Abstract
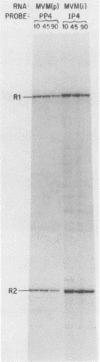
An infectious molecular clone of the immunosuppressive strain of the autonomous parvovirus minute virus of mice [MVM(i)] was constructed deriving left-hand terminal sequences from a rare encapsidated plus strand. Progeny virus was shown to package the same proportions of plus and minus strands as did authentic MVM(i) virions. Rescue of virus from this clone also resulted in the repair of a 21-base truncation at the junction between the right-hand end of the viral insert and the vector and generated the same heterogeneous 5' end as is present in standard MVM(i) DNA. Progeny virus rescued by transfection of this clone into mouse cell lines displayed the lymphotropic phenotype characteristic of the parental MVM(i) virus from which it was derived. However, analysis of viral RNA from transfected mouse fibroblasts revealed that the MVM(i) and MVM(p) genomic clones are transcribed at the same low level. Furthermore, transfected fibroblasts yielded similar numbers of infectious centers regardless of which MVM clone was introduced. These results contrast markedly with the different infectivities of MVM(i) and MVM(p) particles and with the observation that viral transcription in fibroblasts productively infected with MVM(p) virions is 100-fold greater than that seen in the restrictive MVM(i) particle-mediated infection. These results suggest that the developmentally regulated intracellular factors controlling host cell susceptibility at the level of viral transcription interact with a component of the incoming viral capsid, rather than with a sequence within the viral DNA.
Full text
PDF


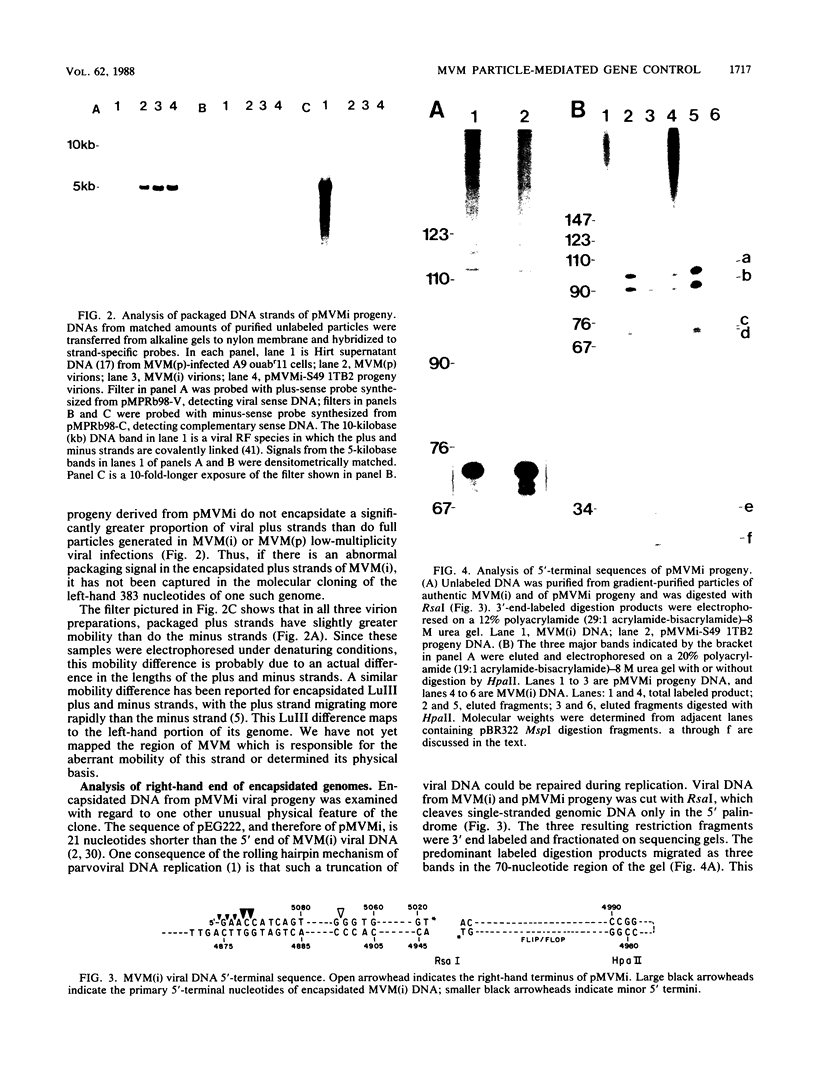

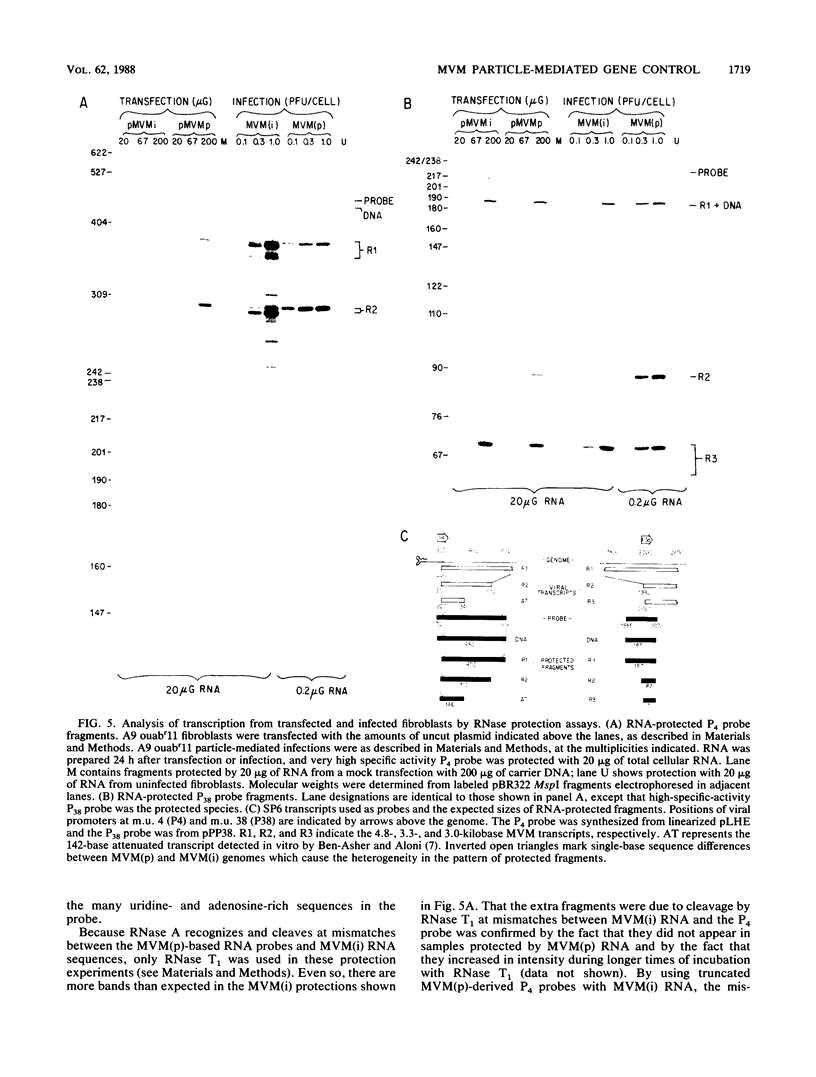



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Astell C. R., Chow M. B., Ward D. C. Sequence analysis of the termini of virion and replicative forms of minute virus of mice DNA suggests a modified rolling hairpin model for autonomous parvovirus DNA replication. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):171–177. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.171-177.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astell C. R., Thomson M., Merchlinsky M., Ward D. C. The complete DNA sequence of minute virus of mice, an autonomous parvovirus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Feb 25;11(4):999–1018. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.4.999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avila J., Saral R., Martin R. G., Khoury G. The temperature-sensitive defect in SV40 group D mutants. Virology. 1976 Aug;73(1):89–95. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90063-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates R. C., Snyder C. E., Banerjee P. T., Mitra S. Autonomous parvovirus LuIII encapsidates equal amounts of plus and minus DNA strands. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):319–324. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.319-324.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter J. D., Harris A. W., Tomkins G. M., Cohn M. Glucocorticoid receptors in lymphoma cells in culture: relationship to glucocorticoid killing activity. Science. 1971 Jan 15;171(3967):189–191. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3967.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Asher E., Aloni Y. Transcription of minute virus of mice, an autonomous parvovirus, may be regulated by attenuation. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):266–276. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.266-276.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boissy R., Astell C. R. An Escherichia coli recBCsbcBrecF host permits the deletion-resistant propagation of plasmid clones containing the 5'-terminal palindrome of minute virus of mice. Gene. 1985;35(1-2):179–185. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90170-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourguignon G. J., Tattersall P. J., Ward D. C. DNA of minute virus of mice: self-priming, nonpermuted, single-stranded genome with a 5'-terminal hairpin duplex. J Virol. 1976 Oct;20(1):290–306. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.1.290-306.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan M. B., Stark G. R. Interferon pretreatment inhibits simian virus 40 infections by blocking the onset of early transcription. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):811–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90023-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J. Y., Martin R. G. DNA infectivity and the induction of host DNA synthesis with temperature-sensitive mutants of simian virus 40. J Virol. 1975 Jan;15(1):145–150. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.1.145-150.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow M., Bodnar J. W., Polvino-Bodnar M., Ward D. C. Identification and characterization of a protein covalently bound to DNA of minute virus of mice. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):1094–1104. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.1094-1104.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotmore S. F., Tattersall P. The NS-1 polypeptide of minute virus of mice is covalently attached to the 5' termini of duplex replicative-form DNA and progeny single strands. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):851–860. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.851-860.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotmore S. F., Tattersall P. The autonomously replicating parvoviruses of vertebrates. Adv Virus Res. 1987;33:91–174. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60317-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engers H. D., Louis J. A., Zubler R. H., Hirt B. Inhibition of T cell-mediated functions by MVM(i), a parvovirus closely related to minute virus of mice. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2280–2285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields B. N. Molecular basis of reovirus virulence. Arch Virol. 1982;71(2):95–107. doi: 10.1007/BF01314880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohara M., Omata T., Kameda A., Semler B. L., Itoh H., Wimmer E., Nomoto A. In vitro phenotypic markers of a poliovirus recombinant constructed from infectious cDNA clones of the neurovirulent Mahoney strain and the attenuated Sabin 1 strain. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):786–792. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.786-792.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linser P., Bruning H., Armentrout R. W. Specific binding sites for a parvovirus, minute virus of mice, on cultured mouse cells. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):211–221. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.211-221.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
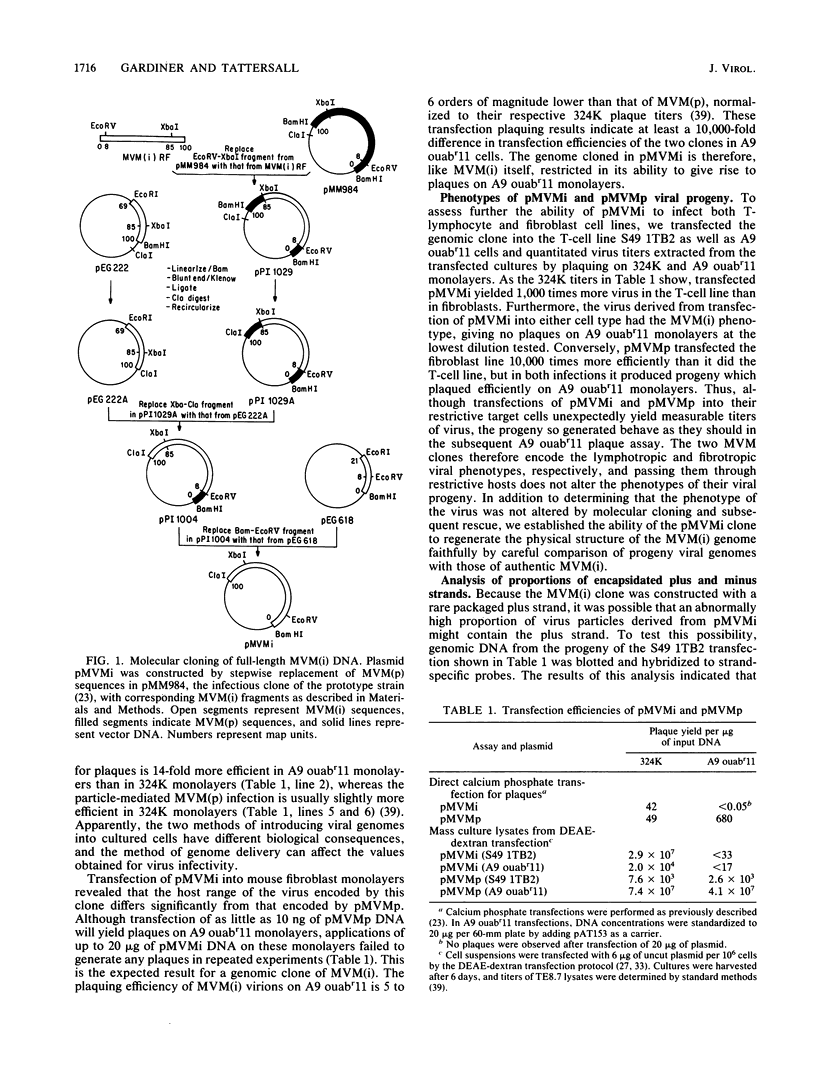
- Merchlinsky M. J., Tattersall P. J., Leary J. J., Cotmore S. F., Gardiner E. M., Ward D. C. Construction of an infectious molecular clone of the autonomous parvovirus minute virus of mice. J Virol. 1983 Jul;47(1):227–232. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.1.227-232.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. A., Ward D. C., Ruddle F. H. Embryonal carcinoma cells (and their somatic cell hybrids) are resistant to infection by the murine parvovirus MVM, which does infect other teratocarcinoma-derived cell lines. J Cell Physiol. 1977 Jun;91(3):393–401. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040910309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naeve C. W., Hinshaw V. S., Webster R. G. Mutations in the hemagglutinin receptor-binding site can change the biological properties of an influenza virus. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):567–569. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.567-569.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrish C. R., Carmichael L. E. Characterization and recombination mapping of an antigenic and host range mutation of canine parvovirus. Virology. 1986 Jan 15;148(1):121–132. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90408-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C., Baltimore D. Immunoglobulin gene transcription is activated by downstream sequence elements. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):741–748. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ron D., Tal J. Coevolution of cells and virus as a mechanism for the persistence of lymphotropic minute virus of mice in L-cells. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):424–430. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.424-430.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ron D., Tattersall P., Tal J. Formation of a host range mutant of the lymphotropic strain of minute virus of mice during persistent infection in mouse L cells. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):63–69. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.63-69.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEIN H. M., ENDERS J. F. Multiplication and cytopathogenicity of Simian vacuolating virus 40 in cultures of human tissues. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Mar;109:495–500. doi: 10.3181/00379727-109-27246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahli R., McMaster G. K., Hirt B. DNA sequence comparison between two tissue-specific variants of the autonomous parvovirus, minute virus of mice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 24;13(10):3617–3633. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.10.3617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodroski J., Rosen C., Wong-Staal F., Salahuddin S. Z., Popovic M., Arya S., Gallo R. C., Haseltine W. A. Trans-acting transcriptional regulation of human T-cell leukemia virus type III long terminal repeat. Science. 1985 Jan 11;227(4683):171–173. doi: 10.1126/science.2981427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spalholz B. A., Tattersall P. Interaction of minute virus of mice with differentiated cells: strain-dependent target cell specificity is mediated by intracellular factors. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):937–943. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.937-943.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tattersall P., Bratton J. Reciprocal productive and restrictive virus-cell interactions of immunosuppressive and prototype strains of minute virus of mice. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):944–955. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.944-955.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tattersall P. Replication of the parvovirus MVM. I. Dependence of virus multiplication and plaque formation on cell growth. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):586–590. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.586-590.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twigg A. J., Sherratt D. Trans-complementable copy-number mutants of plasmid ColE1. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):216–218. doi: 10.1038/283216a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., DiMaio D., Maniatis T. Identification of two distinct regulatory regions adjacent to the human beta-interferon gene. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):865–879. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90544-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]