Abstract
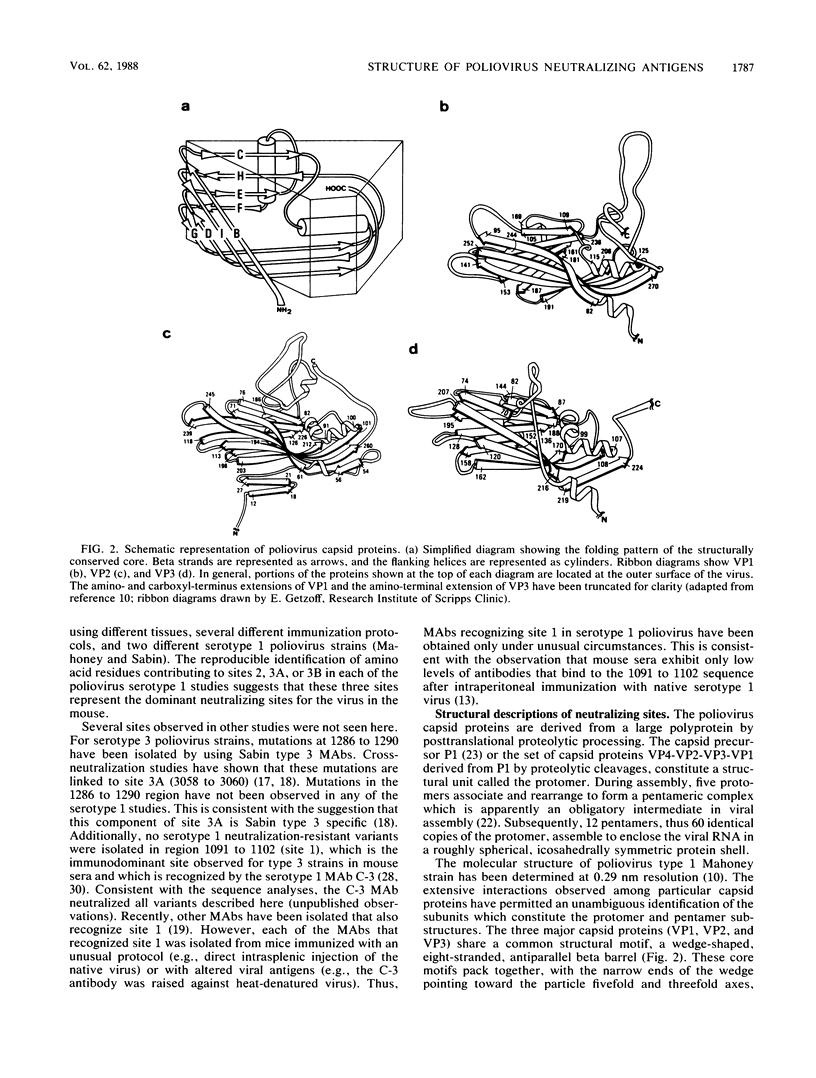
Antigenic mutants of poliovirus (Sabin strain, serotype 1) were isolated by the resistance of the virus to anti-Sabin neutralizing monoclonal antibodies. The amino acid replacements within the capsid protein sequence causing the altered antigenicity were identified for each of 63 isolates. The mutations cluster into distinct nonoverlapping peptide segments that group into three general immunological phenotypes on the basis of cross-neutralization analyses with 15 neutralizing anti-Sabin monoclonal antibodies. Location of the mutated amino acid residues within the three-dimensional structure of the virion indicates that the majority of these amino acid residues are highly exposed and located within prominent structural features of the viral surface. Those mutated amino acid residues that are less accessible to antibody interaction are often involved in hydrogen bonds or salt bridges that would stabilize the local tertiary structure of the antigenic site. The interactions of the peptide segments that form these neutralizing sites suggest specific models for the generation of neutralization-resistant variants and for the interaction between the viral surface and antibody.
Full text
PDF




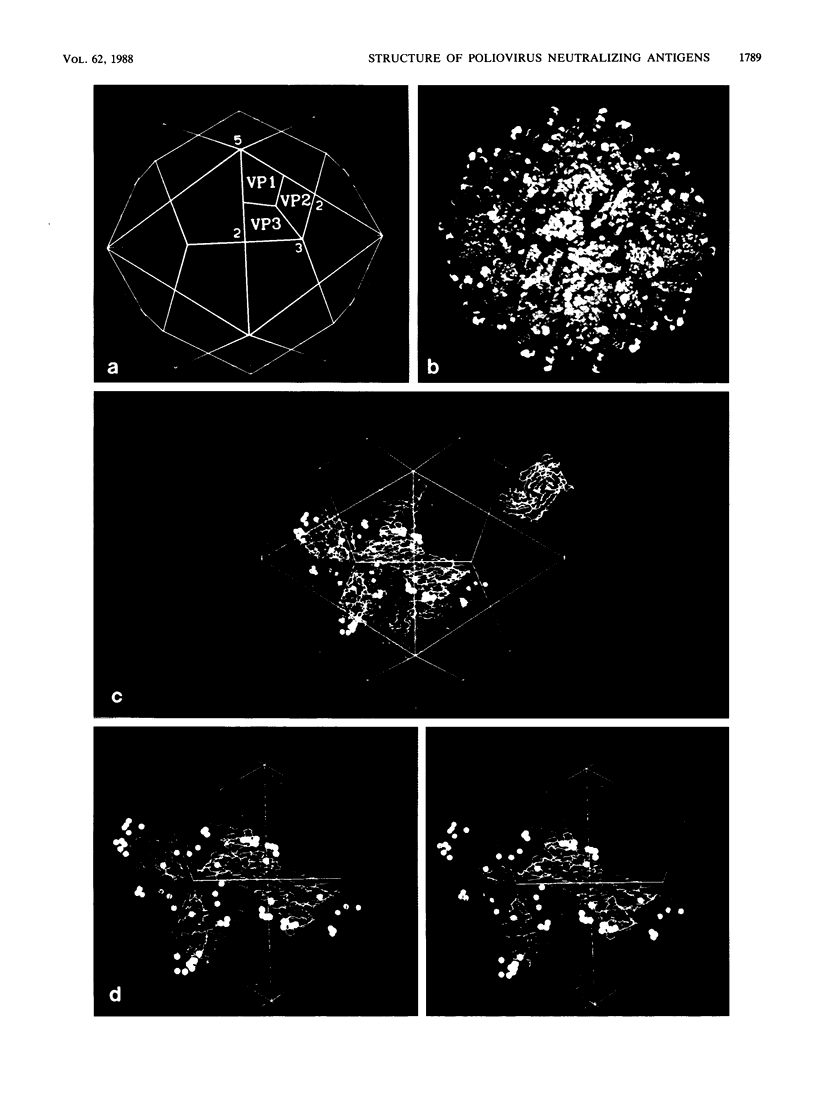



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blondel B., Crainic R., Fichot O., Dufraisse G., Candrea A., Diamond D., Girard M., Horaud F. Mutations conferring resistance to neutralization with monoclonal antibodies in type 1 poliovirus can be located outside or inside the antibody-binding site. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):81–90. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.81-90.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow M., Yabrov R., Bittle J., Hogle J., Baltimore D. Synthetic peptides from four separate regions of the poliovirus type 1 capsid protein VP1 induce neutralizing antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):910–914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claflin L., Williams K. Mouse myeloma--spleen cell hybrids: Enhanced hybridization frequencies and rapid screening procedures. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;81:107–109. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67448-8_16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman P. M., Varghese J. N., Laver W. G. Structure of the catalytic and antigenic sites in influenza virus neuraminidase. Nature. 1983 May 5;303(5912):41–44. doi: 10.1038/303041a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly M. L. Solvent-accessible surfaces of proteins and nucleic acids. Science. 1983 Aug 19;221(4612):709–713. doi: 10.1126/science.6879170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond D. C., Jameson B. A., Bonin J., Kohara M., Abe S., Itoh H., Komatsu T., Arita M., Kuge S., Nomoto A. Antigenic variation and resistance to neutralization in poliovirus type 1. Science. 1985 Sep 13;229(4718):1090–1093. doi: 10.1126/science.2412292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emini E. A., Dorner A. J., Dorner L. F., Jameson B. A., Wimmer E. Identification of a poliovirus neutralization epitope through use of neutralizing antiserum raised against a purified viral structural protein. Virology. 1983 Jan 15;124(1):144–151. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90297-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emini E. A., Jameson B. A., Lewis A. J., Larsen G. R., Wimmer E. Poliovirus neutralization epitopes: analysis and localization with neutralizing monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):997–1005. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.997-1005.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emini E. A., Jameson B. A., Wimmer E. Priming for and induction of anti-poliovirus neutralizing antibodies by synthetic peptides. Nature. 1983 Aug 25;304(5928):699–703. doi: 10.1038/304699a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogle J. M., Chow M., Filman D. J. Three-dimensional structure of poliovirus at 2.9 A resolution. Science. 1985 Sep 27;229(4720):1358–1365. doi: 10.1126/science.2994218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Icenogle J. P., Minor P. D., Ferguson M., Hogle J. M. Modulation of humoral response to a 12-amino-acid site on the poliovirus virion. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):297–301. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.297-301.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Icenogle J., Gilbert S. F., Grieves J., Anderegg J., Rueckert R. A neutralizing monoclonal antibody against poliovirus and its reaction with related antigens. Virology. 1981 Nov;115(1):211–215. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90103-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Icenogle J., Shiwen H., Duke G., Gilbert S., Rueckert R., Anderegg J. Neutralization of poliovirus by a monoclonal antibody: kinetics and stoichiometry. Virology. 1983 Jun;127(2):412–425. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90154-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo M., Vriend G., Kamer G., Minor I., Arnold E., Rossmann M. G., Boege U., Scraba D. G., Duke G. M., Palmenberg A. C. The atomic structure of Mengo virus at 3.0 A resolution. Science. 1987 Jan 9;235(4785):182–191. doi: 10.1126/science.3026048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medappa K. C., McLean C., Rueckert R. R. On the structure of rhinovirus 1A. Virology. 1971 May;44(2):259–270. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90258-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minor P. D., Evans D. M., Ferguson M., Schild G. C., Westrop G., Almond J. W. Principal and subsidiary antigenic sites of VP1 involved in the neutralization of poliovirus type 3. J Gen Virol. 1985 May;66(Pt 5):1159–1165. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-5-1159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minor P. D., Ferguson M., Evans D. M., Almond J. W., Icenogle J. P. Antigenic structure of polioviruses of serotypes 1, 2 and 3. J Gen Virol. 1986 Jul;67(Pt 7):1283–1291. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-7-1283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minor P. D., Ferguson M., Phillips A., Magrath D. I., Huovilainen A., Hovi T. Conservation in vivo of protease cleavage sites in antigenic sites of poliovirus. J Gen Virol. 1987 Jul;68(Pt 7):1857–1865. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-7-1857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minor P. D., Schild G. C., Bootman J., Evans D. M., Ferguson M., Reeve P., Spitz M., Stanway G., Cann A. J., Hauptmann R. Location and primary structure of a major antigenic site for poliovirus neutralization. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):674–679. doi: 10.1038/301674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossmann M. G., Arnold E., Erickson J. W., Frankenberger E. A., Griffith J. P., Hecht H. J., Johnson J. E., Kamer G., Luo M., Mosser A. G. Structure of a human common cold virus and functional relationship to other picornaviruses. Nature. 1985 Sep 12;317(6033):145–153. doi: 10.1038/317145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rueckert R. R., Wimmer E. Systematic nomenclature of picornavirus proteins. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):957–959. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.957-959.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherry B., Mosser A. G., Colonno R. J., Rueckert R. R. Use of monoclonal antibodies to identify four neutralization immunogens on a common cold picornavirus, human rhinovirus 14. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):246–257. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.246-257.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherry B., Rueckert R. Evidence for at least two dominant neutralization antigens on human rhinovirus 14. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):137–143. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.137-143.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh S. W., Bhat T. N., Navia M. A., Cohen G. H., Rao D. N., Rudikoff S., Davies D. R. The galactan-binding immunoglobulin Fab J539: an X-ray diffraction study at 2.6-A resolution. Proteins. 1986 Sep;1(1):74–80. doi: 10.1002/prot.340010112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sures I., Levy S., Kedes L. H. Leader sequences of Strongylocentrotus purpuratus histone mRNAs start at a unique heptanucleotide common to all five histone genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1265–1269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley D. C., Wilson I. A., Skehel J. J. Structural identification of the antibody-binding sites of Hong Kong influenza haemagglutinin and their involvement in antigenic variation. Nature. 1981 Jan 29;289(5796):373–378. doi: 10.1038/289373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wychowski C., van der Werf S., Siffert O., Crainic R., Bruneau P., Girard M. A poliovirus type 1 neutralization epitope is located within amino acid residues 93 to 104 of viral capsid polypeptide VP1. EMBO J. 1983;2(11):2019–2024. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01694.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Werf S., Wychowski C., Bruneau P., Blondel B., Crainic R., Horodniceanu F., Girard M. Localization of a poliovirus type 1 neutralization epitope in viral capsid polypeptide VP1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):5080–5084. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.5080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]