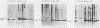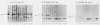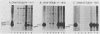Abstract
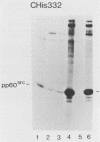
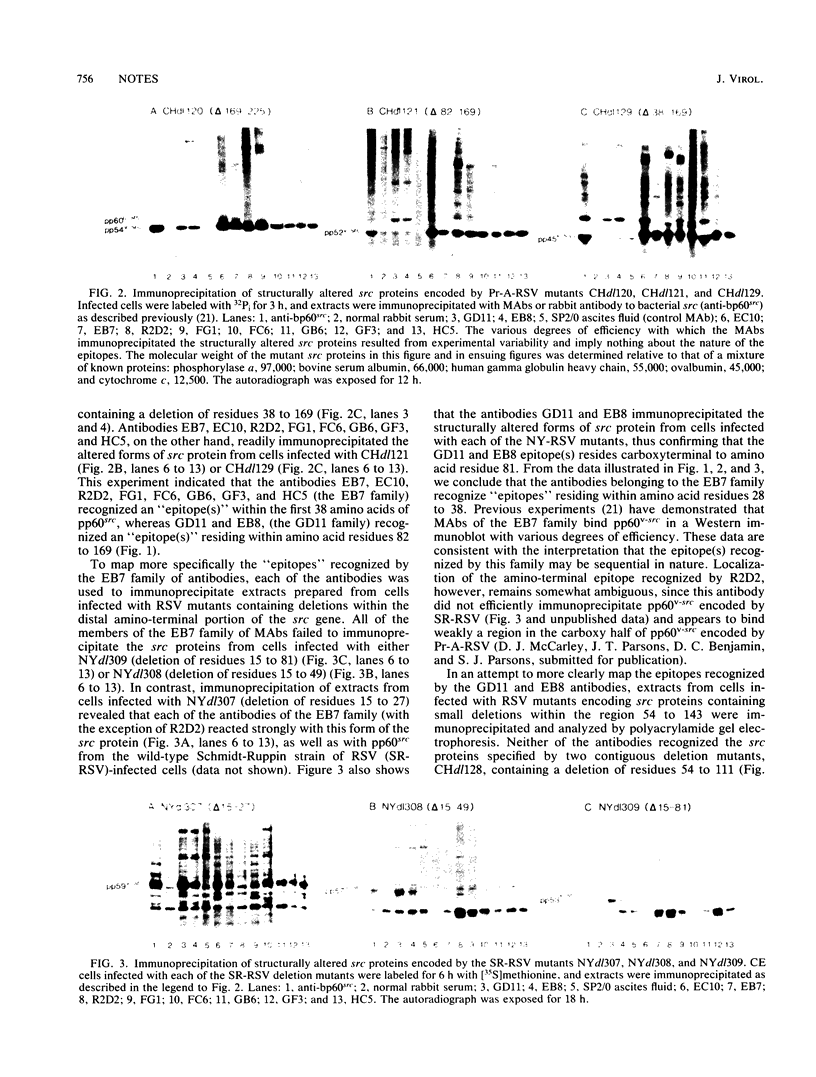
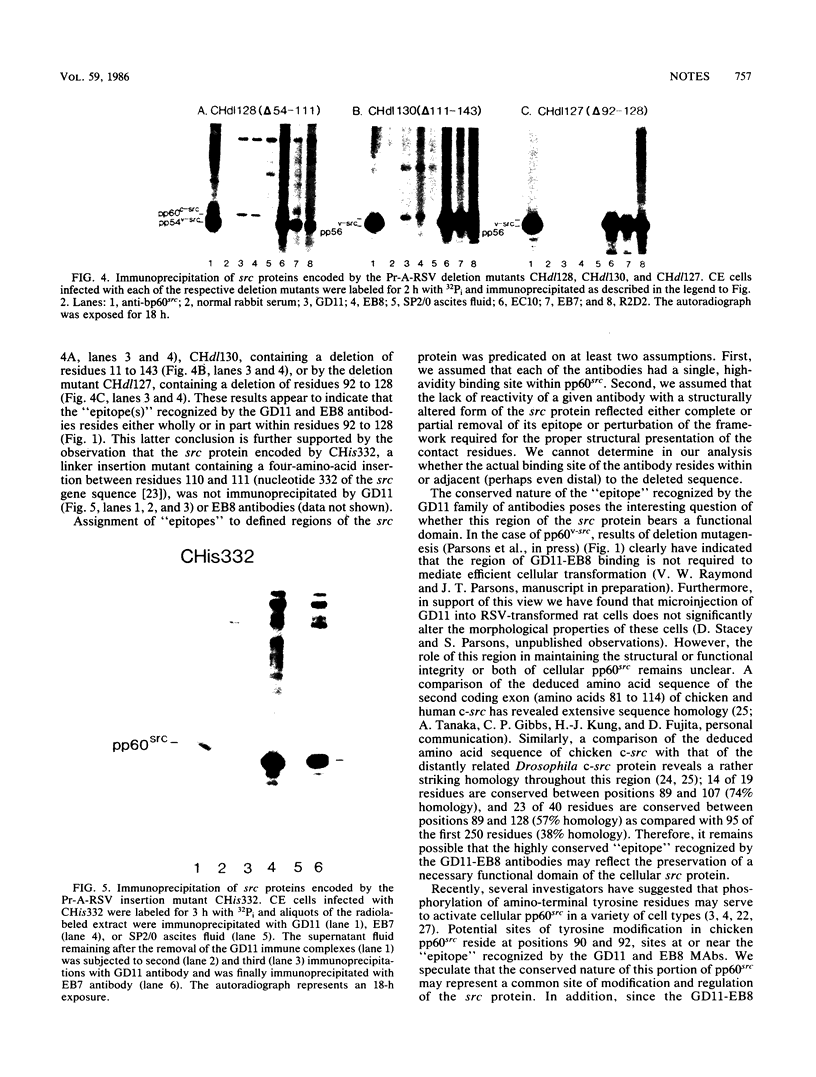
We investigated the location of binding sites of pp60src-specific monoclonal antibodies by immunoprecipitating a panel of structurally altered src proteins. Two families of antibodies which recognized epitopes mapping to either amino acid residues 28 to 38 or 92 to 128 were identified. The highly conserved nature of the epitope defined by residues 92 to 128 suggests that it may represent an important functional region of the cellular src protein.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bishop J. M. Cellular oncogenes and retroviruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:301–354. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.001505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. Viral oncogenes. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):23–38. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80098-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolen J. B., Rosen N., Israel M. A. Increased pp60c-src tyrosyl kinase activity in human neuroblastomas is associated with amino-terminal tyrosine phosphorylation of the src gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7275–7279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Cotton P. C., Queral A. E., Barrett J. N., Nonner D., Keane R. W. Neurones express high levels of a structurally modified, activated form of pp60c-src. Nature. 1985 Aug 8;316(6028):554–557. doi: 10.1038/316554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Erikson R. L. Identification of a transformation-specific antigen induced by an avian sarcoma virus. Nature. 1977 Sep 22;269(5626):346–348. doi: 10.1038/269346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant D., Parsons J. T. Site-directed mutagenesis of the src gene of Rous sarcoma virus: construction and characterization of a deletion mutant temperature sensitive for transformation. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):683–691. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.683-691.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Erikson R. L. Protein kinase activity associated with the avian sarcoma virus src gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):2021–2024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.2021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Hunter T. Changes in protein phosphorylation in Rous sarcoma virus-transformed chicken embryo cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Feb;1(2):165–178. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.2.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Reiss N. A., Schwartz R. J., Hunter T. Three glycolytic enzymes are phosphorylated at tyrosine in cells transformed by Rous sarcoma virus. Nature. 1983 Mar 17;302(5905):218–223. doi: 10.1038/302218a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J., Nakamura K. D., Hunter T., Weber M. J. Phosphotyrosine-containing proteins and expression of transformation parameters in cells infected with partial transformation mutants of Rous sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):15–28. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.15-28.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R., Garber E. A., Pellman D., Hanafusa H. A short sequence in the p60src N terminus is required for p60src myristylation and membrane association and for cell transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1834–1842. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Protein-tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Sefton B. M. Transforming gene product of Rous sarcoma virus phosphorylates tyrosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1311–1315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson A. D., Oppermann H., Levintow L., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Evidence that the transforming gene of avian sarcoma virus encodes a protein kinase associated with a phosphoprotein. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):561–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsich L. A., Lewis A. J., Brugge J. S. Isolation of monoclonal antibodies that recognize the transforming proteins of avian sarcoma viruses. J Virol. 1983 Nov;48(2):352–360. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.2.352-360.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons S. J., Creutz C. E. p60c-src activity detected in the chromaffin granule membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jan 29;134(2):736–742. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80482-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons S. J., McCarley D. J., Ely C. M., Benjamin D. C., Parsons J. T. Isolation and partial characterization of a monoclonal antibody to the Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein pp60src. J Virol. 1983 Mar;45(3):1190–1194. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.3.1190-1194.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons S. J., McCarley D. J., Ely C. M., Benjamin D. C., Parsons J. T. Monoclonal antibodies to Rous sarcoma virus pp60src react with enzymatically active cellular pp60src of avian and mammalian origin. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):272–282. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.272-282.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralston R., Bishop J. M. The product of the protooncogene c-src is modified during the cellular response to platelet-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7845–7849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. E., Tizard R., Gilbert W. Nucleotide sequence of Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):853–869. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90071-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. A., Drees B., Kornberg T., Bishop J. M. The nucleotide sequence and the tissue-specific expression of Drosophila c-src. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):831–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90279-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeya T., Hanafusa H. Structure and sequence of the cellular gene homologous to the RSV src gene and the mechanism for generating the transforming virus. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):881–890. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Kurth R. Monoclonal antibodies specific for the avian sarcoma virus transforming protein pp60src. Virology. 1984 Feb;133(1):202–210. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90440-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonemoto W., Jarvis-Morar M., Brugge J. S., Bolen J. B., Israel M. A. Tyrosine phosphorylation within the amino-terminal domain of pp60c-src molecules associated with polyoma virus middle-sized tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4568–4572. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]