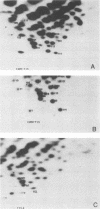
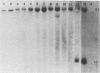
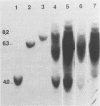
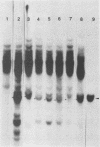
Abstract
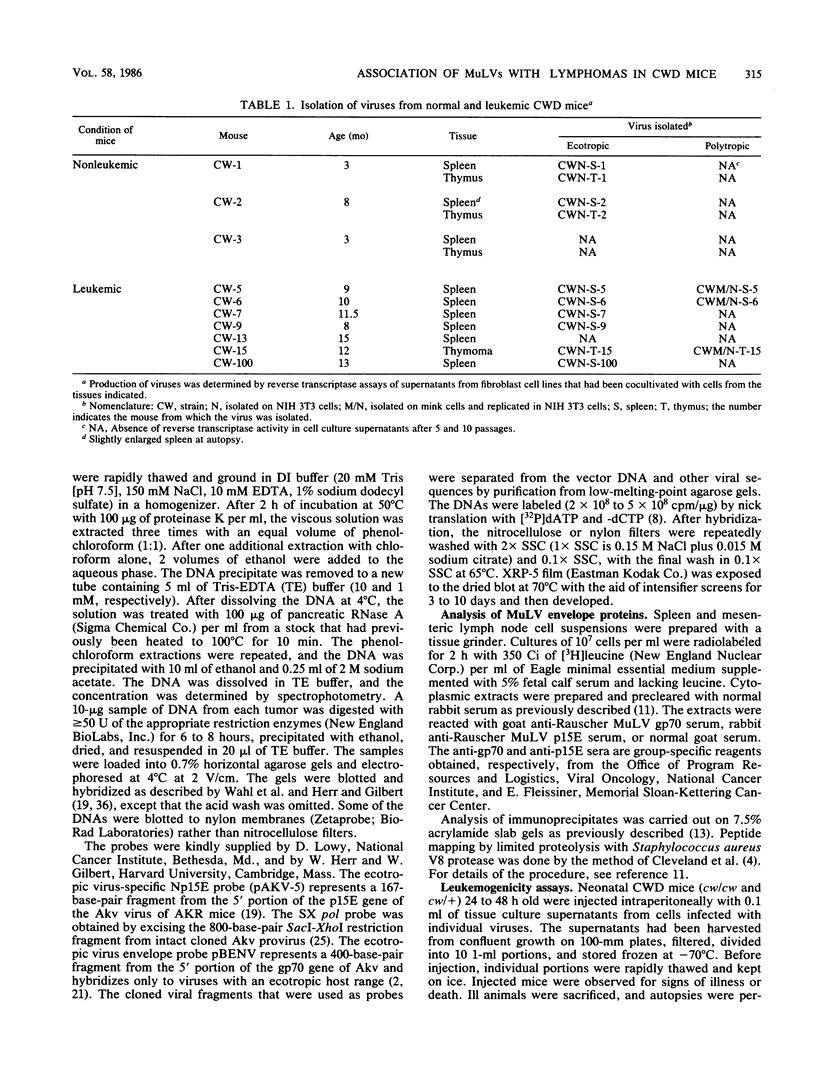
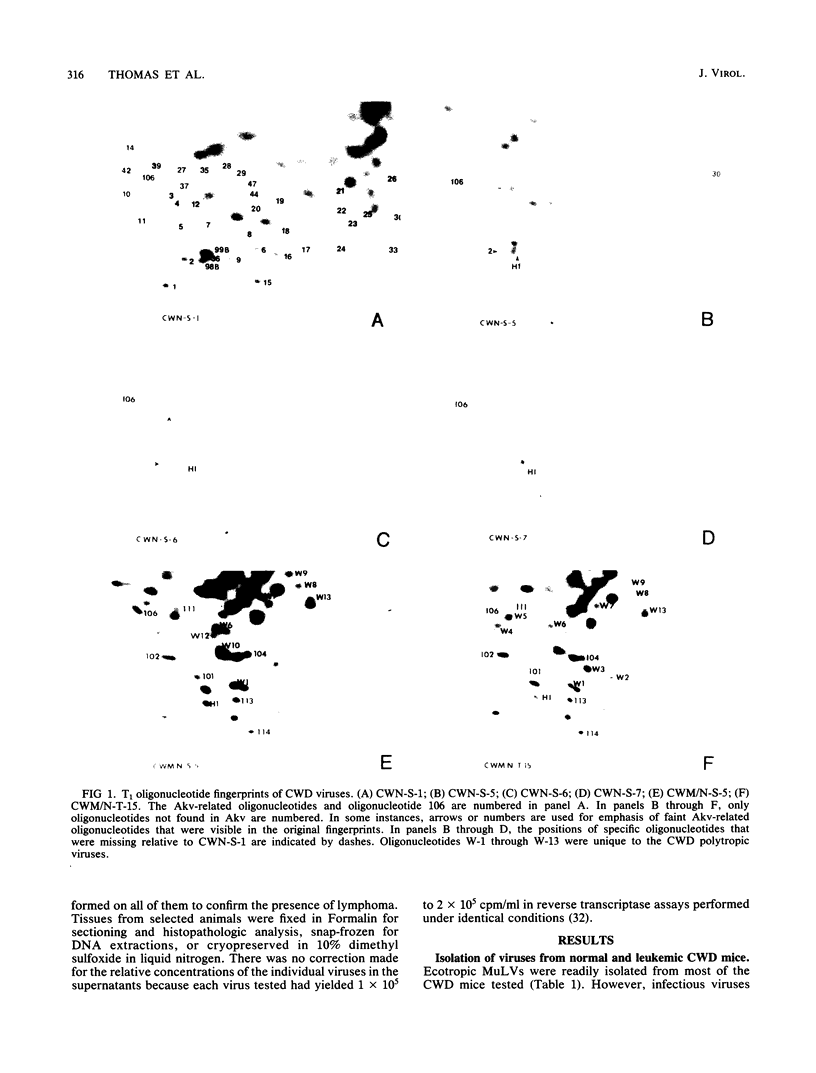
We determined the phenotype and genotype of murine leukemia viruses associated with the development of spontaneous nonthymic lymphomas in the high-leukemia mouse strain CWD/J. By T1 oligonucleotide fingerprint analysis of the viral RNA, the ecotropic viruses recovered from the spleen or thymus of preleukemic CWD/J mice were found to represent the progeny of the two endogenous ecotropic proviruses present in this strain. Polytropic murine leukemia viruses were produced by tissues from one-half of the leukemic mice, and fresh tumor cells from one of the two animals tested expressed recombinant envelope glycoproteins. The genomic structure of the recombinant viruses resembled those of class II polytropic viruses of NFS X Akv mice and differed from those of class I recombinant viruses that are commonly isolated from other high-leukemia strains such as AKR and HRS. Acquired retroviral sequences with the structural features of class II recombinant proviruses were detected in the DNA from each CWD/J tumor by the Southern blot technique. Finally, the injection of a mixture of CWD/J ecotropic and class II recombinant polytropic viruses into neonatal CWD/J mice accelerated the onset of lymphoma, whereas the endogenous ecotropic virus was inactive in these assays.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel J. M., Bedigian H. G. Expression of murine leukemia viruses in B-cell lymphomas of CWD/Agl mice. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):691–694. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.691-694.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Lander M. R., Gupta S., Rands E., Lowy D. R. Origin of mink cytopathic focus-forming (MCF) viruses:comparison with ecotropic and xenotropic murine leukemia virus genomes. Virology. 1981 Sep;113(2):465–483. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90175-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Wehrly K., Nishio J., Evans L. Leukemia induction by a new strain of Friend mink cell focus-inducing virus: synergistic effect of Friend ecotropic murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):63–70. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.63-70.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloyd M. W., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Lymphomagenicity of recombinant mink cell focus-inducing murine leukemia viruses. J Exp Med. 1980 Mar 1;151(3):542–552. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.3.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffin J. M., Tsichlis P. N., Conklin K. F., Senior A., Robinson H. L. Genomes of endogenous and exogenous avian retroviruses. Virology. 1983 Apr 15;126(1):51–72. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90461-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland N. G., Bedigian H. G., Thomas C. Y., Jenkins N. A. DNAs of two molecularly cloned endogenous ecotropic proviruses are poorly infectious in DNA transfection assays. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):437–444. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.437-444.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DesGroseillers L., Jolicoeur P. The tandem direct repeats within the long terminal repeat of murine leukemia viruses are the primary determinant of their leukemogenic potential. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):945–952. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.945-952.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faller D. V., Hopkins N. RNase T1-resistant oligonucleotides of an N- and a B-tropic murine leukemia virus of BALB/c: evidence for recombination between these viruses. J Virol. 1977 Nov;24(2):609–617. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.2.609-617.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Famulari N. G., Cieplensky D. A time-course study of MuLV env gene expression in the AKR thymus: qualitative and quantitative analysis of ecotropic and recombinant virus gene products. Virology. 1984 Jan 30;132(2):282–291. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Famulari N. G., English K. J. Env gene products of AKR dual-tropic viruses: examination of peptide maps and cell surface expression. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):971–976. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.971-976.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Famulari N. G., Koehne C. F., O'Donnell P. V. Leukemogenesis by Gross passage A murine leukemia virus: expression of viruses with recombinant env genes in transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(12):3872–3876. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.12.3872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredrickson T. N., Morse H. C., 3rd, Rowe W. P. Spontaneous tumors of NFS mice congenic for ecotropic murine leukemia virus induction loci. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1984 Aug;73(2):521–524. doi: 10.1093/jnci/73.2.521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N., Hiai H., Elder J. H., Schwartz R. S., Khiroya R. H., Thomas C. Y., Tsichlis P. N., Coffin J. M. Expression of leukemogenic recombinant viruses associated with a recessive gene in HRS/J mice. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2):249–264. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.2.249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas M., Patch V. Genomic masking and rescue of dual-tropic murine leukemia viruses: role of pseudotype virions in viral lymphomagenesis. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):583–591. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.583-591.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Gilbert W. Somatically acquired recombinant murine leukemia proviruses in thymic leukemias of AKR/J mice. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):70–82. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.70-82.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W. Nucleotide sequence of AKV murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):471–478. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.471-478.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland C. A., Wozney J., Hopkins N. Nucleotide sequence of the gp70 gene of murine retrovirus MCF 247. J Virol. 1983 Sep;47(3):413–420. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.3.413-420.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Taylor B. A., Lee B. K. Dilute (d) coat colour mutation of DBA/2J mice is associated with the site of integration of an ecotropic MuLV genome. Nature. 1981 Oct 1;293(5831):370–374. doi: 10.1038/293370a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Taylor B. A., Lee B. K. Organization, distribution, and stability of endogenous ecotropic murine leukemia virus DNA sequences in chromosomes of Mus musculus. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):26–36. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.26-36.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M., Holland C. A., Lung M. L., Chattopadhyay S. K., Lowy D. R., Hopkins N. H. Nucleotide sequence of the 3' end of MCF 247 murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):291–298. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.291-298.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenz J., Celander D., Crowther R. L., Patarca R., Perkins D. W., Haseltine W. A. Determination of the leukaemogenicity of a murine retrovirus by sequences within the long terminal repeat. 1984 Mar 29-Apr 4Nature. 308(5958):467–470. doi: 10.1038/308467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowy D. R., Rands E., Chattopadhyay S. K., Garon C. F., Hager G. L. Molecular cloning of infectious integrated murine leukemia virus DNA from infected mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):614–618. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lung M. L., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P., Hopkins N. H. Large RNase T1-resistant oligonucleotides encoding p15E and the U3 region of the long terminal repeat distinguish two biological classes of mink cell focus-forming type C viruses of inbred mice. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):275–290. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.275-290.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lung M. L., Hering C., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P., Hopkins N. Analysis of the genomes of mink cell focus-inducing murine type-C viruses: a progress report. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 2):1269–1274. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell P. V., Stockert E., Obata Y., DeLeo A. B., Old L. J. Murine-leukemia-virus-related cell-surface antigens as serological markers of AKR ecotropic, xenotropic, and dualtropic viruses. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 2):1255–1264. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliff A. I., Hager G. L., Chang E. H., Scolnick E. M., Chan H. W., Lowy D. R. Transfection of molecularly cloned Friend murine leukemia virus DNA yields a highly leukemogenic helper-independent type C virus. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):475–486. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.475-486.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen F. S., Haseltine W. A. Analysis of the genome of an endogenous, ecotropic retrovirus of the AKR strain of mice: micromethod for detailed characterization of high-molecular-weight RNA. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):349–365. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.349-365.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rommelaere J., Faller D. V., Hopkins N. Characterization and mapping of RNase T1-resistant oligonucleotides derived from the genomes of Akv and MCF murine leukemia viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):495–499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg N., Baltimore D. The effect of helper virus on Abelson virus-induced transformation of lymphoid cells. J Exp Med. 1978 Apr 1;147(4):1126–1141. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.4.1126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P., Cloyd M. W., Hartley J. W. Status of the association of mink cell focus-forming viruses with leukemogenesis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 2):1265–1268. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas C. Y., Coffin J. M. Genetic alterations of RNA leukemia viruses associated with the development of spontaneous thymic leukemia in AKR/J mice. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):416–426. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.416-426.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas C. Y., Khiroya R., Schwartz R. S., Coffin J. M. Role of recombinant ecotropic and polytropic viruses in the development of spontaneous thymic lymphomas in HRS/J mice. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):397–407. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.397-407.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]