Abstract
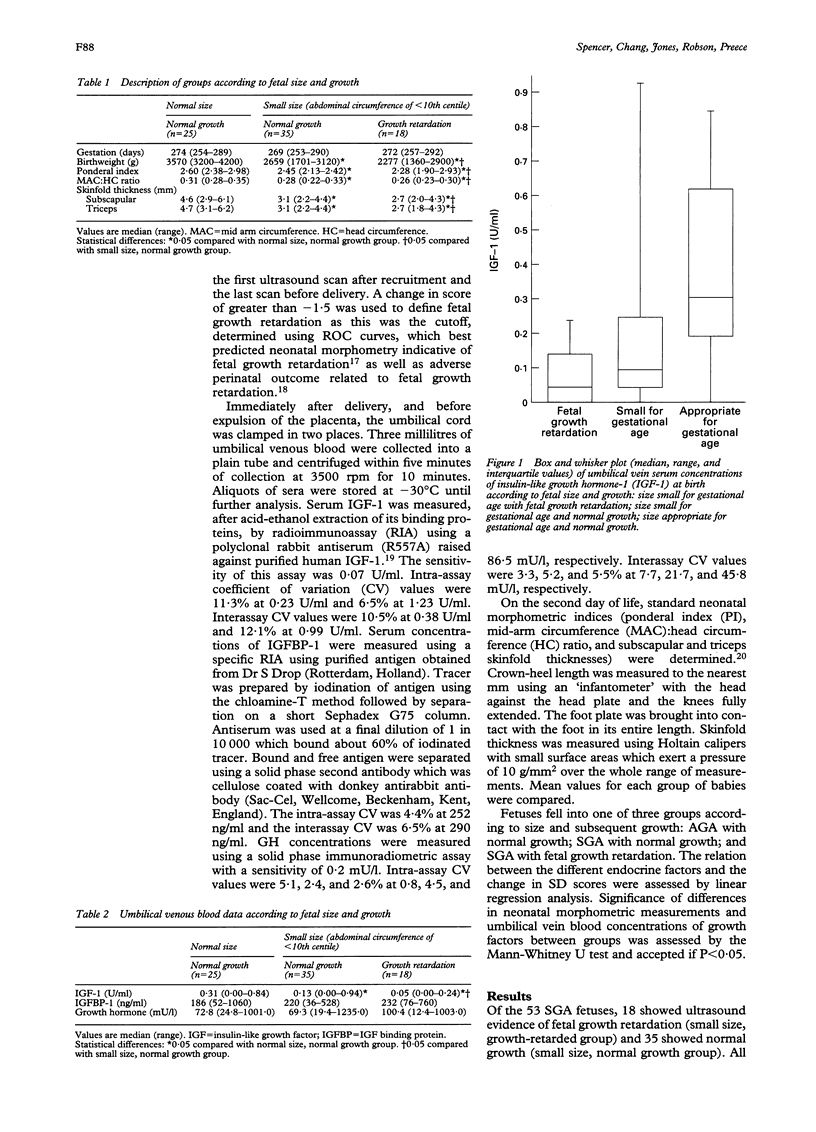
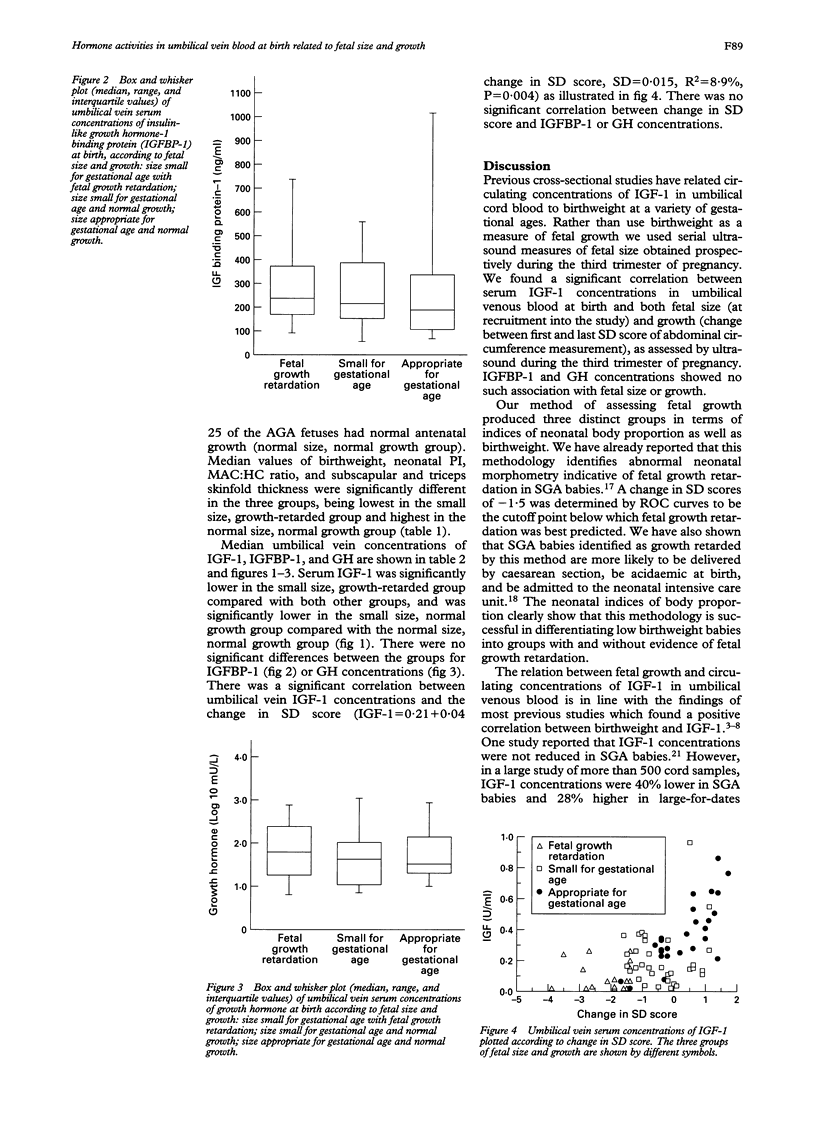
Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 (IGFBP-1) and growth hormone (GH) concentrations were measured in umbilical venous blood after delivery of 78 term newborn infants. Three groups of pregnancies were prospectively identified during the third trimester, according to fetal size and subsequent fetal growth, assessed by repeated ultrasound scans. Fetal size was considered either appropriate for gestational age (AGA) or small for gestational age (SGA), according to whether the first ultrasound measurement of abdominal circumference was equal to or above, or below the tenth centile for gestational age, respectively. Subsequent fetal growth was quantified by the change in the standard deviation score of abdominal circumference measurements between the first and last scans before delivery. Fetal growth retardation (FGR) was defined as a (negative) change in SD score of greater than -1.5. Eighteen SGA fetuses with evidence of FGR had significantly lower IGF-1 (median 0.05 (range 0.0-0.24) U/ml) at delivery than 35 SGA fetuses with normal growth (median 0.13 (range 0.0-0.94) U/ml; P < 0.05) and 25 AGA fetuses with normal growth (median 0.31 (range 0.0-0.84) U/ml; P < 0.05). The median concentration in the SGA group with normal growth was also significantly lower than that of the AGA group with normal growth. There were no significant differences in IGFBP-1 or GH concentrations between the three groups. These observations indicate that umbilical blood concentrations at birth of IGF-1, but not IGFBP-1 or GH, relate to both fetal size and fetal growth during the third trimester of pregnancies reaching term.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altman D. G., Hytten F. E. Intrauterine growth retardation: let's be clear about it. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1989 Oct;96(10):1127–1132. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1989.tb03185.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bang P., Westgren M., Schwander J., Blum W. F., Rosenfeld R. G., Stangenberg M. Ontogeny of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-1, -2, and -3: quantitative measurements by radioimmunoassay in human fetal serum. Pediatr Res. 1994 Oct;36(4):528–536. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199410000-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett A., Wilson D. M., Liu F., Nagashima R., Rosenfeld R. G., Hintz R. L. Levels of insulin-like growth factors I and II in human cord blood. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Sep;57(3):609–612. doi: 10.1210/jcem-57-3-609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang T. C., Robson S. C., Spencer J. A., Gallivan S. Identification of fetal growth retardation: comparison of Doppler waveform indices and serial ultrasound measurements of abdominal circumference and fetal weight. Obstet Gynecol. 1993 Aug;82(2):230–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang T. C., Robson S. C., Spencer J. A., Gallivan S. Prediction of perinatal morbidity at term in small fetuses: comparison of fetal growth and Doppler ultrasound. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1994 May;101(5):422–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1994.tb11916.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang T. C., Robson S. C., Spencer J. A. Neonatal morphometric indices of fetal growth: analysis of observer variability. Early Hum Dev. 1993 Nov 1;35(1):37–43. doi: 10.1016/0378-3782(93)90137-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Ercole A. J. Somatomedins/insulin-like growth factors and fetal growth. J Dev Physiol. 1987 Dec;9(6):481–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday W. H., Heath E. Physiological and possible clinical significance of epidermal and nerve growth factors. Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Mar;13(1):207–226. doi: 10.1016/s0300-595x(84)80014-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fant M., Salafia C., Baxter R. C., Schwander J., Vogel C., Pezzullo J., Moya F. Circulating levels of IGFs and IGF binding proteins in human cord serum: relationships to intrauterine growth. Regul Pept. 1993 Oct 20;48(1-2):29–39. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(93)90333-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallivan S., Robson S. C., Chang T. C., Vaughan J., Spencer J. A. An investigation of fetal growth using serial ultrasound data. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 1993 Mar 1;3(2):109–114. doi: 10.1046/j.1469-0705.1993.03020109.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluckman P. D., Johnson-Barrett J. J., Butler J. H., Edgar B. W., Gunn T. R. Studies of insulin-like growth factor -I and -II by specific radioligand assays in umbilical cord blood. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1983 Sep;19(3):405–413. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1983.tb00014.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunt J. A., Reynolds D. W. Insulin, blood sugar, and growth hormone levels in an anencephalic infant before and after intravenous administration of glucose. J Pediatr. 1970 Jan;76(1):112–116. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(70)80139-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. J., Freemark M., Strain A. J., Handwerger S., Milner R. D. Placental lactogen and growth hormone receptors in human fetal tissues: relationship to fetal plasma human placental lactogen concentrations and fetal growth. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988 Jun;66(6):1283–1290. doi: 10.1210/jcem-66-6-1283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassarre C., Hardouin S., Daffos F., Forestier F., Frankenne F., Binoux M. Serum insulin-like growth factors and insulin-like growth factor binding proteins in the human fetus. Relationships with growth in normal subjects and in subjects with intrauterine growth retardation. Pediatr Res. 1991 Mar;29(3):219–225. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199103000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson A., Lindahl A., Edén S., Isaksson O. G. Demonstration of growth hormone receptors in cultured rat epiphyseal chondrocytes by specific binding of growth hormone and immunohistochemistry. J Endocrinol. 1989 Jul;122(1):69–77. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1220069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens J. A., Kind K. L., Carbone F., Robinson J. S., Owens P. C. Circulating insulin-like growth factors-I and -II and substrates in fetal sheep following restriction of placental growth. J Endocrinol. 1994 Jan;140(1):5–13. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1400005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson R. M., Pouliot M. R. Neonatal morphometrics and perinatal outcome: who is growth retarded? Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1987 Sep;157(3):691–693. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(87)80030-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reece E. A., Wiznitzer A., Le E., Homko C. J., Behrman H., Spencer E. M. The relation between human fetal growth and fetal blood levels of insulin-like growth factors I and II, their binding proteins, and receptors. Obstet Gynecol. 1994 Jul;84(1):88–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salardi S., Orsini L. F., Cacciari E., Righetti F., Donati S., Mandini M., Cicognani A., Bovicelli L. Growth hormone, insulin-like growth factor I, insulin and C-peptide during human fetal life: in-utero study. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1991 Mar;34(3):187–190. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1991.tb00292.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimasaki S., Ling N. Identification and molecular characterization of insulin-like growth factor binding proteins (IGFBP-1, -2, -3, -4, -5 and -6). Prog Growth Factor Res. 1991;3(4):243–266. doi: 10.1016/0955-2235(91)90003-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A. M., Dunger D. B., Grant D. B., Preece M. A. Somatomedin-C/IGF-I measured by radioimmunoassay and somatomedin bioactivity in adolescents with insulin dependent diabetes compared with puberty matched controls. Diabetes Res. 1988 Dec;9(4):177–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unterman T. G., Simmons R. A., Glick R. P., Ogata E. S. Circulating levels of insulin, insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I), IGF-II, and IGF-binding proteins in the small for gestational age fetal rat. Endocrinology. 1993 Jan;132(1):327–336. doi: 10.1210/endo.132.1.7678218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhaeghe J., Van Bree R., Van Herck E., Laureys J., Bouillon R., Van Assche F. A. C-peptide, insulin-like growth factors I and II, and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 in umbilical cord serum: correlations with birth weight. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1993 Jul;169(1):89–97. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(93)90137-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H. S., Chard T. The role of insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-1 in the control of human fetal growth. J Endocrinol. 1992 Jan;132(1):11–19. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1320011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H. S., Lim J., English J., Irvine L., Chard T. The concentration of insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-1 in human umbilical cord serum at delivery: relation to fetal weight. J Endocrinol. 1991 Jun;129(3):459–464. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1290459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


