Abstract
Morphologically altered and established human fibroblasts, obtained either by 60Co gamma irradiation, treatment with the carcinogen 4-nitroquinoline 1-oxide, or simian virus 40 (SV40) infection, were compared with their normal finite-life parental strains for susceptibility to the autonomous parvoviruses H-1 virus and the prototype strain of minute virus of mice (MVMp). All transformed cells suffered greater virus-induced killing than their untransformed progenitors. The cytotoxic effect of H-1 virus was more severe than that of MVMp. Moreover, the level of viral DNA replication was much (10- to 85-fold) enhanced in the transformants compared with their untransformed parent cells. Thus, in this system, cell transformation appears to correlate with an increase in both DNA amplification and cytotoxicity of the parvoviruses. However, the accumulation of parvovirus DNA in the transformants was not always accompanied by the production of infectious virus. Like in vitro-transformed fibroblasts, a fibrosarcoma-derived cell line was sensitive to the killing effect of both H-1 virus and MVMp and amplified viral DNA to high extents. The results indicate that oncogenic transformation can be included among cellular states which modulate permissiveness to parvoviruses under defined growth conditions.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson M. J., Pattison J. R. The human parvovirus. Brief review. Arch Virol. 1984;82(3-4):137–148. doi: 10.1007/BF01311158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourguignon G. J., Tattersall P. J., Ward D. C. DNA of minute virus of mice: self-priming, nonpermuted, single-stranded genome with a 5'-terminal hairpin duplex. J Virol. 1976 Oct;20(1):290–306. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.1.290-306.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
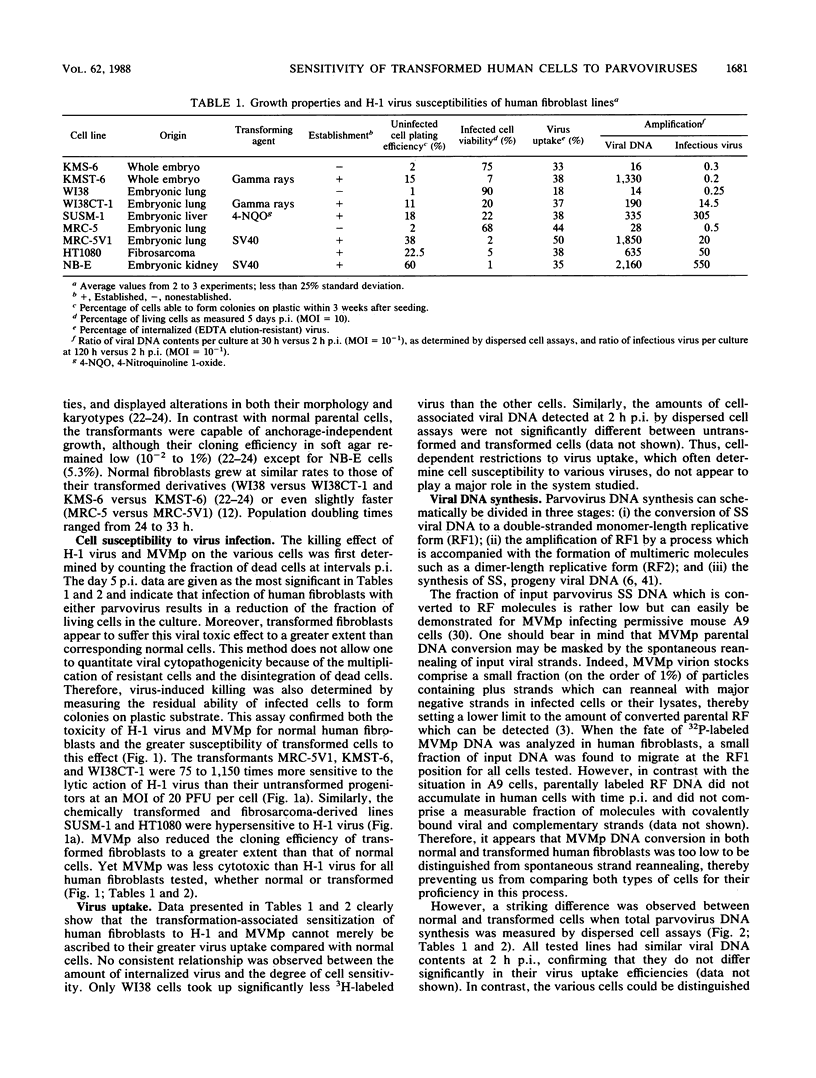
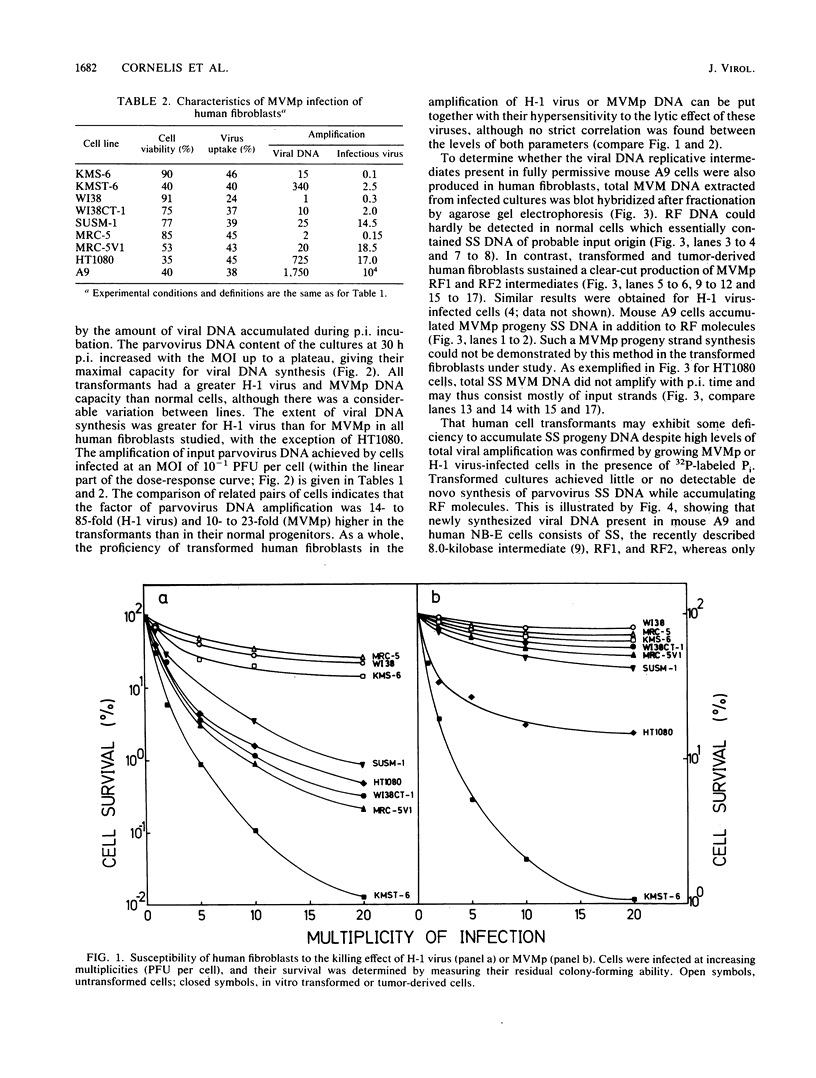
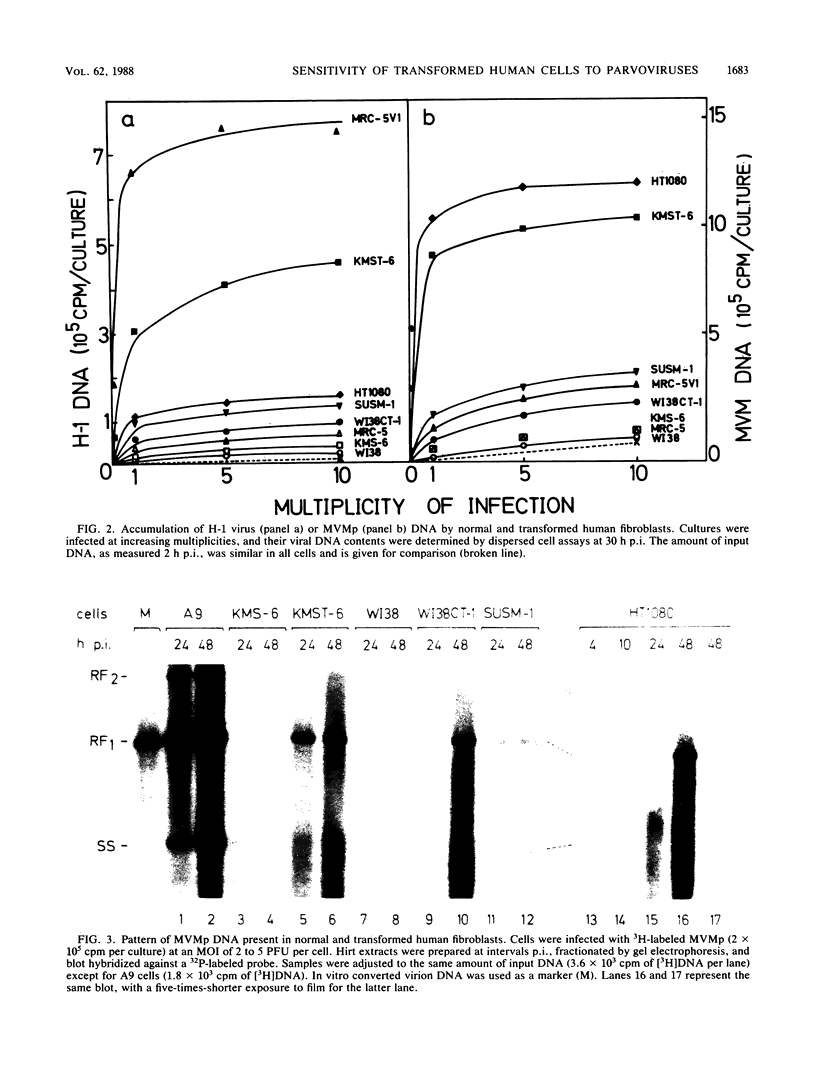
- Cornelis J. J., Su Z. Z., Rommelaere J. Direct and indirect effects of ultraviolet light on the mutagenesis of parvovirus H-1 in human cells. EMBO J. 1982;1(6):693–699. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01232.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotmore S. F., Tattersall P. The autonomously replicating parvoviruses of vertebrates. Adv Virus Res. 1987;33:91–174. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60317-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duesberg P. H. Cancer genes: rare recombinants instead of activated oncogenes (a review). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2117–2124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faust E. A., Gloor G. Characterization of a metastable, partially replicated dimeric intermediate of minute virus of mice. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):621–625. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.621-625.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guetta E., Ron D., Tal J. Development-dependent replication of minute virus of mice in differentiated mouse testicular cell lines. J Gen Virol. 1986 Nov;67(Pt 11):2549–2554. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-11-2549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilbronn R., Schlehofer J. R., zur Hausen H. Selective killing of carcinogen-treated SV40-transformed Chinese hamster cells by a defective parvovirus. Virology. 1984 Jul 30;136(2):439–441. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90180-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huschtscha L. I., Holliday R. Limited and unlimited growth of SV40-transformed cells from human diploid MRC-5 fibroblasts. J Cell Sci. 1983 Sep;63:77–99. doi: 10.1242/jcs.63.1.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledinko N., Hopkins S., Toolan H. Relationship between potentiation of H-1 growth by human adenovirus 12 and inhibition of the 'helper' adenovirus by H-1. J Gen Virol. 1969 Jul;5(1):19–31. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-5-1-19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linser P., Bruning H., Armentrout R. W. Uptake of minute virus of mice into cultured rodent cells. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):537–545. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.537-545.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall C. J., Hall A., Weiss R. A. A transforming gene present in human sarcoma cell lines. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):171–173. doi: 10.1038/299171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Beard P., Engers H. D., Hirt B. Characterization of an immunosuppressive parvovirus related to the minute virus of mice. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):317–326. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.317-326.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merchlinsky M. J., Tattersall P. J., Leary J. J., Cotmore S. F., Gardiner E. M., Ward D. C. Construction of an infectious molecular clone of the autonomous parvovirus minute virus of mice. J Virol. 1983 Jul;47(1):227–232. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.1.227-232.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuki K., Nose K., Okamoto H., Tsuchida N., Hayashi K. Amplification of c-Ki-ras gene and aberrant expression of c-myc in WI-38 cells transformed in vitro by gamma-irradiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Apr 30;128(2):1037–1043. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90152-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mousset S., Cornelis J., Spruyt N., Rommelaere J. Transformation of established murine fibroblasts with an activated cellular Harvey-ras oncogene or the polyoma virus middle T gene increases cell permissiveness to parvovirus minute-virus-of-mice. Biochimie. 1986 Jul-Aug;68(7-8):951–955. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(86)81058-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mousset S., Rommelaere J. Minute virus of mice inhibits cell transformation by simian virus 40. Nature. 1982 Dec 9;300(5892):537–539. doi: 10.1038/300537a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mousset S., Rommelaere J. Susceptibility to parvovirus Minute virus of mice as a function of the degree of host cell transformation: little effect of simian virus 40 infection and phorbol ester treatment. Virus Res. 1988 Feb;9(2-3):107–117. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(88)90026-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller D. E., Siegl G. Maturation of parvovirus LuIII in a subcellular system. I. Optimal conditions for in vitro synthesis and encapsidation of viral DNA. J Gen Virol. 1983 May;64(Pt 5):1043–1054. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-5-1043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namba M., Nishitani K., Hyodoh F., Fukushima F., Kimoto T. Neoplastic transformation of human diploid fibroblasts (KMST-6) by treatment with 60Co gamma rays. Int J Cancer. 1985 Feb 15;35(2):275–280. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910350221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namba M., Nishitani K., Kimoto T. Characteristics of WI-38 cells (WI-38 CT-1) transformed by treatment with Co-60 gamma rays. Gan. 1980 Jun;71(3):300–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paradiso P. R. Identification of multiple forms of the noncapsid parvovirus protein NCVP1 in H-1 parvovirus-infected cells. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):82–87. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.82-87.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paradiso P. R., Williams K. R., Costantino R. L. Mapping of the amino terminus of the H-1 parvovirus major capsid protein. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):77–81. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.77-81.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhode S. L., 3rd Construction of a genetic switch for inducible trans-activation of gene expression in eucaryotic cells. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1448–1456. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1448-1456.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rommelaere J., Ward D. C. Effect of UV-irradiation on DNA replication of the parvovirus minute-virus-of-mice in mouse fibroblasts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Apr 24;10(8):2577–2596. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.8.2577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ron D., Tal J. Spontaneous curing of a minute virus of mice carrier state by selection of cells with an intracellular block of viral replication. J Virol. 1986 Apr;58(1):26–30. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.1.26-30.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ron D., Tattersall P., Tal J. Formation of a host range mutant of the lymphotropic strain of minute virus of mice during persistent infection in mouse L cells. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):63–69. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.63-69.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schutzbank T., Robinson R., Oren M., Levine A. J. SV40 large tumor antigen can regulate some cellular transcripts in a positive fashion. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):481–490. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90245-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegl G. The parvoviruses. Virol Monogr. 1976;15:1–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spalholz B. A., Tattersall P. Interaction of minute virus of mice with differentiated cells: strain-dependent target cell specificity is mediated by intracellular factors. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):937–943. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.937-943.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tattersall P., Bratton J. Reciprocal productive and restrictive virus-cell interactions of immunosuppressive and prototype strains of minute virus of mice. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):944–955. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.944-955.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tattersall P., Cawte P. J., Shatkin A. J., Ward D. C. Three structural polypeptides coded for by minite virus of mice, a parvovirus. J Virol. 1976 Oct;20(1):273–289. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.1.273-289.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toolan H., Ledinko N. Growth and cytopathogenicity of H-viruses in human and simian cell cultures. Nature. 1965 Nov 20;208(5012):812–813. doi: 10.1038/208812a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winocour E., Keshet I. Indiscriminate recombination in simian virus 40-infected monkey cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4861–4865. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolter S., Richards R., Armentrout R. W. Cell cycle-dependent replication of the DNA of minute virus of mice, a parvovirus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 May 30;607(3):420–431. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(80)90152-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yakobson B., Koch T., Winocour E. Replication of adeno-associated virus in synchronized cells without the addition of a helper virus. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):972–981. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.972-981.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]