Abstract
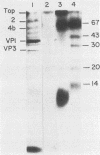
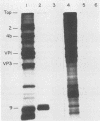
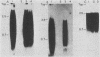
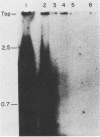
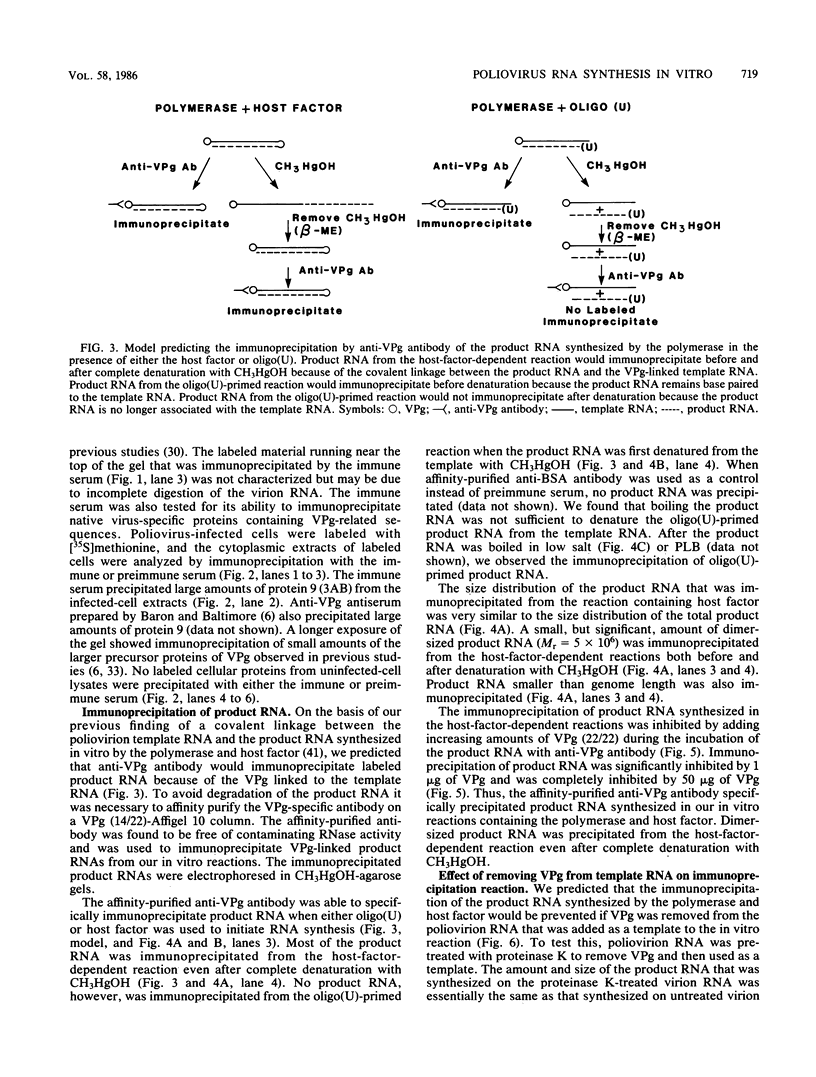
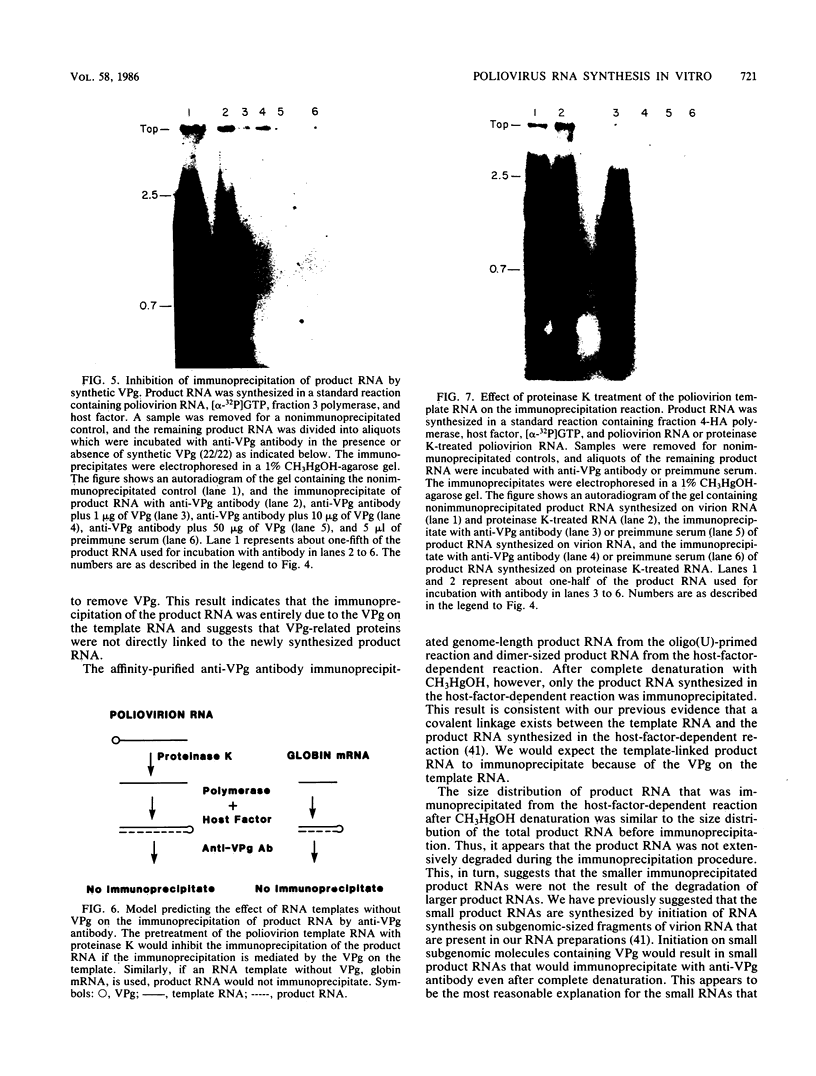
Antibody to the poliovirus genome-linked protein, VPg, specifically immunoprecipitated the product RNA synthesized in vitro by the poliovirus RNA polymerase and HeLa cell host factor when VPg-linked poliovirion RNA was used as a template. The largest product RNA that was immunoprecipitated was twice the size of the template RNA. The complete denaturation of the product RNA with CH3HgOH had no effect on the immunoprecipitation reaction. In contrast, CH3HgOH denaturation prevented the immunoprecipitation of the oligo(U)-primed product RNA. Immunoprecipitation of the product RNA synthesized in the host-factor-dependent reaction was prevented if VPg was removed from the template RNA by pretreatment with proteinase K or if an RNA template without VPg was used in the reaction. The results support our previous evidence that a covalent linkage exists between the labeled negative-strand product RNA and the VPg-linked template RNA and suggest that the purified polymerase and host factor initiated RNA synthesis in vitro in the absence of VPg or a VPg-precursor protein.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong J. A., Edmonds M., Nakazato H., Phillips B. A., Vaughn M. H. Polyadenylic acid sequences in the virion RNA of poliovirus and Eastern Equine Encephalitis virus. Science. 1972 May 5;176(4034):526–528. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4034.526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey J. M., Davidson N. Methylmercury as a reversible denaturing agent for agarose gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron M. H., Baltimore D. Anti-VPg antibody inhibition of the poliovirus replicase reaction and production of covalent complexes of VPg-related proteins and RNA. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):745–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90279-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron M. H., Baltimore D. Antibodies against a synthetic peptide of the poliovirus replicase protein: reaction with native, virus-encoded proteins and inhibition of virus-specific polymerase activities in vitro. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):969–978. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.969-978.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron M. H., Baltimore D. Antibodies against the chemically synthesized genome-linked protein of poliovirus react with native virus-specific proteins. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):395–404. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90357-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron M. H., Baltimore D. In vitro copying of viral positive strand RNA by poliovirus replicase. Characterization of the reaction and its products. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12359–12366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron M. H., Baltimore D. Purification and properties of a host cell protein required for poliovirus replication in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12351–12358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford N. M., Baltimore D. Genome-linked protein VPg of poliovirus is present as free VPg and VPg-pUpU in poliovirus-infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7452–7455. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta A., Baron M. H., Baltimore D. Poliovirus replicase: a soluble enzyme able to initiate copying of poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2679–2683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta A. Purification of host factor required for in vitro transcription of poliovirus RNA. Virology. 1983 Jul 15;128(1):245–251. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90335-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta A., Zabel P., Baltimore D. Dependence of the activity of the poliovirus replicase on the host cell protein. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):423–429. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90516-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn B. M., Kammermann B., McCurry K. R. The synthesis, purification, and evaluation of a chromophoric substrate for pepsin and other aspartyl proteases: design of a substrate based on subsite preferences. Anal Biochem. 1984 Apr;138(1):68–73. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90770-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn B. M., Lewitt M., Pham C. Inhibition of pepsin by analogues of pepsinogen-(1-12)-peptide with substitutions in the 4-7 sequence region. Biochem J. 1983 Feb 1;209(2):355–362. doi: 10.1042/bj2090355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanegan J. B., Baltimore D. Poliovirus polyuridylic acid polymerase and RNA replicase have the same viral polypeptide. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):352–360. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.352-360.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanegan J. B., Baltimore D. Poliovirus-specific primer-dependent RNA polymerase able to copy poly(A). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3677–3680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanegan J. B., Petterson R. F., Ambros V., Hewlett N. J., Baltimore D. Covalent linkage of a protein to a defined nucleotide sequence at the 5'-terminus of virion and replicative intermediate RNAs of poliovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):961–965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanegan J. B., Van Dyke T. A. Isolation of a soluble and template-dependent poliovirus RNA polymerase that copies virion RNA in vitro. J Virol. 1979 Oct;32(1):155–161. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.1.155-161.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. F., Nomoto A., Detjen B. M., Wimmer E. A protein covalently linked to poliovirus genome RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):59–63. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow C. D., Dasgupta A. Antibody to a synthetic nonapeptide corresponding to the NH2 terminus of poliovirus genome-linked protein VPg reacts with native VPg and inhibits in vitro replication of poliovirus RNA. J Virol. 1983 Nov;48(2):429–439. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.2.429-439.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow C. D., Hocko J., Navab M., Dasgupta A. ATP is required for initiation of poliovirus RNA synthesis in vitro: demonstration of tyrosine-phosphate linkage between in vitro-synthesized RNA and genome-linked protein. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):515–523. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.515-523.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow C. D., Navab M., Peterson C., Hocko J., Dasgupta A. Antibody to poliovirus genome-linked protein (VPg) precipitates in vitro synthesized RNA attached to VPg-precursor polypeptide(s). Virus Res. 1984;1(2):89–100. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(84)90066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto A., Detjen B., Pozzatti R., Wimmer E. The location of the polio genome protein in viral RNAs and its implication for RNA synthesis. Nature. 1977 Jul 21;268(5617):208–213. doi: 10.1038/268208a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson R. F., Ambros V., Baltimore D. Identification of a protein linked to nascent poliovirus RNA and to the polyuridylic acid of negative-strand RNA. J Virol. 1978 Aug;27(2):357–365. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.2.357-365.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rueckert R. R., Wimmer E. Systematic nomenclature of picornavirus proteins. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):957–959. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.957-959.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarin V. K., Kent S. B., Tam J. P., Merrifield R. B. Quantitative monitoring of solid-phase peptide synthesis by the ninhydrin reaction. Anal Biochem. 1981 Oct;117(1):147–157. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90704-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semler B. L., Anderson C. W., Hanecak R., Dorner L. F., Wimmer E. A membrane-associated precursor to poliovirus VPg identified by immunoprecipitation with antibodies directed against a synthetic heptapeptide. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):405–412. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90358-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. H., Baltimore D. Requirement of 3'-terminal poly(adenylic acid) for the infectivity of poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):2983–2987. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.2983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takegami T., Kuhn R. J., Anderson C. W., Wimmer E. Membrane-dependent uridylylation of the genome-linked protein VPg of poliovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7447–7451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuschall D. M., Hiebert E., Flanegan J. B. Poliovirus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase synthesizes full-length copies of poliovirion RNA, cellular mRNA, and several plant virus RNAs in vitro. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):209–216. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.209-216.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke T. A., Flanegan J. B. Identification of poliovirus polypeptide P63 as a soluble RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):732–740. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.732-740.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke T. A., Rickles R. J., Flanegan J. B. Genome-length copies of poliovirion RNA are synthesized in vitro by the poliovirus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4610–4617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villa-Komaroff L., McDowell M., Baltimore D., Lodish H. F. Translation of reovirus mRNA, poliovirus RNA and bacteriophage Qbeta RNA in cell-free extracts of mammalian cells. Methods Enzymol. 1974;30:709–723. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)30068-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yogo Y., Wimmer E. Polyadenylic acid at the 3'-terminus of poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1877–1882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. C., Tuschall D. M., Flanegan J. B. Poliovirus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase and host cell protein synthesize product RNA twice the size of poliovirion RNA in vitro. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):256–264. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.256-264.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]