Abstract
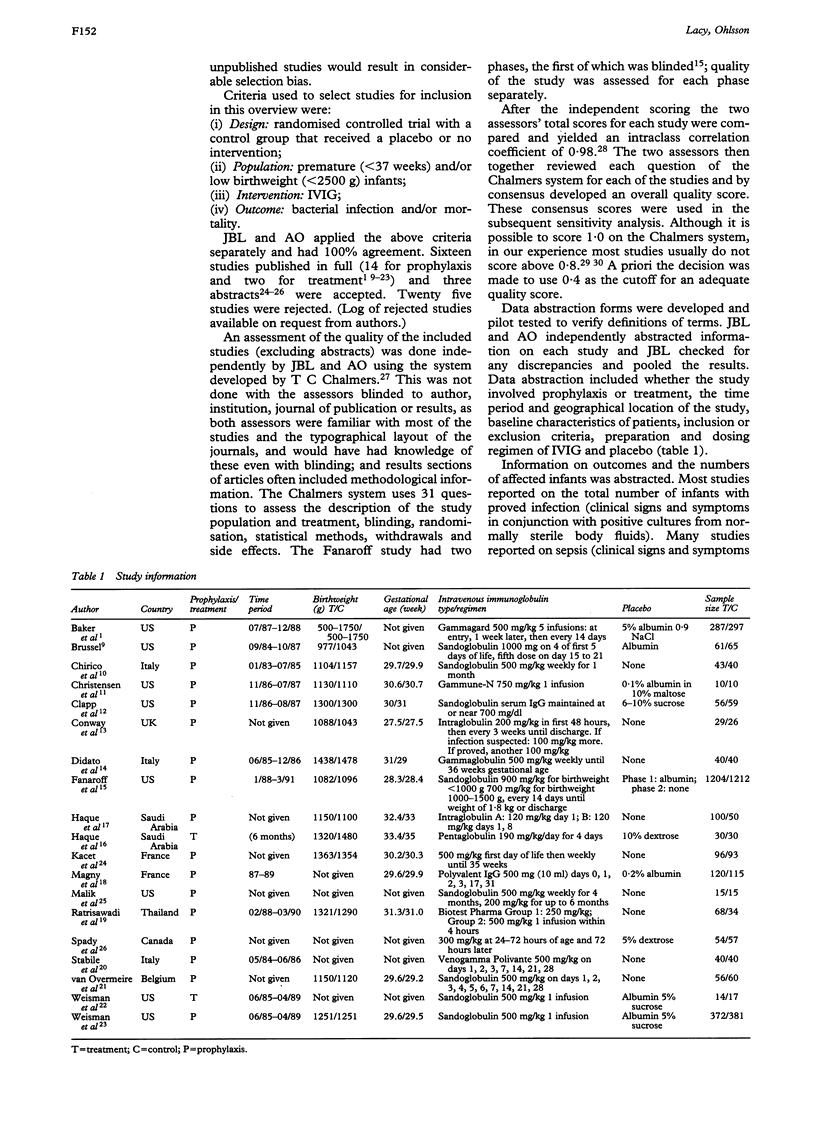
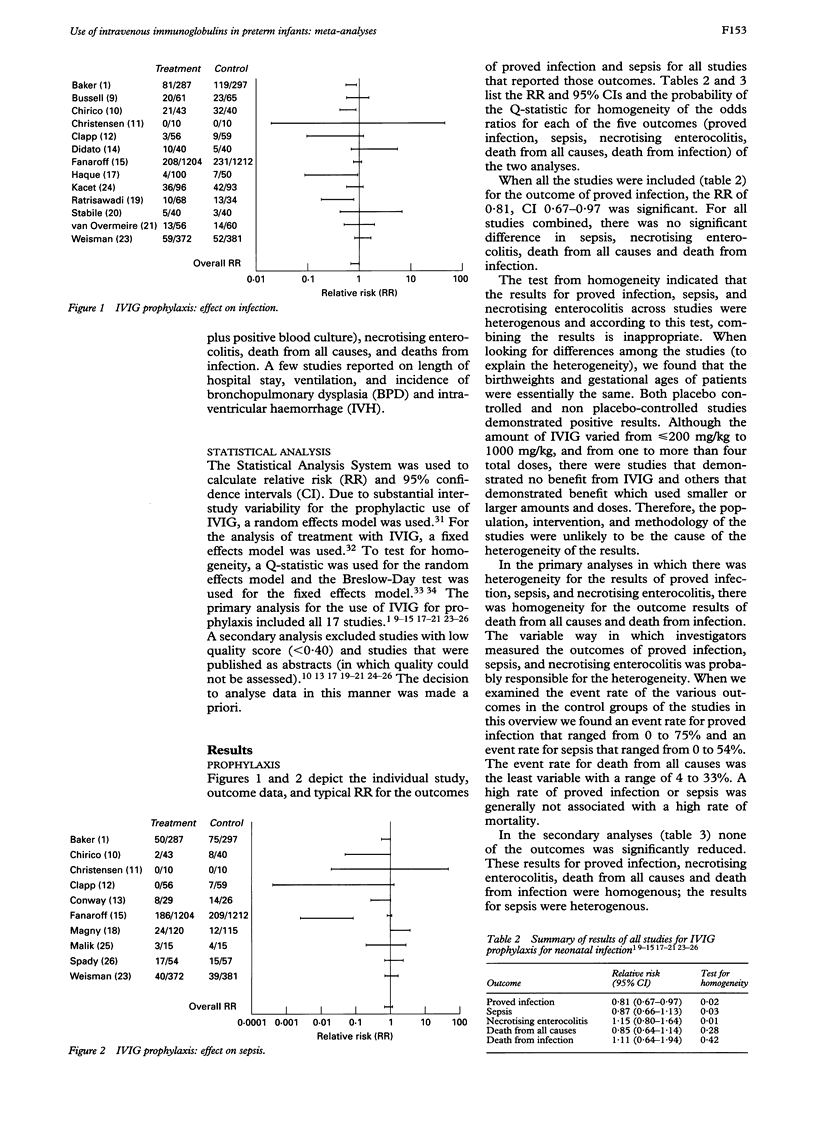
AIMS--To determine the effectiveness of intravenous immunoglobulin administration to premature infants in the prevention and/or treatment of bacterial infection. METHODS--Computer searches of MEDLINE, EMBASE, SCISEARCH and Oxford Database of Perinatal Trials were made. Two independent researchers applied inclusion criteria of: randomised controlled trial; premature and/or low birthweight infant; use of intravenous immunoglobulin; and infection or mortality. Nineteen of 44 identified studies fulfilled these criteria. Study quality was assessed and information on study population, intervention, and outcomes were collected. RESULTS--Studies were divided into prophylaxis or treatment; results were tabulated for infection, sepsis, and death from all causes. For 17 studies of prophylaxis (n = 5245), the relative risk and confidence interval were, for proved infection 0.81, 0.67-0.97; for sepsis 0.87, 0.66-1.13; for death from all causes 0.85, 0.64-1.14. Some outcome results were heterogeneous. Two treatment studies showed no reduction in mortality when combined. CONCLUSIONS--Routine administration of intravenous immunoglobulin to preterm infants is not recommended.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker C. J., Melish M. E., Hall R. T., Casto D. T., Vasan U., Givner L. B. Intravenous immune globulin for the prevention of nosocomial infection in low-birth-weight neonates. The Multicenter Group for the Study of Immune Globulin in Neonates. N Engl J Med. 1992 Jul 23;327(4):213–219. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199207233270401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussel J. B. Intravenous gammaglobulin in the prophylaxis of late sepsis in very-low-birth-weight infants: preliminary results of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Rev Infect Dis. 1990 May-Jun;12 (Suppl 4):S457–S462. doi: 10.1093/clinids/12.supplement_4.s457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalmers T. C., Smith H., Jr, Blackburn B., Silverman B., Schroeder B., Reitman D., Ambroz A. A method for assessing the quality of a randomized control trial. Control Clin Trials. 1981 May;2(1):31–49. doi: 10.1016/0197-2456(81)90056-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirico G., Rondini G., Plebani A., Chiara A., Massa M., Ugazio A. G. Intravenous gammaglobulin therapy for prophylaxis of infection in high-risk neonates. J Pediatr. 1987 Mar;110(3):437–442. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(87)80514-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen R. D., Hardman T., Thornton J., Hill H. R. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled investigation of the safety of intravenous immune globulin administration to preterm neonates. J Perinatol. 1989 Jun;9(2):126–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clapp D. W., Kliegman R. M., Baley J. E., Shenker N., Kyllonen K., Fanaroff A. A., Berger M. Use of intravenously administered immune globulin to prevent nosocomial sepsis in low birth weight infants: report of a pilot study. J Pediatr. 1989 Dec;115(6):973–978. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(89)80753-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway S. P., Ng P. C., Howel D., Maclain B., Gooi H. C. Prophylactic intravenous immunoglobulin in pre-term infants: a controlled trial. Vox Sang. 1990;59(1):6–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1990.tb02105.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DerSimonian R., Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 1986 Sep;7(3):177–188. doi: 10.1016/0197-2456(86)90046-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickersin K. The existence of publication bias and risk factors for its occurrence. JAMA. 1990 Mar 9;263(10):1385–1389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanaroff A. A., Korones S. B., Wright L. L., Wright E. C., Poland R. L., Bauer C. B., Tyson J. E., Philips J. B., 3rd, Edwards W., Lucey J. F. A controlled trial of intravenous immune globulin to reduce nosocomial infections in very-low-birth-weight infants. National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network. N Engl J Med. 1994 Apr 21;330(16):1107–1113. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199404213301602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer G. W., Weisman L. E. Therapeutic intervention of clinical sepsis with intravenous immunoglobulin, white blood cells and antibiotics. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1990;73:17–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haque K. N., Zaidi M. H., Bahakim H. IgM-enriched intravenous immunoglobulin therapy in neonatal sepsis. Am J Dis Child. 1988 Dec;142(12):1293–1296. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1988.02150120047038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haque K. N., Zaidi M. H., Haque S. K., Bahakim H., el-Hazmi M., el-Swailam M. Intravenous immunoglobulin for prevention of sepsis in preterm and low birth weight infants. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1986 Nov-Dec;5(6):622–625. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198611000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irani S. F., Wagle S. U., Deshpande P. G. Role of intravenous immunoglobulin in prevention and treatment of neonatal infection. Indian Pediatr. 1991 Apr;28(4):443–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliegman R. M., Clapp D. W. Rational principles for immunoglobulin prophylaxis and therapy of neonatal infections. Clin Perinatol. 1991 Jun;18(2):303–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy J. B., Ohlsson A. Intravenous immune globulin to reduce nosocomial infections. N Engl J Med. 1994 Sep 8;331(10):678–678. doi: 10.1056/nejm199409083311015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANTEL N., HAENSZEL W. Statistical aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies of disease. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1959 Apr;22(4):719–748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magny J. F., Bremard-Oury C., Brault D., Menguy C., Voyer M., Landais P., Dehan M., Gabilan J. C. Intravenous immunoglobulin therapy for prevention of infection in high-risk premature infants: report of a multicenter, double-blind study. Pediatrics. 1991 Sep;88(3):437–443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson A., Lacy J. Perinatal clinical epidemiology. Curr Opin Pediatr. 1993 Apr;5(2):142–149. doi: 10.1097/00008480-199304000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson A. Treatments of preterm premature rupture of the membranes: a meta-analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1989 Apr;160(4):890–906. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(89)90306-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratrisawadi V., Srisuwanporn T., Puapondh Y. Intravenous immunoglobulin prophylaxis for infection in very low birth-weight infants. J Med Assoc Thai. 1991 Jan;74(1):14–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stabile A., Miceli Sopo S., Romanelli V., Pastore M., Pesaresi M. A. Intravenous immunoglobulin for prophylaxis of neonatal sepsis in premature infants. Arch Dis Child. 1988 Apr;63(4):441–443. doi: 10.1136/adc.63.4.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisman L. E., Cruess D. F., Fischer G. W. Current status of intravenous immunoglobulin in preventing or treating neonatal bacterial infections. Clin Rev Allergy. 1992 Spring-Summer;10(1-2):13–28. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4612-0417-6_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisman L. E., Cruess D. F., Fischer G. W. Opsonic activity of commercially available standard intravenous immunoglobulin preparations. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1994 Dec;13(12):1122–1125. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199412000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisman L. E., Cruess D. F., Fischer G. W. Standard versus hyperimmune intravenous immunoglobulin in preventing or treating neonatal bacterial infections. Clin Perinatol. 1993 Mar;20(1):211–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisman L. E., Stoll B. J., Kueser T. J., Rubio T. T., Frank C. G., Heiman H. S., Subramanian K. N., Hankins C. T., Anthony B. F., Cruess D. F. Intravenous immune globulin therapy for early-onset sepsis in premature neonates. J Pediatr. 1992 Sep;121(3):434–443. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)81802-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisman L. E., Stoll B. J., Kueser T. J., Rubio T. T., Frank C. G., Heiman H. S., Subramanian K. N., Hankins C. T., Cruess D. F., Hemming V. G. Intravenous immune globulin prophylaxis of late-onset sepsis in premature neonates. J Pediatr. 1994 Dec;125(6 Pt 1):922–930. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)82011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Overmeire B., Bleyaert S., van Reempts P. J., van Acker K. J. The use of intravenously administered immunoglobulins in the prevention of severe infection in very low birth weight neonates. Biol Neonate. 1993;64(2-3):110–115. doi: 10.1159/000243980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


