Abstract
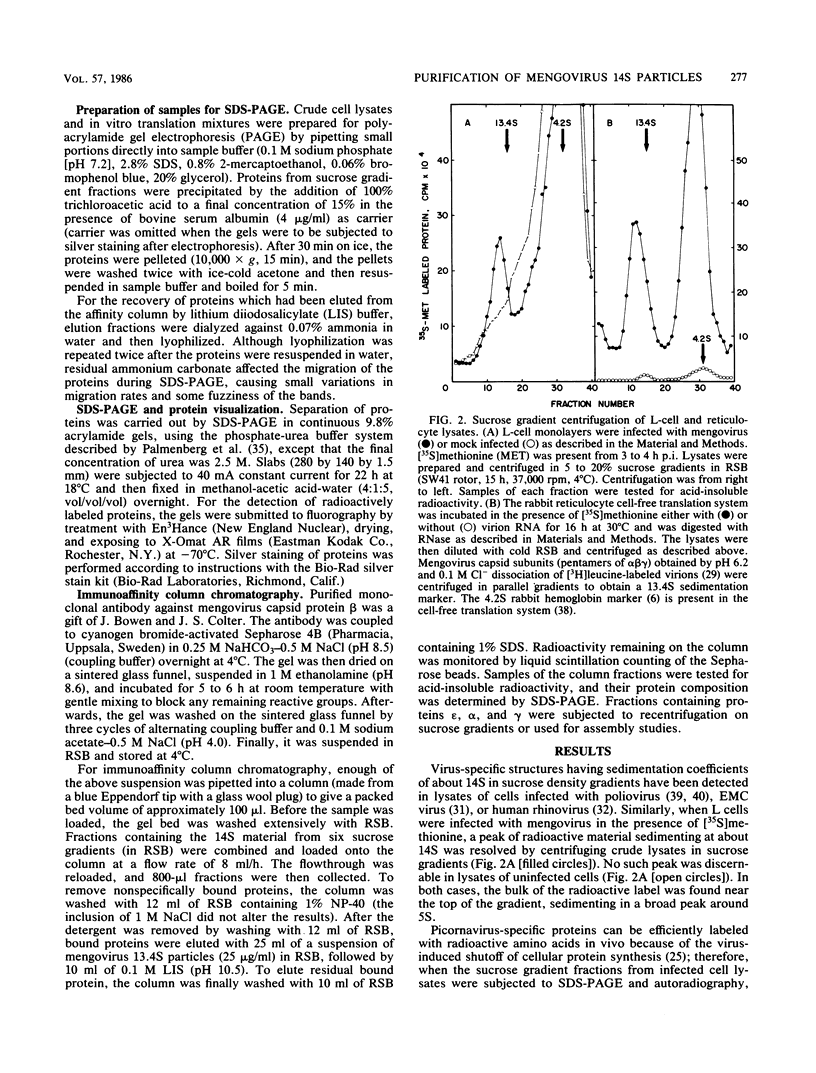
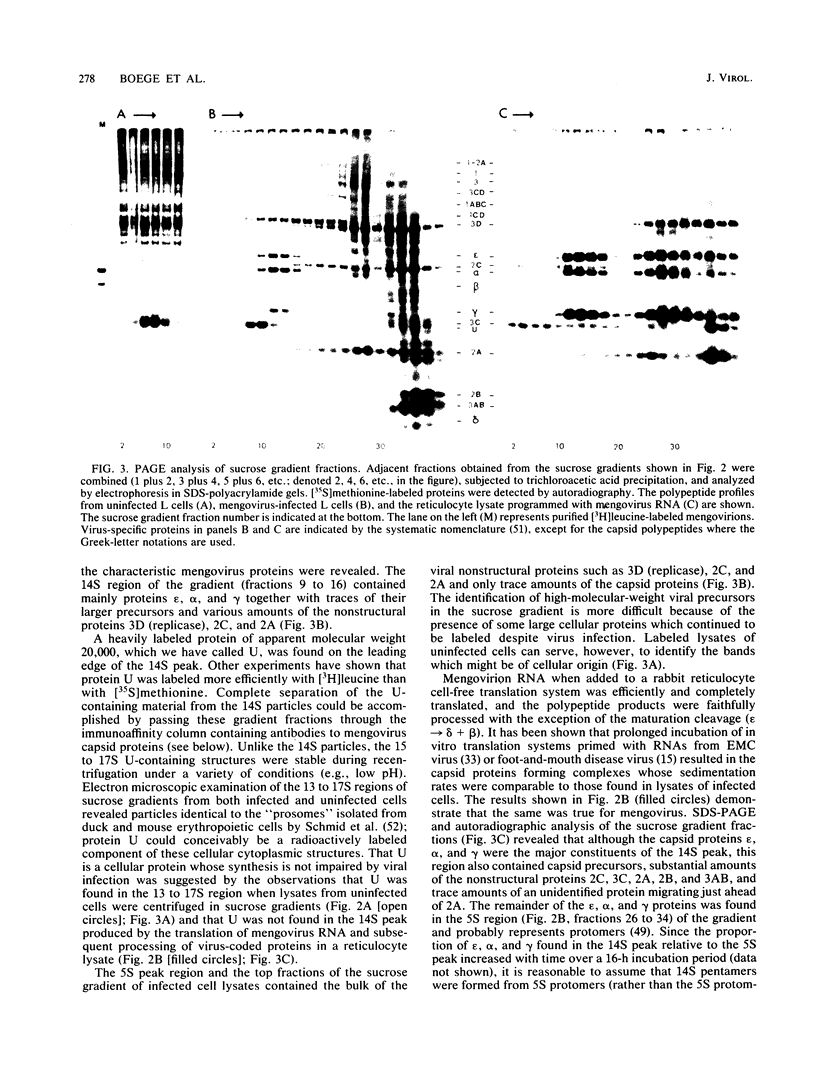
Mengovirus 14S subviral protein particles generated in infected L cells and in a cell-free translation system primed with mengovirus RNA were purified by sucrose gradient centrifugation and immunoaffinity chromatography. The preparations from both sources contained essentially pure proteins epsilon, alpha, and gamma, as was demonstrated in terms of virus-specific proteins (by autoradiography) and total protein content (by silver staining of sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide electrophoresis gels). These purified proteins sedimented as discrete particles at the 14S position when recentrifuged in sucrose gradients. Although their assembly properties have not yet been studied in detail, preliminary results indicate that during incubation with virion RNA the 14S particles purified from infected cells can form a structure cosedimenting with mature mengovirus.
Full text
PDF

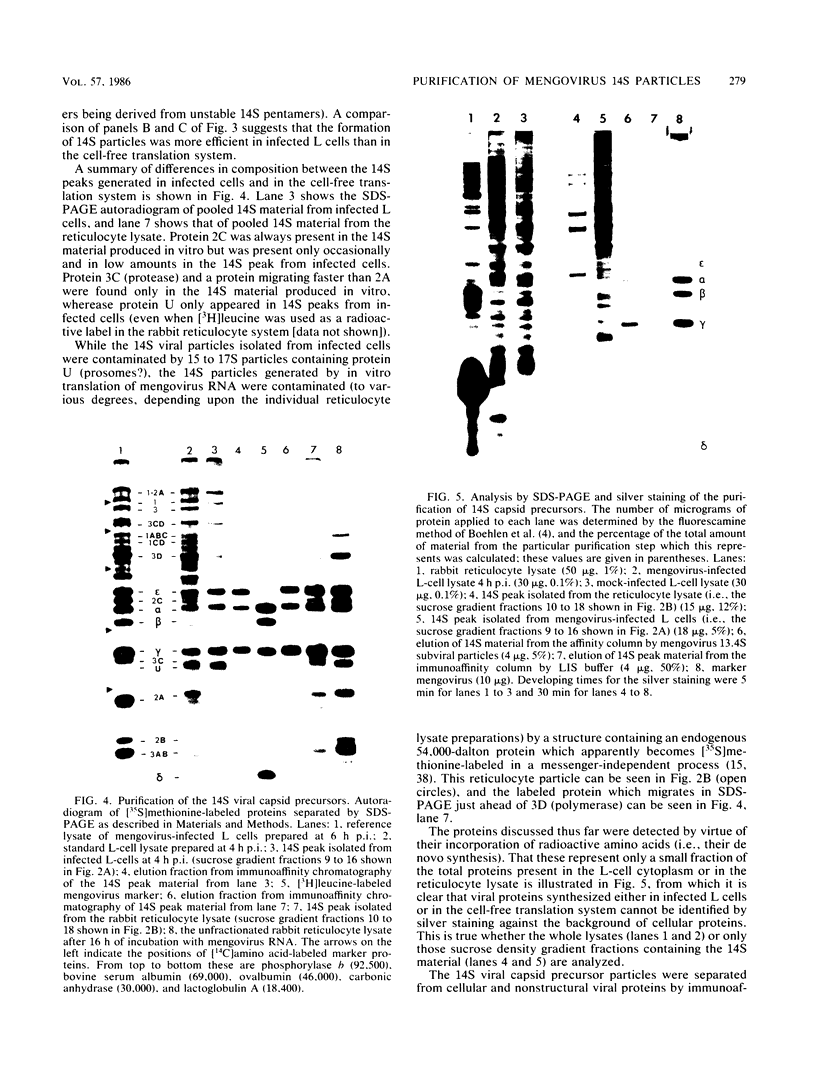
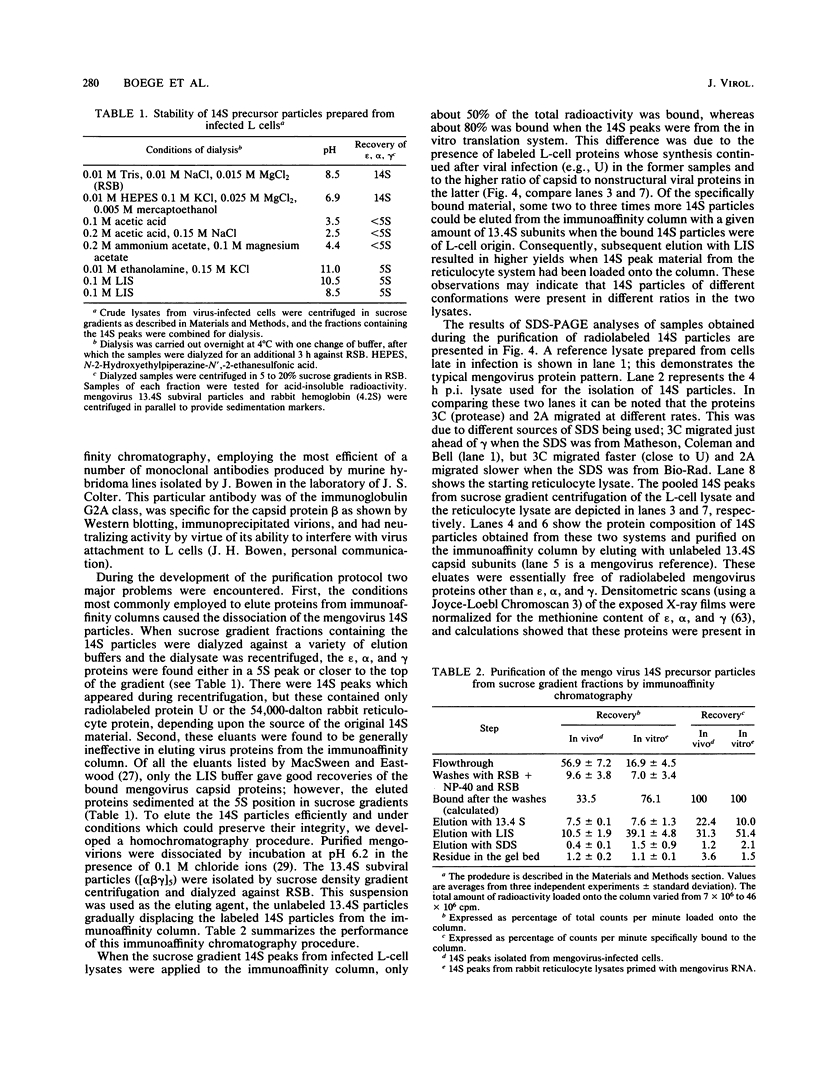
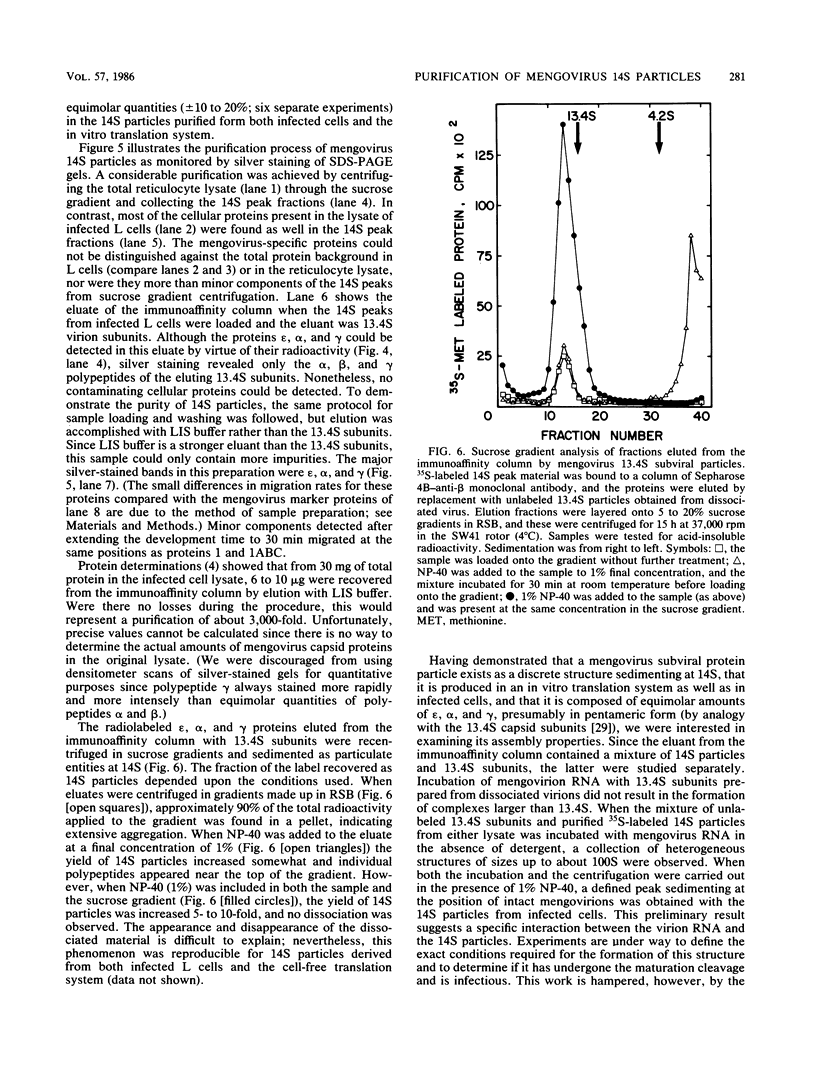



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambros V., Pettersson R. F., Baltimore D. An enzymatic activity in uninfected cells that cleaves the linkage between poliovirion RNA and the 5' terminal protein. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1439–1446. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90067-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong J. A., Edmonds M., Nakazato H., Phillips B. A., Vaughn M. H. Polyadenylic acid sequences in the virion RNA of poliovirus and Eastern Equine Encephalitis virus. Science. 1972 May 5;176(4034):526–528. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4034.526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold E., Erickson J. W., Fout G. S., Frankenberger E. A., Hecht H. J., Luo M., Rossman M. G., Rueckert R. R. Virion orientation in cubic crystals of the human common cold virus HRV14. J Mol Biol. 1984 Aug 15;177(3):417–430. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90293-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhlen P., Stein S., Dairman W., Udenfriend S. Fluorometric assay of proteins in the nanogram range. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Mar;155(1):213–220. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(73)80023-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callahan P. L., Mizutani S., Colonno R. J. Molecular cloning and complete sequence determination of RNA genome of human rhinovirus type 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):732–736. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiancone E., Vecchini P., Forlani L., Antonini E., Wyman J. Dissociation of hemoglobin from different animal species into subunits. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Oct 31;127(2):549–552. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90415-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan K. M., Graves J. H. A third antigenic component associated with foot-and-mouth disease infection. Virology. 1966 Nov;30(3):528–540. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90128-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drescher-Lincoln C. K., Putnak J. R., Phillips B. A. Use of temperature-sensitive mutants to study the morphogenesis of poliovirus. Virology. 1983 Apr 15;126(1):301–316. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90480-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunker A. K., Rueckert R. R. Fragments generated by pH dissociation of ME-virus and their relation to the structure of the virion. J Mol Biol. 1971 May 28;58(1):217–235. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90242-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLEM K. A., COLTER J. S. The isolation of three variants of Mengo virus differing in plaque morphology and hemagglutinating characteristics. Virology. 1961 Nov;15:340–347. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90365-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Tomas C. B., Baltimore D. Morphogenesis of poliovirus. II. Demonstration of a new intermediate, the proviron. J Virol. 1973 Nov;12(5):1122–1130. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.5.1122-1130.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forss S., Strebel K., Beck E., Schaller H. Nucleotide sequence and genome organization of foot-and-mouth disease virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 24;12(16):6587–6601. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.16.6587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghendon Y., Yakobson E., Mikhejeva A. Study of some stages of poliovirus morphogenesis in MiO cells. J Virol. 1972 Aug;10(2):261–266. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.2.261-266.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubman M. J. In vitro morphogenesis of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):760–765. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.760-765.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanecak R., Semler B. L., Anderson C. W., Wimmer E. Proteolytic processing of poliovirus polypeptides: antibodies to polypeptide P3-7c inhibit cleavage at glutamine-glycine pairs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):3973–3977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.3973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanecak R., Semler B. L., Ariga H., Anderson C. W., Wimmer E. Expression of a cloned gene segment of poliovirus in E. coli: evidence for autocatalytic production of the viral proteinase. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1063–1073. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90441-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hordern J. S., Leonard J. D., Scraba D. G. Structure of the mengo virion. VI. Spatial relationships of the capsid polypeptides as determined by chemical cross-linking analyses. Virology. 1979 Aug;97(1):131–140. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90379-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. F., Baltimore D. Polypeptide cleavages in the formation of poliovirus proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Sep;61(1):77–84. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura N., Semler B. L., Rothberg P. G., Larsen G. R., Adler C. J., Dorner A. J., Emini E. A., Hanecak R., Lee J. J., van der Werf S. Primary structure, gene organization and polypeptide expression of poliovirus RNA. Nature. 1981 Jun 18;291(5816):547–553. doi: 10.1038/291547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klump W., Marquardt O., Hofschneider P. H. Biologically active protease of foot and mouth disease virus is expressed from cloned viral cDNA in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3351–3355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korant B. D., Lonberg-Holm K., Yin F. H., Noble-Harvey J. Fractionation of biologically active and inactive populations of human rhinovirus type 2. Virology. 1975 Feb;63(2):384–394. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90311-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korant B., Chow N., Lively M., Powers J. Virus-specified protease in poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2992–2995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. W., Colter J. S. Further characterization of Mengo subviral particles: a new hypothesis for picornavirus assembly. Virology. 1979 Sep;97(2):266–274. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90338-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo M., Arnold E., Erickson J. W., Rossmann M. G., Boege U., Scraba D. G. Picornaviruses of two different genera have similar structures. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 15;180(3):703–714. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90033-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacSween J. M., Eastwood S. L. Recovery of antigen from staphylococcal protein A--antibody adsorbents. Methods Enzymol. 1981;73(Pt B):459–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mak T. W., Colter J. S., Scraba D. G. Structure of the Mengo virion. II. Physicochemical and electron microscopic analysis of degraded virus. Virology. 1974 Feb;57(2):543–553. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90193-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marongiu M. E., Pani A., Corrias M. V., Sau M., La Colla P. Poliovirus morphogenesis. I. Identification of 80S dissociable particles and evidence for the artifactual production of procapsids. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):341–347. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.341-347.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor S. Evidence for the existence of protomers in the assembly of encephalomyocarditis virus. J Virol. 1975 May;15(5):1107–1120. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.5.1107-1120.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor S., Rueckert R. R. Picornaviral capsid assembly: similarity of rhinovirus and enterovirus precursor subunits. J Virol. 1977 Feb;21(2):548–553. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.2.548-553.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmenberg A. C. In vitro synthesis and assembly of picornaviral capsid intermediate structures. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):900–906. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.900-906.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmenberg A. C., Kirby E. M., Janda M. R., Drake N. L., Duke G. M., Potratz K. F., Collett M. S. The nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of the encephalomyocarditis viral polyprotein coding region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):2969–2985. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.2969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmenberg A. C., Pallansch M. A., Rueckert R. R. Protease required for processing picornaviral coat protein resides in the viral replicase gene. J Virol. 1979 Dec;32(3):770–778. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.3.770-778.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmenberg A. C., Rueckert R. R. Evidence for intramolecular self-cleavage of picornaviral replicase precursors. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):244–249. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.244-249.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paucha E., Seehafer J., Colter J. S. Synthesis of viral-specific polypeptides in Mengo virus-infected L cells: evidence for asymmetric translation of the viral genome. Virology. 1974 Oct;61(2):315–326. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90269-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips B. A. In vitro assembly of polioviruses. I. Kinetics of the assembly of empty capsids and the role of extracts from infected cells. Virology. 1969 Dec;39(4):811–821. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90018-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips B. A., Summers D. F., Maizel J. V., Jr In vitro assembly of poliovirus-related particles. Virology. 1968 Jun;35(2):216–226. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90262-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips B. A., Wiemert S. In vitro assembly of poliovirus. V. Evidence that the self-assembly activity of 14 S particles is independent of extract assembly factor(s) and host proteins. Virology. 1978 Jul 1;88(1):92–104. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90113-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putnak J. R., Phillips B. A. Differences between poliovirus empty capsids formed in vivo and those formed in vitro: a role for the morphopoietic factor. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):173–183. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.173-183.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putnak J. R., Phillips B. A. Picornaviral structure and assembly. Microbiol Rev. 1981 Jun;45(2):287–315. doi: 10.1128/mr.45.2.287-315.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putnak J. R., Phillips B. A. Poliovirus empty capsid morphogenesis: evidence for conformational differences between self- and extract-assembled empty capsids. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):792–800. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.792-800.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racaniello V. R., Baltimore D. Molecular cloning of poliovirus cDNA and determination of the complete nucleotide sequence of the viral genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4887–4891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rombaut B., Vrijsen R., Boeyé A. Epitope evolution in poliovirus maturation. Arch Virol. 1983;76(4):289–298. doi: 10.1007/BF01311196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rombaut B., Vrijsen R., Boeyé A. In vitro assembly of poliovirus empty capsids: antigenic consequences and immunological assay of the morphopoietic factor. Virology. 1984 Jun;135(2):546–550. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90209-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rombaut B., Vrijsen R., Brioen P., Boeyé A. A pH-dependent antigenic conversion of empty capsids of poliovirus studied with the aid of monoclonal antibodies to N and H antigen. Virology. 1982 Oct 15;122(1):215–218. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90393-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rueckert R. R., Wimmer E. Systematic nomenclature of picornavirus proteins. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):957–959. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.957-959.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid H. P., Akhayat O., Martins De Sa C., Puvion F., Koehler K., Scherrer K. The prosome: an ubiquitous morphologically distinct RNP particle associated with repressed mRNPs and containing specific ScRNA and a characteristic set of proteins. EMBO J. 1984 Jan;3(1):29–34. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01757.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scraba D. G., Kay C. M., Colter J. S. Physico-chemical studies of three variants of Mengo virus and their constituent ribonucleates. J Mol Biol. 1967 May 28;26(1):67–79. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90261-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih D. S., Shih C. T., Zimmern D., Rueckert R. R., Kaesberg P. Translation of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA in reticulocyte lysates: kinetic analysis of the formation of virion proteins and a protein required for processing. J Virol. 1979 May;30(2):472–480. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.2.472-480.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. H., Baltimore D. Poly(A) on mengovirus RNA. J Virol. 1975 Oct;16(4):1081–1084. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.4.1081-1084.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanway G., Hughes P. J., Mountford R. C., Minor P. D., Almond J. W. The complete nucleotide sequence of a common cold virus: human rhinovirus 14. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 25;12(20):7859–7875. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.20.7859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su R. T., Taylor M. W. Morphogenesis of picornaviruses: characterization and assembly of bovine enterovirus subviral particles. J Gen Virol. 1976 Mar;30(3):317–328. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-30-3-317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATANABE Y., WATANABE K., HINUMA Y. Synthesis of poliovirus-specific proteins in HeLa cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Dec 31;61:976–977. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(62)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yafal A. G., Palma E. L. Morphogenesis of foot-and-mouth disease virus. I. Role of procapsids as virion Precursors. J Virol. 1979 Jun;30(3):643–649. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.3.643-649.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yogo Y., Wimmer E. Polyadenylic acid at the 3'-terminus of poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1877–1882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziola B. R., Scraba D. G. Structure of the Mengo virion. I. Polypeptide and ribonucleate components of the virus particle. Virology. 1974 Feb;57(2):531–542. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90192-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziola B. R., Scraba D. G. Structure of the mengo virion. III. Purification and amino acid compositions of the major capsid polypeptides. Virology. 1975 Mar;64(1):228–235. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90094-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]