Abstract
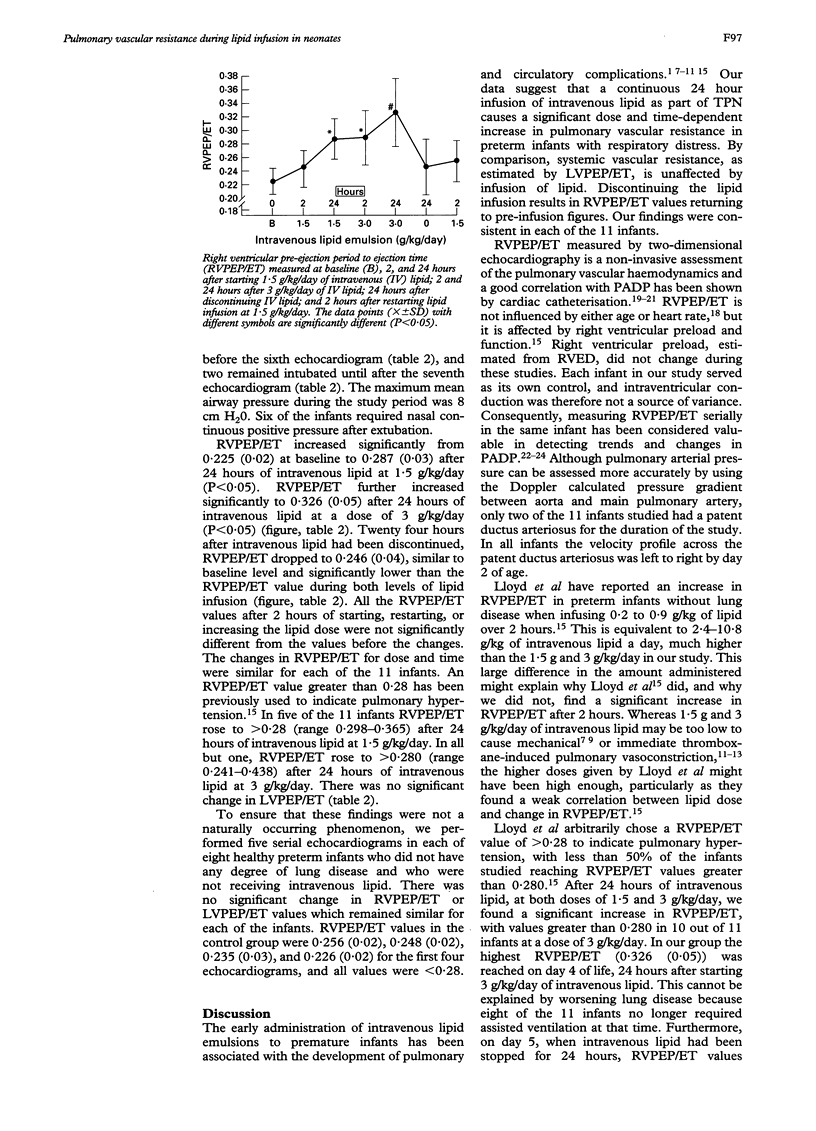
Using two-dimensional echocardiography, pulmonary vascular resistance was estimated from right ventricular pre-ejection period to ejection time (RVPEP/ET) in 11 preterm infants with respiratory distress, to test the effect of different doses of continuous lipid infusion. Echocardiography was performed at baseline with no lipid infusing 2 and 24 hours after 1.5 and 3 g/kg/day of intravenous lipid, 24 hours after discontinuing intravenous lipid emulsion, and 2 hours after restarting intravenous lipid. After 24 hours of intravenous lipid at 1.5 g/kg/day the RVPEP/ET rose to mean (SD) 0.287 (0.03) from a baseline value of 0.225 (0.02) and to 0.326 (0.05) after 24 hours of intravenous lipid at 3 g/kg/day. Pulmonary arterial pressure returned to baseline 24 hours after the intravenous lipid had been discontinued. Continuous 24 hour infusion of lipid caused significant dose and time-dependent increases in pulmonary vascular resistance. Intravenous lipid may aggravate pulmonary hypertension.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed T., Marchette B., Wanner A., Yerger L. Direct and indirect effects of leukotriene D4 on the pulmonary and systemic circulations. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Apr;131(4):554–558. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.131.4.554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brans Y. W., Andrew D. S., Carrillo D. W., Dutton E. P., Menchaca E. M., Puleo-Scheppke B. A. Tolerance of fat emulsions in very-low-birth-weight neonates. Am J Dis Child. 1988 Feb;142(2):145–152. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1988.02150020047024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coe J. Y., Olley P. M., Coceani F. The effect of leukotriene D4 on pulmonary and systemic circulation in conscious newborn piglets. Prostaglandins. 1988 Jul;36(1):31–47. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(88)90100-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke R. W. Factors associated with chronic lung disease in preterm infants. Arch Dis Child. 1991 Jul;66(7 Spec No):776–779. doi: 10.1136/adc.66.7_spec_no.776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahms B. B., Halpin T. C., Jr Pulmonary arterial lipid deposit in newborn infants receiving intravenous lipid infusion. J Pediatr. 1980 Nov;97(5):800–805. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80274-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhanireddy R., Hamosh M., Sivasubramanian K. N., Chowdhry P., Scanlon J. W., Hamosh P. Postheparin lipolytic activity and Intralipid clearance in very low-birth-weight infants. J Pediatr. 1981 Apr;98(4):617–622. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80777-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fouron J. C., Le Guennec J. C., Villemant D., Perreault G., Davignon A. Value of echocardiography in assessing the outcome of bronchopulmonary dysplasia of the newborn. Pediatrics. 1980 Mar;65(3):529–535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbertson N., Kovar I. Z., Cox D. J., Crowe L., Palmer N. T. Introduction of intravenous lipid administration on the first day of life in the very low birth weight neonate. J Pediatr. 1991 Oct;119(4):615–623. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)82416-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene H. L., Hazlett D., Demaree R. Relationship between Intralipid-induced hyperlipemia and pulmonary function. Am J Clin Nutr. 1976 Feb;29(2):127–135. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/29.2.127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurtner G. H., Knoblauch A., Smith P. L., Sies H., Adkinson N. F. Oxidant- and lipid-induced pulmonary vasoconstriction mediated by arachidonic acid metabolites. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1983 Sep;55(3):949–954. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1983.55.3.949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hageman J. R., McCulloch K., Gora P., Olsen E. K., Pachman L., Hunt C. E. Intralipid alterations in pulmonary prostaglandin metabolism and gas exchange. Crit Care Med. 1983 Oct;11(10):794–798. doi: 10.1097/00003246-198310000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerman C., Aramburo M. J. Decreased lipid intake reduces morbidity in sick premature neonates. J Pediatr. 1988 Dec;113(6):1083–1088. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(88)80587-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerman C., Aramburo M. J., Hill V. Intravenous lipids in newborn lungs: thromboxane-mediated effects. Crit Care Med. 1989 May;17(5):430–436. doi: 10.1097/00003246-198905000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschfeld S., Meyer R., Schwartz D. C., Kofhagen J., Kaplan S. The echocardiographic assessment of pulmonary artery pressure and pulmonary vascular resistance. Circulation. 1975 Oct;52(4):642–650. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.52.4.642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inwood R. J., Gora P., Hunt C. E. Indomethacin inhibition of intralipid-induced lung dysfunction. Prostaglandins Med. 1981 May;6(5):503–514. doi: 10.1016/0161-4630(81)90109-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inwood R. J., Gora P., Hunt C. E. Indomethacin inhibition of intralipid-induced lung dysfunction. Prostaglandins Med. 1981 May;6(5):503–514. doi: 10.1016/0161-4630(81)90109-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjaeve J. C., Dahl P. E. Pulmonary hypertension and microvascular injury in rats given parenteral nutrition. Acta Chir Scand. 1989 Sep;155(9):439–443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levene M. I., Wigglesworth J. S., Desai R. Pulmonary fat accumulation after intralipid infusion in the preterm infant. Lancet. 1980 Oct 18;2(8199):815–818. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)90170-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd T. R., Boucek M. M. Effect of intralipid on the neonatal pulmonary bed: an echographic study. J Pediatr. 1986 Jan;108(1):130–133. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80787-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeen C. R., Brigham K. L., Bowers R. E., Harris T. R. Pulmonary vascular effects of fat emulsion infusion in unanesthetized sheep. Prevention by indomethacin. J Clin Invest. 1978 May;61(5):1291–1297. doi: 10.1172/JCI109046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussbaum E., Hirschfeld S. S., Wood R. E., Boat T. F., Doershuk C. F. Echocardiographic changes in children with pulmonary hypertension secondary to upper airway obstruction. J Pediatr. 1978 Dec;93(6):931–936. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)81214-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Periera G. R., Fox W. W., Stanley C. A., Baker L., Schwartz J. G. Decreased oxygenation and hyperlipemia during intravenous fat infusions in premature infants. Pediatrics. 1980 Jul;66(1):26–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs T., Hirschfeld S., Fanaroff A., Liebman J., Fletcher B., Meyer R. Persistence of fetal circulation syndrome: an echocardiographic study. J Pediatr. 1977 Oct;91(4):626–631. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)80521-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman R. J., Langston C., Schanler R. J. Pulmonary vascular lipid deposition after administration of intravenous fat to infants. Pediatrics. 1987 Jan;79(1):99–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teague W. G., Jr, Raj J. U., Braun D., Berner M. E., Clyman R. I., Bland R. D. Lung vascular effects of lipid infusion in awake lambs. Pediatr Res. 1987 Dec;22(6):714–719. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198712000-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


