Abstract
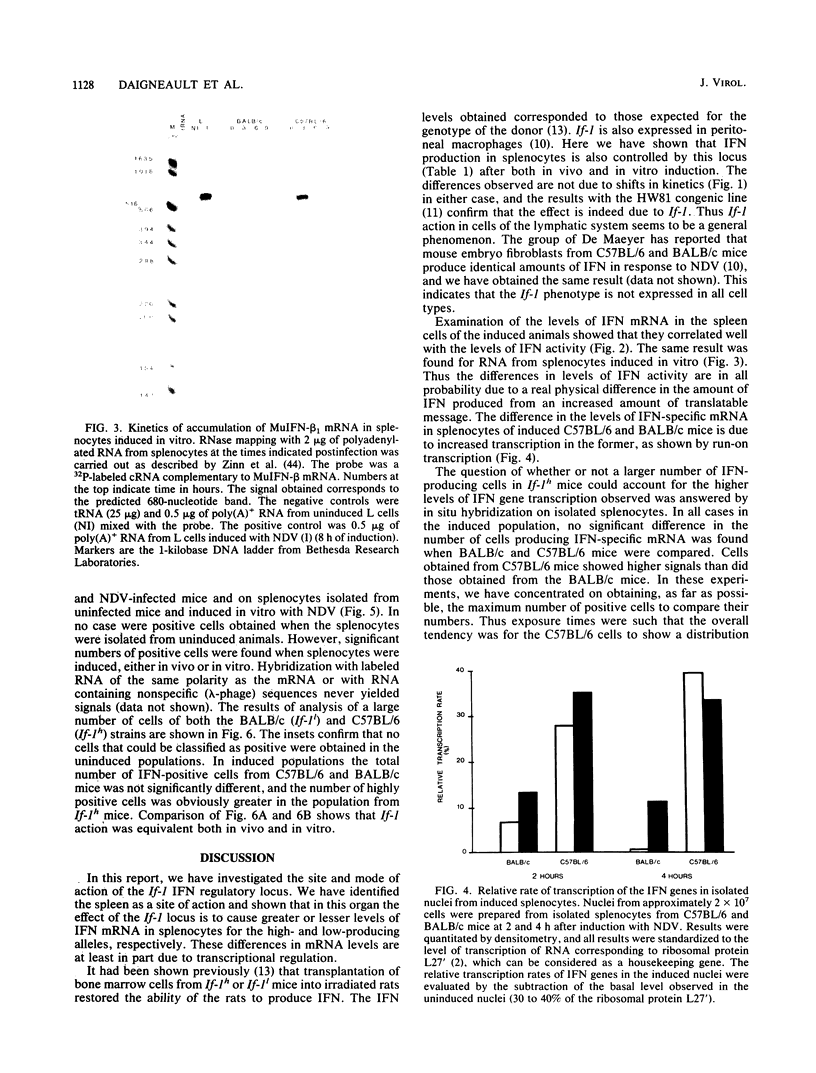
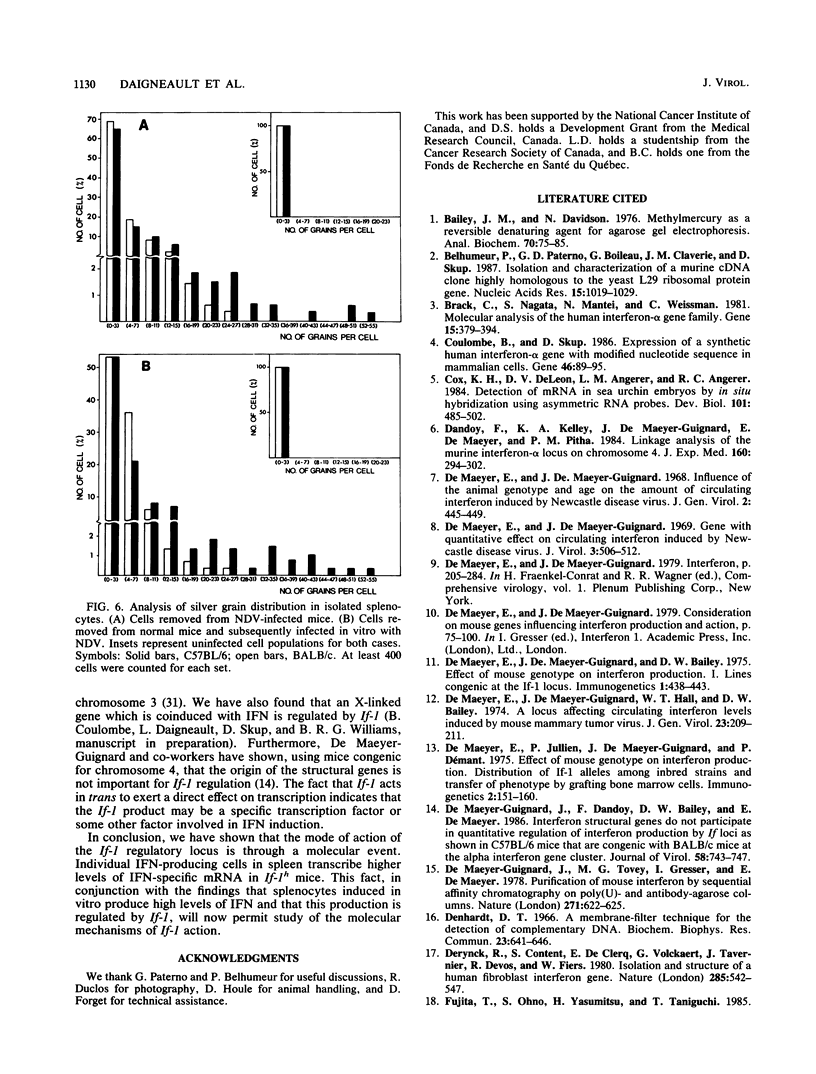
We have examined the mechanism of action of the If-1 interferon (IFN) regulatory locus. This locus controls the level of circulating IFN produced in inbred mice in response to intravenous injection of Newcastle disease virus. Mice carrying the If-1h (high) allele show circulating IFN levels 10- to 15-fold higher than those carrying the If-1l (low) allele. In this report we show that induced splenocytes from If-1h and If-1l mice produce IFN at levels which are in the same proportions as those found in the circulation. Higher levels of IFN-specific mRNA were observed in splenocyte populations from If-1h animals. This was due to increased transcription of IFN genes. At the same time, the high- and low-producing populations showed no significant difference in the number of IFN mRNA-containing cells. We conclude that the effect of If-1 in the spleen is to control the levels of transcription of the IFN genes in individual induced splenocytes.
Full text
PDF



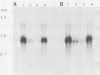
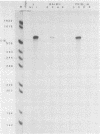
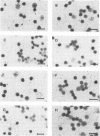
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey J. M., Davidson N. Methylmercury as a reversible denaturing agent for agarose gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belhumeur P., Paterno G. D., Boileau G., Claverie J. M., Skup D. Isolation and characterisation of a murine cDNA clone highly homologous to the yeast L29 ribosomal protein gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):1019–1029. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.1019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brack C., Nagata S., Mantei N., Weissmann C. Molecular analysis of the human interferon-alpha gene family. Gene. 1981 Dec;15(4):379–394. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90181-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulombe B., Skup D. Expression of a synthetic human interferon-alpha 1 gene with modified nucleotide sequence in mammalian cells. Gene. 1986;46(1):89–95. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90170-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox K. H., DeLeon D. V., Angerer L. M., Angerer R. C. Detection of mrnas in sea urchin embryos by in situ hybridization using asymmetric RNA probes. Dev Biol. 1984 Feb;101(2):485–502. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90162-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dandoy F., Kelley K. A., DeMaeyer-Guignard J., DeMaeyer E., Pitha P. M. Linkage analysis of the murine interferon-alpha locus on chromosome 4. J Exp Med. 1984 Jul 1;160(1):294–302. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.1.294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Maeyer-Guignard J., Dandoy F., Bailey D. W., De Maeyer E. Interferon structural genes do not participate in quantitative regulation of interferon production by If loci as shown in C57BL/6 mice that are congenic with BALB/c mice at the alpha interferon gene cluster. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):743–747. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.743-747.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Maeyer-Guignard J., Tovey M. G., Gresser I., De Maeyer E. Purification of mouse interferon by sequential affinity chromatography on poly(U)--and antibody--agarose columns. Nature. 1978 Feb 16;271(5646):622–625. doi: 10.1038/271622a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Maeyer E., De Maeyer-Guignard J. Influence of animal genotype and age on the amount of circulating interferoh induced by Newcastle disease virus. J Gen Virol. 1968 May;2(3):445–449. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-2-3-445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R., Content J., DeClercq E., Volckaert G., Tavernier J., Devos R., Fiers W. Isolation and structure of a human fibroblast interferon gene. Nature. 1980 Jun 19;285(5766):542–547. doi: 10.1038/285542a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Ohno S., Yasumitsu H., Taniguchi T. Delimitation and properties of DNA sequences required for the regulated expression of human interferon-beta gene. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):489–496. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodbourn S., Burstein H., Maniatis T. The human beta-interferon gene enhancer is under negative control. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):601–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90292-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodbourn S., Zinn K., Maniatis T. Human beta-interferon gene expression is regulated by an inducible enhancer element. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):509–520. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80024-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Peretz M., Weintraub H. Transcriptional regulation of hemoglobin switching in chicken embryos. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Mar;1(3):281–288. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.3.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi Y., Sokawa Y., Watanabe Y., Kawade Y., Ohno S., Takaoka C., Taniguchi T. Structure and expression of a cloned cDNA for mouse interferon-beta. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9522–9529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley K. A., Kozak C. A., Dandoy F., Sor F., Skup D., Windass J. D., DeMaeyer-Guignard J., Pitha P. M., DeMaeyer E. Mapping of murine interferon-alpha genes to chromosome 4. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(2-3):181–188. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90188-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohase M., Henriksen-DeStefano D., May L. T., Vilcek J., Sehgal P. B. Induction of beta 2-interferon by tumor necrosis factor: a homeostatic mechanism in the control of cell proliferation. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):659–666. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90780-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Melton D. A. Functional messenger RNAs are produced by SP6 in vitro transcription of cloned cDNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7057–7070. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett M., Cox D. R., Yee D., Boll W., Weissmann C., Epstein C. J., Epstein L. B. The chromosomal location of mouse interferon alpha genes. EMBO J. 1984 Jul;3(7):1643–1646. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02023.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelson J., Glasgow L. A. The in vitro and in vivo effects of cortisol on interferon production and action. J Immunol. 1966 Feb;96(2):345–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobraaten L. E., Bunker H. P., DeMaeyer-Guignard J., DeMaeyer E., Bailey D. W. Location of histocompatibility and interferon loci on chromosome 3 of the mouse. J Hered. 1984 May-Jun;75(3):233–234. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a109921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy D., Brickell P. M., Latchman D. S., Willison K., Rigby P. W. Transcripts regulated during normal embryonic development and oncogenic transformation share a repetitive element. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):865–871. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90119-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno S., Taniguchi T. The 5'-flanking sequence of human interferon-beta 1 gene is responsible for viral induction of transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 25;11(16):5403–5412. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.16.5403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raj N. B., Pitha P. M. Two levels of regulation of beta-interferon gene expression in human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3923–3927. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rytel M. W., Kilbourne E. D. The influence of cortisone on experimental viral infection. 8. Suppression by cortisone of interferon formation in mice injected with Newcastle disease virus. J Exp Med. 1966 May 1;123(5):767–775. doi: 10.1084/jem.123.5.767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagar A. D., Sehgal P. B., May L. T., Inouye M., Slate D. L., Shulman L., Ruddle F. H. Interferon-beta-related DNA is dispersed in the human genome. Science. 1984 Mar 23;223(4642):1312–1315. doi: 10.1126/science.6546621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal P. B., Sagar A. D. Heterogeneity of poly(I) x poly(C)-induced human fibroblast interferon mRNA species. Nature. 1980 Nov 6;288(5786):95–97. doi: 10.1038/288095a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G. D., Boll W., Taira H., Mantei N., Lengyel P., Weissmann C. Structure and expression of cloned murine IFN-alpha genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Feb 11;11(3):555–573. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.3.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skup D., Zarbl H., Millward S. Regulation of translation in L-cells infected with reovirus. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 5;151(1):35–55. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90220-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T., Ohno S., Fujii-Kuriyama Y., Muramatsu M. The nucleotide sequence of human fibroblast interferon cDNA. Gene. 1980 Jun;10(1):11–15. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90138-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissenbach J., Chernajovsky Y., Zeevi M., Shulman L., Soreq H., Nir U., Wallach D., Perricaudet M., Tiollais P., Revel M. Two interferon mRNAs in human fibroblasts: in vitro translation and Escherichia coli cloning studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7152–7156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., DiMaio D., Maniatis T. Identification of two distinct regulatory regions adjacent to the human beta-interferon gene. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):865–879. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90544-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., Maniatis T. Detection of factors that interact with the human beta-interferon regulatory region in vivo by DNAase I footprinting. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):611–618. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90293-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Maeyer E., de Maeyer-Guignard J. Gene with quantitative effect on circulating interferon induced by Newcastle disease virus. J Virol. 1969 May;3(5):506–512. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.5.506-512.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Maeyer E., de Maeyer-Guignard J., Hall W. T., Bailey D. W. A locus affecting circulating interferon levels induced by mouse mammary tumour virus. J Gen Virol. 1974 May;23(2):209–211. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-23-2-209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]