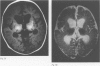
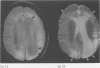
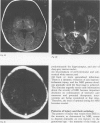
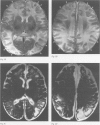
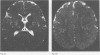
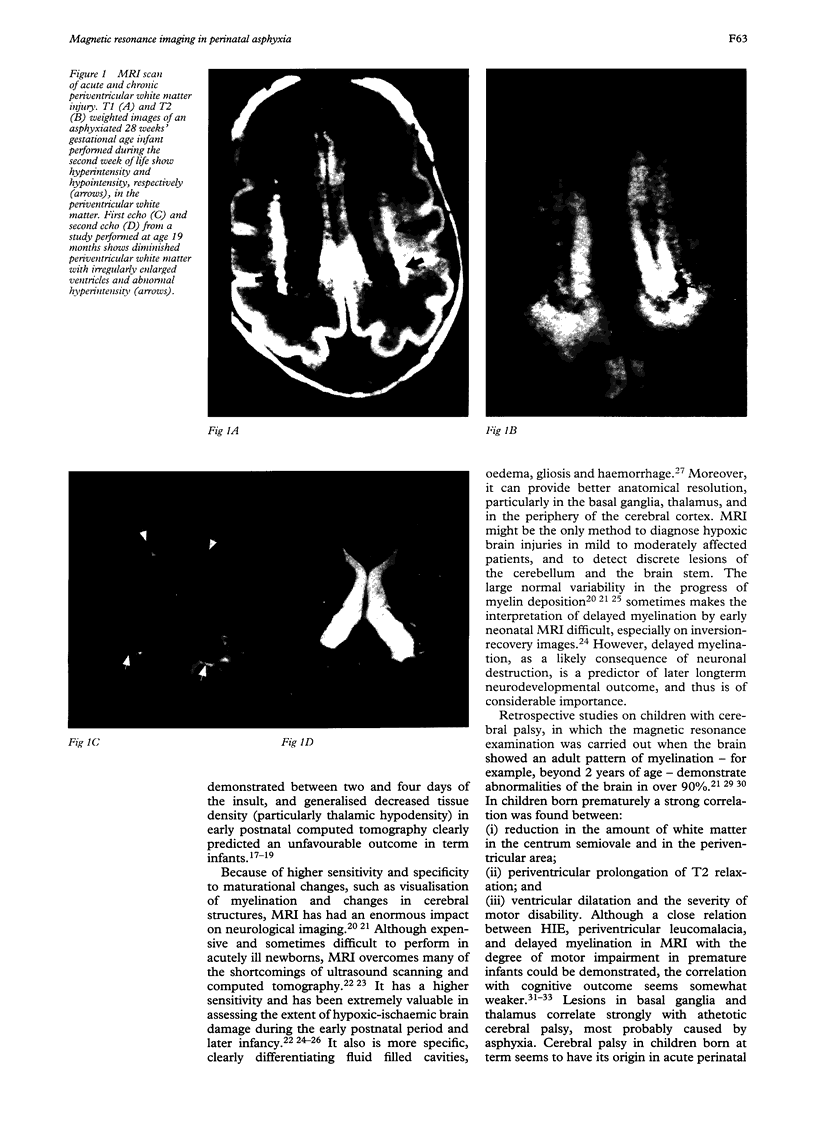
Full text
PDF
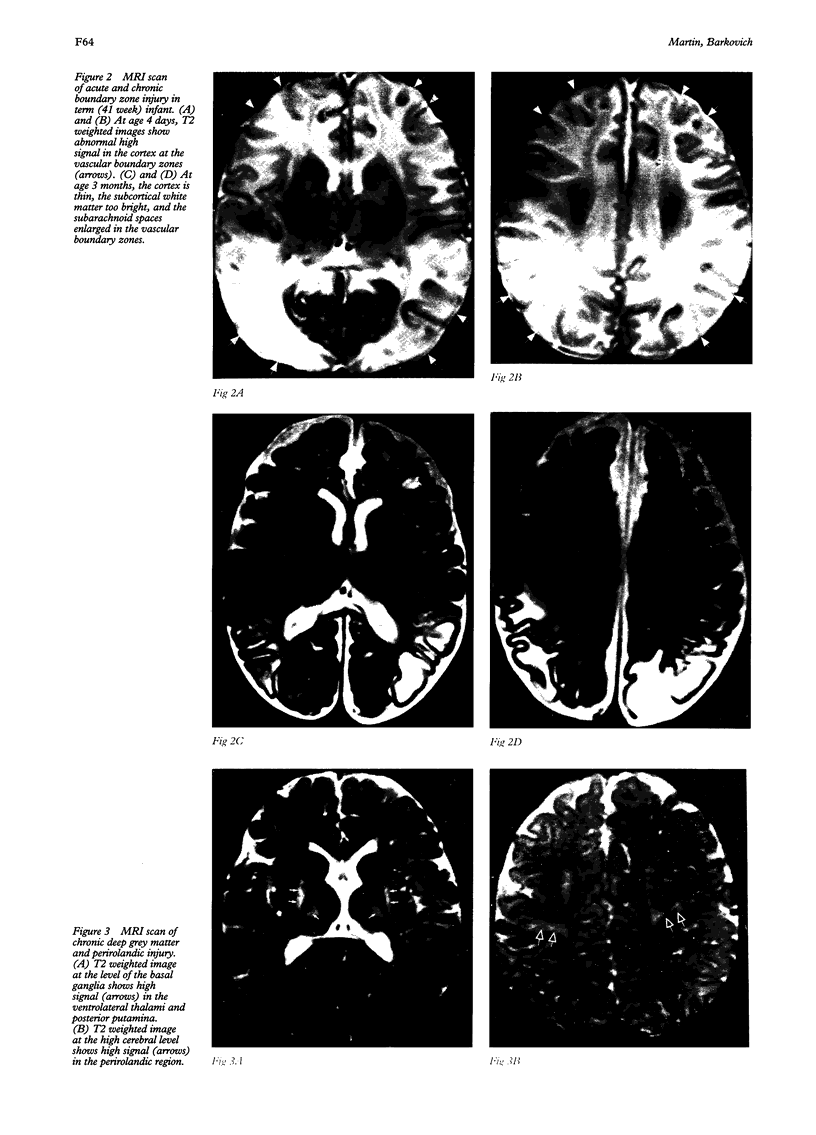
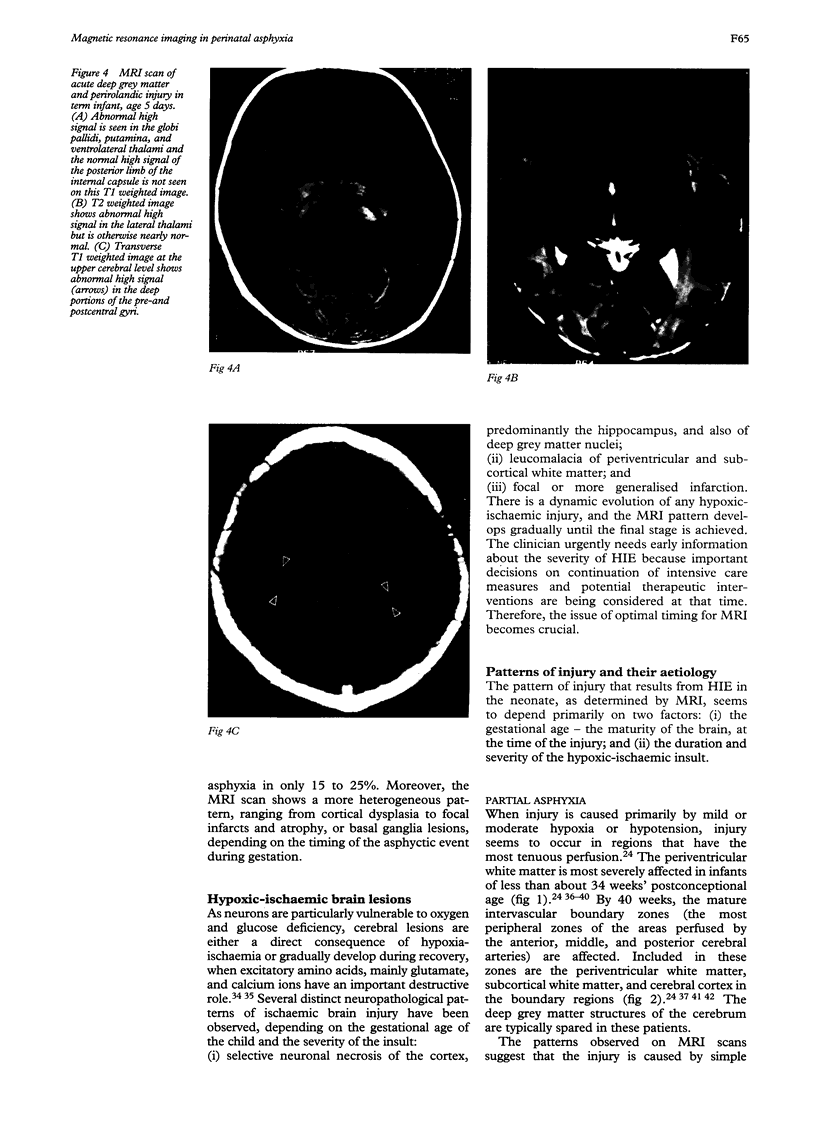
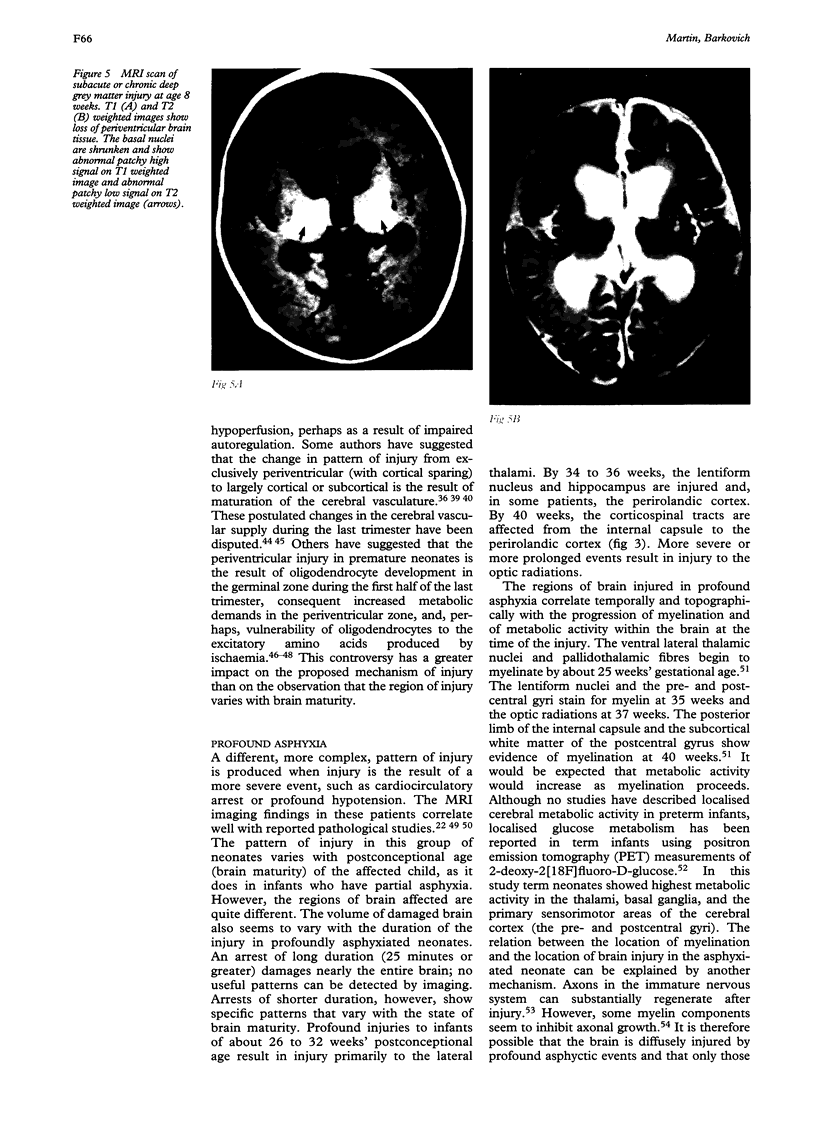
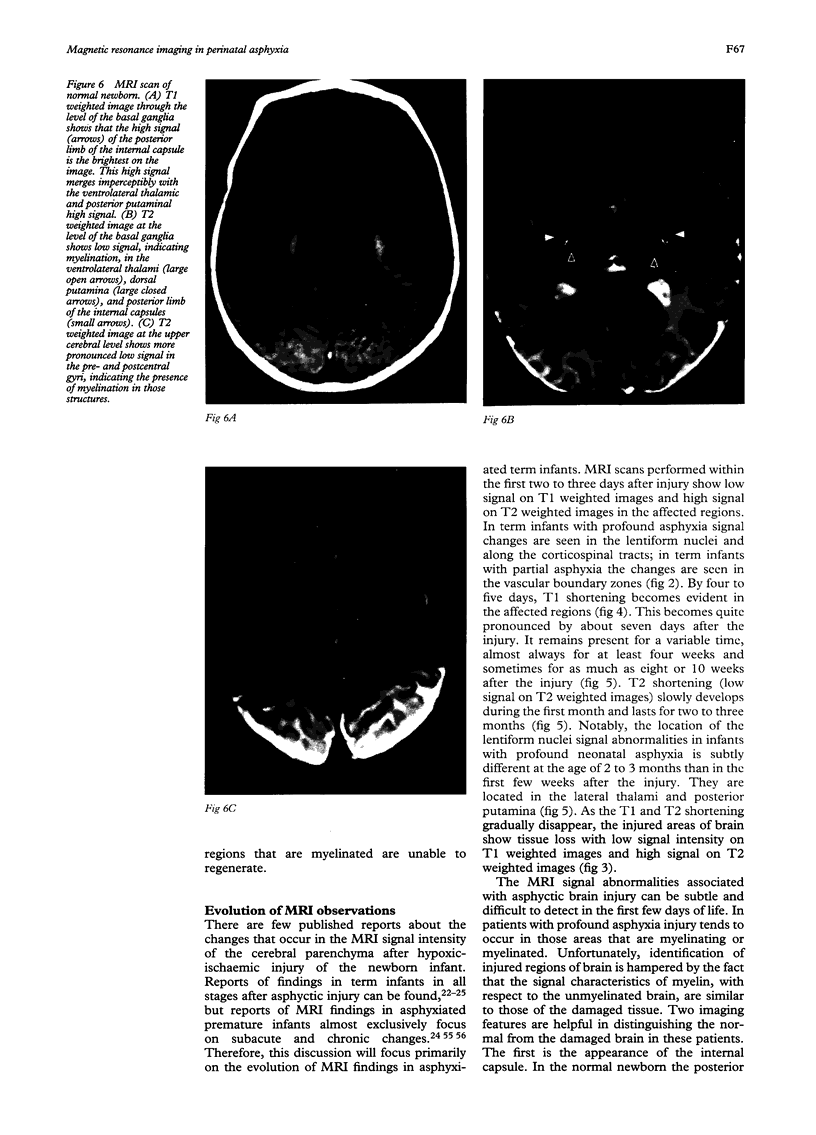
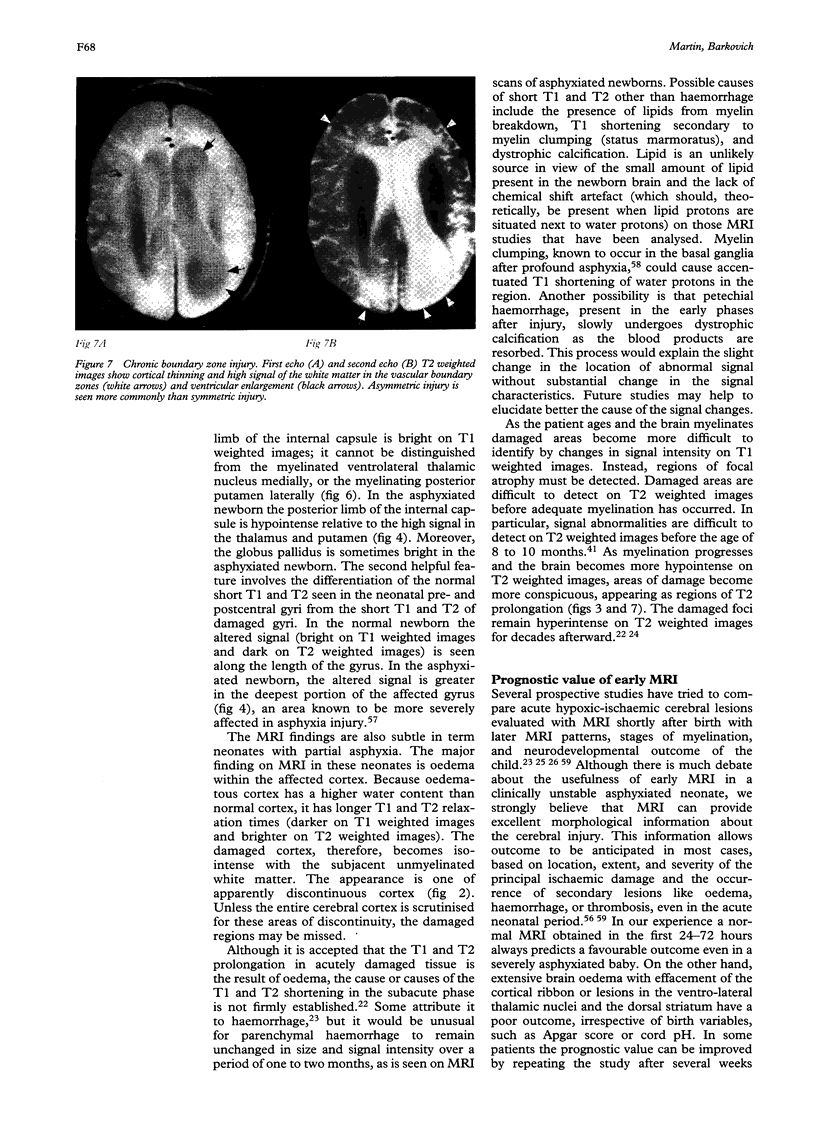


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BANKER B. Q., LARROCHE J. C. Periventricular leukomalacia of infancy. A form of neonatal anoxic encephalopathy. Arch Neurol. 1962 Nov;7:386–410. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1962.04210050022004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baenziger O., Martin E., Steinlin M., Good M., Largo R., Burger R., Fanconi S., Duc G., Buchli R., Rumpel H. Early pattern recognition in severe perinatal asphyxia: a prospective MRI study. Neuroradiology. 1993;35(6):437–442. doi: 10.1007/BF00602824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barkovich A. J., Kjos B. O., Jackson D. E., Jr, Norman D. Normal maturation of the neonatal and infant brain: MR imaging at 1.5 T. Radiology. 1988 Jan;166(1 Pt 1):173–180. doi: 10.1148/radiology.166.1.3336675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barkovich A. J. MR and CT evaluation of profound neonatal and infantile asphyxia. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1992 May-Jun;13(3):959–975. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barkovich A. J., Truwit C. L. Brain damage from perinatal asphyxia: correlation of MR findings with gestational age. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1990 Nov-Dec;11(6):1087–1096. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brody B. A., Kinney H. C., Kloman A. S., Gilles F. H. Sequence of central nervous system myelination in human infancy. I. An autopsy study of myelination. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1987 May;46(3):283–301. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198705000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne P., Welch R., Johnson M. A., Darrah J., Piper M. Serial magnetic resonance imaging in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. J Pediatr. 1990 Nov;117(5):694–700. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)83323-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caroni P., Schwab M. E. Two membrane protein fractions from rat central myelin with inhibitory properties for neurite growth and fibroblast spreading. J Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;106(4):1281–1288. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.4.1281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chugani H. T., Phelps M. E., Mazziotta J. C. Positron emission tomography study of human brain functional development. Ann Neurol. 1987 Oct;22(4):487–497. doi: 10.1002/ana.410220408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark G. D. Role of excitatory amino acids in brain injury caused by hypoxia-ischemia, status epilepticus, and hypoglycemia. Clin Perinatol. 1989 Jun;16(2):459–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costello A. M., Hamilton P. A., Baudin J., Townsend J., Bradford B. C., Stewart A. L., Reynolds E. O. Prediction of neurodevelopmental impairment at four years from brain ultrasound appearance of very preterm infants. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1988 Dec;30(6):711–722. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1988.tb14633.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Reuck J. The human periventricular arterial blood supply and the anatomy of cerebral infarctions. Eur Neurol. 1971;5(6):321–334. doi: 10.1159/000114088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vries L. S., Connell J. A., Dubowitz L. M., Oozeer R. C., Dubowitz V., Pennock J. M. Neurological, electrophysiological and MRI abnormalities in infants with extensive cystic leukomalacia. Neuropediatrics. 1987 May;18(2):61–66. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1052453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vries L. S., Pierrat V., Eken P., Minami T., Daniels H., Casaer P. Prognostic value of early somatosensory evoked potentials for adverse outcome in full-term infants with birth asphyxia. Brain Dev. 1991 Sep;13(5):320–325. doi: 10.1016/s0387-7604(12)80126-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawer C. L., Diebold P., Calame A. Periventricular leucomalacia and neurodevelopmental outcome in preterm infants. Arch Dis Child. 1987 Jan;62(1):30–36. doi: 10.1136/adc.62.1.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman H. M., Scher M. S., Kemp S. S. Neurodevelopmental outcome of children with evidence of periventricular leukomalacia on late MRI. Pediatr Neurol. 1990 Sep-Oct;6(5):296–302. doi: 10.1016/0887-8994(90)90020-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flodmark O., Roland E. H., Hill A., Whitfield M. F. Periventricular leukomalacia: radiologic diagnosis. Radiology. 1987 Jan;162(1 Pt 1):119–124. doi: 10.1148/radiology.162.1.3538143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii Y., Konishi Y., Kuriyama M., Maeda M., Saito M., Ishii Y., Sudo M. MRI assessment of myelination patterns in high-risk infants. Pediatr Neurol. 1993 May-Jun;9(3):194–197. doi: 10.1016/0887-8994(93)90083-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. H., Tudehope D. I., Masel J. P., Burns Y. R., Mohay H. A., O'Callaghan M. J., Williams G. M. Perinatal hypoxic-ischaemic brain injury: prediction of outcome. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1993 Nov;35(11):965–973. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1993.tb11578.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi M., Satoh J., Sakamoto K., Morimatsu Y. Clinical and neuropathological findings in severe athetoid cerebral palsy: a comparative study of globo-Luysian and thalamo-putaminal groups. Brain Dev. 1991;13(1):47–51. doi: 10.1016/s0387-7604(12)80297-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill A. Current concepts of hypoxic-ischemic cerebral injury in the term newborn. Pediatr Neurol. 1991 Sep-Oct;7(5):317–325. doi: 10.1016/0887-8994(91)90060-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keeney S. E., Adcock E. W., McArdle C. B. Prospective observations of 100 high-risk neonates by high-field (1.5 Tesla) magnetic resonance imaging of the central nervous system. II. Lesions associated with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Pediatrics. 1991 Apr;87(4):431–438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeda T., Suganuma I., Kohno Y., Takamatsu T., Takeshita K. MR imaging of spastic diplegia. Comparative study between preterm and term infants. Neuroradiology. 1990;32(3):187–190. doi: 10.1007/BF00589108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konishi Y., Kuriyama M., Hayakawa K., Konishi K., Yasujima M., Fujii Y., Sudo M. Periventricular hyperintensity detected by magnetic resonance imaging in infancy. Pediatr Neurol. 1990 Jul-Aug;6(4):229–232. doi: 10.1016/0887-8994(90)90112-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuban K. C., Gilles F. H. Human telencephalic angiogenesis. Ann Neurol. 1985 Jun;17(6):539–548. doi: 10.1002/ana.410170603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuenzle C., Baenziger O., Martin E., Thun-Hohenstein L., Steinlin M., Good M., Fanconi S., Boltshauser E., Largo R. H. Prognostic value of early MR imaging in term infants with severe perinatal asphyxia. Neuropediatrics. 1994 Aug;25(4):191–200. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1073021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levene M. I. Cerebral ultrasound and neurological impairment: telling the future. Arch Dis Child. 1990 May;65(5):469–471. doi: 10.1136/adc.65.5.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levene M. I., Fenton A. C., Evans D. H., Archer L. N., Shortland D. B., Gibson N. A. Severe birth asphyxia and abnormal cerebral blood-flow velocity. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1989 Aug;31(4):427–434. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1989.tb04020.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipp-Zwahlen A. E., Deonna T., Micheli J. L., Calame A., Chrzanowski R., Cêtre E. Prognostic value of neonatal CT scans in asphyxiated term babies: low density score compared with neonatal neurological signs. Neuropediatrics. 1985 Nov;16(4):209–217. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1059539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin E., Boesch C., Zuerrer M., Kikinis R., Molinari L., Kaelin P., Boltshauser E., Duc G. MR imaging of brain maturation in normal and developmentally handicapped children. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1990 Sep-Oct;14(5):685–692. doi: 10.1097/00004728-199009000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McArdle C. B., Richardson C. J., Hayden C. K., Nicholas D. A., Amparo E. G. Abnormalities of the neonatal brain: MR imaging. Part II. Hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Radiology. 1987 May;163(2):395–403. doi: 10.1148/radiology.163.2.3550882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson K. B., Ellenberg J. H. Antecedents of cerebral palsy. Multivariate analysis of risk. N Engl J Med. 1986 Jul 10;315(2):81–86. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198607103150202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M. D., Jr, Gonzalez-Gomez I., Gilles F. H. Dyke Award. The search for human telencephalic ventriculofugal arteries. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1991 Mar-Apr;12(2):215–222. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka A., Belliveau M. J., Rosenberg P. A., Volpe J. J. Vulnerability of oligodendroglia to glutamate: pharmacology, mechanisms, and prevention. J Neurosci. 1993 Apr;13(4):1441–1453. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-04-01441.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pharoah P. O., Cooke T., Rosenbloom I., Cooke R. W. Trends in birth prevalence of cerebral palsy. Arch Dis Child. 1987 Apr;62(4):379–384. doi: 10.1136/adc.62.4.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivkin M. J., Volpe J. J. Hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in the newborn. Semin Neurol. 1993 Mar;13(1):30–39. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1041104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorke L. B. Anatomical features of the developing brain implicated in pathogenesis of hypoxic-ischemic injury. Brain Pathol. 1992 Jul;2(3):211–221. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.1992.tb00694.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarnat H. B., Sarnat M. S. Neonatal encephalopathy following fetal distress. A clinical and electroencephalographic study. Arch Neurol. 1976 Oct;33(10):696–705. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1976.00500100030012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders N. R., Balkwill P., Knott G., Habgood M. D., Møllgård K., Treherne J. M., Nicholls J. G. Growth of axons through a lesion in the intact CNS of fetal rat maintained in long-term culture. Proc Biol Sci. 1992 Dec 22;250(1329):171–180. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1992.0146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scher M. S., Belfar H., Martin J., Painter M. J. Destructive brain lesions of presumed fetal onset: antepartum causes of cerebral palsy. Pediatrics. 1991 Nov;88(5):898–906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider H., Ballowitz L., Schachinger H., Hanefeld F., Dröszus J. U. Anoxic encephalopathy with predominant involvement of basal ganglia, brain stem and spinal cord in the perinatal period. Report on seven newborns. Acta Neuropathol. 1975 Oct 1;32(4):287–298. doi: 10.1007/BF00696791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schouman-Claeys E., Henry-Feugeas M. C., Roset F., Larroche J. C., Hassine D., Sadik J. C., Frija G., Gabilan J. C. Periventricular leukomalacia: correlation between MR imaging and autopsy findings during the first 2 months of life. Radiology. 1993 Oct;189(1):59–64. doi: 10.1148/radiology.189.1.8372220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel M. J., Shackelford G. D., Perlman J. M., Fulling K. H. Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in term infants: diagnosis and prognosis evaluated by ultrasound. Radiology. 1984 Aug;152(2):395–399. doi: 10.1148/radiology.152.2.6739805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinlin M., Dirr R., Martin E., Boesch C., Largo R. H., Fanconi S., Boltshauser E. MRI following severe perinatal asphyxia: preliminary experience. Pediatr Neurol. 1991 May-Jun;7(3):164–170. doi: 10.1016/0887-8994(91)90079-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takashima S., Armstrong D. L., Becker L. E. Subcortical leukomalacia. Relationship to development of the cerebral sulcus and its vascular supply. Arch Neurol. 1978 Jul;35(7):470–472. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1978.00500310072015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takashima S., Tanaka K. Development of cerebrovascular architecture and its relationship to periventricular leukomalacia. Arch Neurol. 1978 Jan;35(1):11–16. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1978.00500250015003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truwit C. L., Barkovich A. J., Koch T. K., Ferriero D. M. Cerebral palsy: MR findings in 40 patients. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1992 Jan-Feb;13(1):67–78. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpe J. J. Brain injury in the premature infant--current concepts of pathogenesis and prevention. Biol Neonate. 1992;62(4):231–242. doi: 10.1159/000243876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpe J. J. Edward B. Neuhauser lecture. Current concepts of brain injury in the premature infant. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1989 Aug;153(2):243–251. doi: 10.2214/ajr.153.2.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpe J. J., Herscovitch P., Perlman J. M., Kreusser K. L., Raichle M. E. Positron emission tomography in the asphyxiated term newborn: parasagittal impairment of cerebral blood flow. Ann Neurol. 1985 Mar;17(3):287–296. doi: 10.1002/ana.410170312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpe J. J., Herscovitch P., Perlman J. M., Raichle M. E. Positron emission tomography in the newborn: extensive impairment of regional cerebral blood flow with intraventricular hemorrhage and hemorrhagic intracerebral involvement. Pediatrics. 1983 Nov;72(5):589–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpe J. J. Intraventricular hemorrhage and brain injury in the premature infant. Neuropathology and pathogenesis. Clin Perinatol. 1989 Jun;16(2):361–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigglesworth J. S., Pape K. E. An integrated model for haemorrhagic and ischaemic lesions in the newborn brain. Early Hum Dev. 1978 Jul;2(2):179–199. doi: 10.1016/0378-3782(78)90010-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokochi K., Aiba K., Horie M., Inukai K., Fujimoto S., Kodama M., Kodama K. Magnetic resonance imaging in children with spastic diplegia: correlation with the severity of their motor and mental abnormality. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1991 Jan;33(1):18–25. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1991.tb14781.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries L. S., Dubowitz L. M., Dubowitz V., Kaiser A., Lary S., Silverman M., Whitelaw A., Wigglesworth J. S. Predictive value of cranial ultrasound in the newborn baby: a reappraisal. Lancet. 1985 Jul 20;2(8447):137–140. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90237-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries L. S., Eken P., Pierrat V., Daniels H., Casaer P. Prediction of neurodevelopmental outcome in the preterm infant: short latency cortical somatosensory evoked potentials compared with cranial ultrasound. Arch Dis Child. 1992 Oct;67(10 Spec No):1177–1181. doi: 10.1136/adc.67.10_spec_no.1177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Bor M., Ens-Dokkum M., Schreuder A. M., Veen S., Brand R., Verloove-Vanhorick S. P. Outcome of periventricular-intraventricular haemorrhage at five years of age. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1993 Jan;35(1):33–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Bor M., Guit G. L., Schreuder A. M., Wondergem J., Vielvoye G. J. Early detection of delayed myelination in preterm infants. Pediatrics. 1989 Sep;84(3):407–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]