenes. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):596–602. doi: 10.1038/304596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lania L., Hayday A., Fried M. Loss of functional large T-antigen and free viral genomes from cells transformed in vitro by polyoma virus after passage in vivo as tumor cells. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):422–431. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.422-431.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan J. H., Pagano J. S. Enchancement of the infectivity of simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid with diethylaminoethyl-dextran. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1968 Aug;41(2):351–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mougneau E., Lemieux L., Rassoulzadegan M., Cuzin F. Biological activities of v-myc and rearranged c-myc oncogenes in rat fibroblast cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5758–5762. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller W. J., Mueller C. R., Mes A. M., Hassell J. A. Polyomavirus origin for DNA replication comprises multiple genetic elements. J Virol. 1983 Sep;47(3):586–599. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.3.586-599.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller W. J., Naujokas M. A., Hassell J. A. Polyomavirus-plasmid recombinants capable of replicating have an enhanced transforming potential. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Sep;3(9):1670–1674. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.9.1670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson S. V., Magnusson G. T-antigen expression by polyoma mutants with modified RNA splicing. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2095–2101. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01708.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parada L. F., Land H., Weinberg R. A., Wolf D., Rotter V. Cooperation between gene encoding p53 tumour antigen and ras in cellular transformation. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):649–651. doi: 10.1038/312649a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petit C. A., Gardes M., Feunteun J. Immortalization of rodent embryo fibroblasts by SV40 is maintained by the A gene. Virology. 1983 May;127(1):74–82. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90372-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rassoulzadegan M., Cowie A., Carr A., Glaichenhaus N., Kamen R., Cuzin F. The roles of individual polyoma virus early proteins in oncogenic transformation. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):713–718. doi: 10.1038/300713a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rassoulzadegan M., Naghashfar Z., Cowie A., Carr A., Grisoni M., Kamen R., Cuzin F. Expression of the large T protein of polyoma virus promotes the establishment in culture of "normal" rodent fibroblast cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4354–4358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruley H. E. Adenovirus early region 1A enables viral and cellular transforming genes to transform primary cells in culture. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):602–606. doi: 10.1038/304602a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spandidos D. A., Wilkie N. M. Malignant transformation of early passage rodent cells by a single mutated human oncogene. Nature. 1984 Aug 9;310(5977):469–475. doi: 10.1038/310469a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman D. J., Milman G. Short-term, high-efficiency expression of transfected DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1641–1643. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Novak U., Favaloro J., Kamen R. Transformation of rat cells by an altered polyoma virus genome expressing only the middle-T protein. Nature. 1981 Aug 13;292(5824):595–600. doi: 10.1038/292595a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R. Biochemical transfer of single-copy eucaryotic genes using total cellular DNA as donor. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):725–731. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90254-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winberry L. K., Stewart C. J., Schaffhausen B. S., Fluck M. M. Transformation by polyoma ts-a mutants. I. Characterization of the transformed phenotype. Virology. 1985 Jul 30;144(2):433–447. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90284-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu Z. Y., Veldman G. M., Cowie A., Carr A., Schaffhausen B., Kamen R. Construction and functional characterization of polyomavirus genomes that separately encode the three early proteins. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):170–180. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.170-180.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]