Abstract
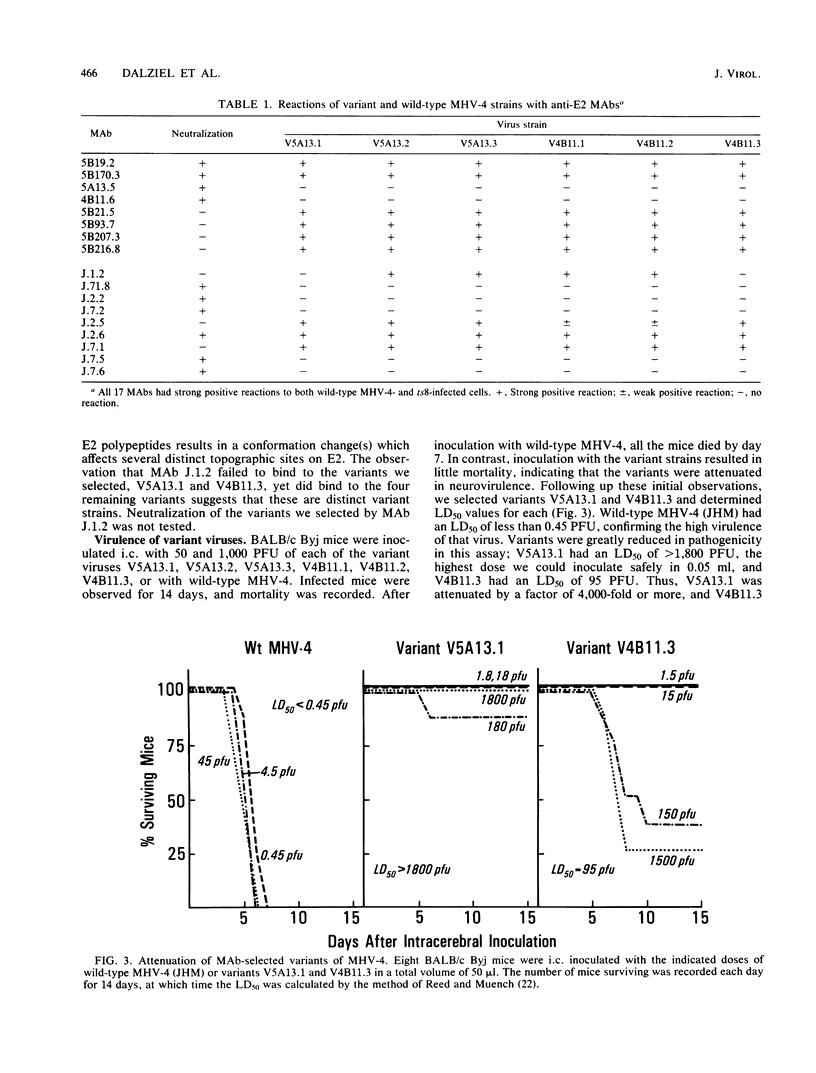
Strains of the murine coronavirus mouse hepatitis virus type 4 (MHV-4) which contained a mutation in the E2 peplomer glycoprotein were obtained by selection for resistance to neutralization by monoclonal antibodies. Characterization of six variants representing two independent epitopes on E2, E2B and E2C, by in vitro neutralization and antibody-binding assays demonstrated that selection for an alteration in epitope E2B also resulted in changes in epitope E2C and vice versa. We observed a mutation frequency of approximately 10(-4.3) to 10(-4.6), which is consistent with the expected occurrence of single point mutations. The variant virus strains were attenuated with respect to neurovirulence when compared with wild-type MHV-4. Mice normally develop encephalomyelitis and die after wild-type MHV-4 infection. Mice receiving 2- to 3-log-higher doses of the variant strains survived and developed demyelinating disease. As the disease progressed, evidence of remyelination and ongoing demyelination was observed up to 65 days after infection. Virus reisolated 15 days after infection retained the variant phenotype. The data indicate that the E2 glycoprotein plays a central role in determining the cellular tropism and virulence of MHV-4 in the mouse.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baybutt H. N., Wege H., Carter M. J., ter Meulen V. Adaptation of coronavirus JHM to persistent infection of murine sac(-) cells. J Gen Virol. 1984 May;65(Pt 5):915–924. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-5-915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmeier M. J., Lewicki H. A., Talbot P. J., Knobler R. L. Murine hepatitis virus-4 (strain JHM)-induced neurologic disease is modulated in vivo by monoclonal antibody. Virology. 1984 Jan 30;132(2):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90033-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmeier M. J., Lewicki H. A., Tomori O., Oldstone M. B. Monoclonal antibodies to lymphocytic choriomeningitis and pichinde viruses: generation, characterization, and cross-reactivity with other arenaviruses. Virology. 1981 Aug;113(1):73–85. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90137-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carp R. I., Warner H. B., Merz G. S. Viral etiology of multiple sclerosis. Prog Med Virol. 1978;24:158–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins A. R., Knobler R. L., Powell H., Buchmeier M. J. Monoclonal antibodies to murine hepatitis virus-4 (strain JHM) define the viral glycoprotein responsible for attachment and cell--cell fusion. Virology. 1982 Jun;119(2):358–371. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90095-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietzschold B., Wunner W. H., Wiktor T. J., Lopes A. D., Lafon M., Smith C. L., Koprowski H. Characterization of an antigenic determinant of the glycoprotein that correlates with pathogenicity of rabies virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):70–74. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming J. O., Stohlman S. A., Harmon R. C., Lai M. M., Frelinger J. A., Weiner L. P. Antigenic relationships of murine coronaviruses: analysis using monoclonal antibodies to JHM (MHV-4) virus. Virology. 1983 Dec;131(2):296–307. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90498-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming J. O., Trousdale M. D., el-Zaatari F. A., Stohlman S. A., Weiner L. P. Pathogenicity of antigenic variants of murine coronavirus JHM selected with monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):869–875. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.869-875.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Scarano F., Janssen R. S., Najjar J. A., Pobjecky N., Nathanson N. An avirulent G1 glycoprotein variant of La Crosse bunyavirus with defective fusion function. J Virol. 1985 Jun;54(3):757–763. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.3.757-763.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haspel M. V., Lampert P. W., Oldstone M. B. Temperature-sensitive mutants of mouse hepatitis virus produce a high incidence of demyelination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):4033–4036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.4033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes K. V., Doller E. W., Sturman L. S. Tunicamycin resistant glycosylation of coronavirus glycoprotein: demonstration of a novel type of viral glycoprotein. Virology. 1981 Dec;115(2):334–344. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90115-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knobler R. L., Haspel M. V., Oldstone M. B. Mouse hepatitis virus type 4 (JHM strains). induced fatal central nervous system disease. I. genetic control and murine neuron as the susceptible site of disease. J Exp Med. 1981 Apr 1;153(4):832–843. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.4.832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knobler R. L., Taylor B. A., Wooddell M. K., Beamer W. G., Oldstone M. B. Host genetic control of mouse hepatitis virus type-4 (JHM strain) replication. II. The gene locus for susceptibility is linked to the Svp-2 locus on mouse chromosome 7. Exp Clin Immunogenet. 1984;1(4):217–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knobler R. L., Tunison L. A., Lampert P. W., Oldstone M. B. Selected mutants of mouse hepatitis virus type 4 (JHM strain) induce different CNS diseases. Pathobiology of disease induced by wild type and mutants ts8 and ts15 in BALB/c and SJL/J mice. Am J Pathol. 1982 Nov;109(2):157–168. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampert P. W., Sims J. K., Kniazeff A. J. Mechanism of demyelination in JHM virus encephalomyelitis. Electron microscopic studies. Acta Neuropathol. 1973 Mar 30;24(1):76–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00691421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laver W. G., Air G. M., Webster R. G., Gerhard W., Ward C. W., Dopheide T. A. Antigenic drift in type A influenza virus: sequence differences in the hemagglutinin of Hong Kong (H3N2) variants selected with monoclonal hybridoma antibodies. Virology. 1979 Oct 15;98(1):226–237. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90540-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton H. L. Theiler's virus infection in mice: an unusual biphasic disease process leading to demyelination. Infect Immun. 1975 May;11(5):1147–1155. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.5.1147-1155.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathanson N., Georgsson G., Pálsson P. A., Najjar J. A., Lutley R., Pétursson G. Experimental visna in Icelandic sheep: the prototype lentiviral infection. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Jan-Feb;7(1):75–82. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.1.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nepom J. T., Tardieu M., Epstein R. L., Noseworthy J. H., Weiner H. L., Gentsch J., Fields B. N., Greene M. I. Virus-binding receptors: similarities to immune receptors as determined by anti-idiotypic antibodies. Surv Immunol Res. 1982;1(3):255–261. doi: 10.1007/BF02918466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portner A., Webster R. G., Bean W. J. Similar frequencies of antigenic variants in Sendai, vesicular stomatitis, and influenza A viruses. Virology. 1980 Jul 15;104(1):235–238. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90382-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spriggs D. R., Bronson R. T., Fields B. N. Hemagglutinin variants of reovirus type 3 have altered central nervous system tropism. Science. 1983 Apr 29;220(4596):505–507. doi: 10.1126/science.6301010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spriggs D. R., Fields B. N. Attenuated reovirus type 3 strains generated by selection of haemagglutinin antigenic variants. Nature. 1982 May 6;297(5861):68–70. doi: 10.1038/297068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stohlman S. A., Brayton P. R., Fleming J. O., Weiner L. P., Lai M. M. Murine coronaviruses: isolation and characterization of two plaque morphology variants of the JHM neurotropic strain. J Gen Virol. 1982 Dec;63(2):265–275. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-63-2-265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturman L. S., Holmes K. V., Behnke J. Isolation of coronavirus envelope glycoproteins and interaction with the viral nucleocapsid. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):449–462. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.449-462.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturman L. S., Holmes K. V. The molecular biology of coronaviruses. Adv Virus Res. 1983;28:35–112. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3527(08)60721-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturman L. S., Ricard C. S., Holmes K. V. Proteolytic cleavage of the E2 glycoprotein of murine coronavirus: activation of cell-fusing activity of virions by trypsin and separation of two different 90K cleavage fragments. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):904–911. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.904-911.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taguchi F., Siddell S. G., Wege H., ter Meulen V. Characterization of a variant virus selected in rat brains after infection by coronavirus mouse hepatitis virus JHM. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):429–435. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.429-435.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot P. J., Buchmeier M. J. Antigenic variation among murine coronaviruses: evidence for polymorphism on the peplomer glycoprotein, E2. Virus Res. 1985 Jun;2(4):317–328. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(85)90028-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot P. J., Salmi A. A., Knobler R. L., Buchmeier M. J. Topographical mapping of epitopes on the glycoproteins of murine hepatitis virus-4 (strain JHM): correlation with biological activities. Virology. 1984 Jan 30;132(2):250–260. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90032-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wege H., Siddell S., ter Meulen V. The biology and pathogenesis of coronaviruses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1982;99:165–200. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68528-6_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wege H., Wege H., Nagashima K., ter Meulen V. Structural polypeptides of the murine coronavirus JHM. J Gen Virol. 1979 Jan;42(1):37–47. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-42-1-37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner L. P. Pathogenesis of demyelination induced by a mouse hepatitis. Arch Neurol. 1973 May;28(5):298–303. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1973.00490230034003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]