Abstract
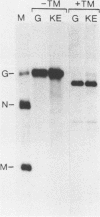
Earlier studies demonstrated that synthetic peptides corresponding to the amino terminus of the vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein (G protein) have a pH-dependent hemolytic activity that is thought to be related to the fusion activity of G protein (R. Schlegel and M. Wade, J. Biol. Chem. 259: 4691-4694, 1984; R. Schlegel and M. Wade, J. Virol. 53: 319-323, 1985). A single amino acid change (lysine to glutamic acid at the amino terminus) abolishes the hemolytic activity of the peptide. Here we used oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis to create a DNA encoding G protein with this same amino acid change at its amino terminus. The mutant protein encoded by this gene was expressed transiently in a monkey fibroblast cell line (COS) and was found to have a pH-dependent fusion activity indistinguishable from wild-type G protein. This result indicates that the hemolytic activity of the synthetic peptides was not related to the fusion activity of the G protein.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey C. A., Miller D. K., Lenard J. Effects of DEAE-dextran on infection and hemolysis by VSV. Evidence that nonspecific electrostatic interactions mediate effective binding of VSV to cells. Virology. 1984 Feb;133(1):111–118. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90429-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan D. P., Sefton B. M. The entry into host cells of Sindbis virus, vesicular stomatitis virus and Sendai virus. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):985–992. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90282-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florkiewicz R. Z., Rose J. K. A cell line expressing vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein fuses at low pH. Science. 1984 Aug 17;225(4663):721–723. doi: 10.1126/science.6087454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irving R. A., Toneguzzo F., Rhee S. H., Hofmann T., Ghosh H. P. Synthesis and assembly of membrane glycoproteins: presence of leader peptide in nonglycosylated precursor of membrane glycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):570–574. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotwal G. J., Capone J., Irving R. A., Rhee S. H., Bilan P., Toneguzzo F., Hofmann T., Ghosh H. P. Viral membrane glycoproteins: comparison of the amino terminal amino acid sequences of the precursor and mature glycoproteins of three serotypes of vesicular stomatitis virus. Virology. 1983 Aug;129(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90390-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlin K. S., Reggio H., Helenius A., Simons K. Pathway of vesicular stomatitis virus entry leading to infection. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 15;156(3):609–631. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90269-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riedel H., Kondor-Koch C., Garoff H. Cell surface expression of fusogenic vesicular stomatitis virus G protein from cloned cDNA. EMBO J. 1984 Jul;3(7):1477–1483. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01999.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Adams G. A., Gallione C. J. The presence of cysteine in the cytoplasmic domain of the vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein is required for palmitate addition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2050–2054. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Bergmann J. E. Expression from cloned cDNA of cell-surface secreted forms of the glycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus in eucaryotic cells. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):753–762. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90280-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel R., Wade M. A synthetic peptide corresponding to the NH2 terminus of vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein is a pH-dependent hemolysin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):4691–4694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel R., Wade M. Biologically active peptides of the vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):319–323. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.319-323.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprague J., Condra J. H., Arnheiter H., Lazzarini R. A. Expression of a recombinant DNA gene coding for the vesicular stomatitis virus nucleocapsid protein. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):773–781. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.773-781.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Matlin K., Helenius A. Cell fusion by Semliki Forest, influenza, and vesicular stomatitis viruses. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jun;89(3):674–679. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.3.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis using M13-derived vectors: an efficient and general procedure for the production of point mutations in any fragment of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 25;10(20):6487–6500. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.20.6487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]