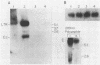
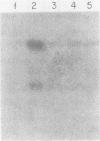
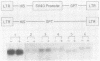
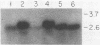
Abstract
Adenovirus E1A gene products are capable of modulating the expression of a variety of integrated genes. To study the mechanisms by which this regulation occurs, recombinant retroviruses have been utilized to establish cell lines containing an integrated copy of either the adenovirus E2 or E3 promoter adjacent to the bacterial guanine phosphoribosyl transferase (GPT) gene. These cell lines have been characterized with respect to both basal and E1A-induced levels of GPT gene expression. Cell lines with low levels of GPT gene expression showed increased expression in the presence of E1A, whereas cell lines with high basal levels of GPT gene expression had decreased GPT RNA levels in the presence of E1A. Further characterization of these cell lines revealed E1A modulation of the accumulation of RNA initiating at a retrovirus promoter adjacent to the E2 or E3 promoter. The use of the GPT gene as a marker of E2 or E3 promoter activity has allowed the isolation of cell lines which have spontaneously increased their levels of GPT RNA. A preliminary characterization of four of these cell lines has indicated that GPT gene expression is increased as a result of cis activation of the E2 promoter.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berk A. J., Lee F., Harrison T., Williams J., Sharp P. A. Pre-early adenovirus 5 gene product regulates synthesis of early viral messenger RNAs. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):935–944. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90333-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Structure of the adenovirus 2 early mRNAs. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):695–711. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90252-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borrelli E., Hen R., Chambon P. Adenovirus-2 E1A products repress enhancer-induced stimulation of transcription. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):608–612. doi: 10.1038/312608a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borrelli E., Hen R., Wasylyk C., Wasylyk B., Chambon P. The immunoglobulin heavy chain enhancer is stimulated by the adenovirus type 2 E1A products in mouse fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2846–2849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlock L. R., Jones N. C. Transformation-defective mutant of adenovirus type 5 containing a single altered E1a mRNA species. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):657–664. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.657-664.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cepko C. L., Roberts B. E., Mulligan R. C. Construction and applications of a highly transmissible murine retrovirus shuttle vector. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1053–1062. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90440-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cone R. D., Weber-Benarous A., Baorto D., Mulligan R. C. Regulated expression of a complete human beta-globin gene encoded by a transmissible retrovirus vector. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):887–897. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtois G., Berk A. Adenovirus E1A protein activation of an integrated viral gene. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1145–1149. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01943.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaynor R. B., Hillman D., Berk A. J. Adenovirus early region 1A protein activates transcription of a nonviral gene introduced into mammalian cells by infection or transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1193–1197. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Treisman R., Maniatis T. Transcriptional activation of cloned human beta-globin genes by viral immediate-early gene products. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):137–148. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90216-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hen R., Borrelli E., Chambon P. Repression of the immunoglobulin heavy chain enhancer by the adenovirus-2 E1A products. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1391–1394. doi: 10.1126/science.2999984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hen R., Borrelli E., Fromental C., Sassone-Corsi P., Chambon P. A mutated polyoma virus enhancer which is active in undifferentiated embryonal carcinoma cells is not repressed by adenovirus-2 E1A products. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):249–251. doi: 10.1038/321249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz D. R., Chinnadurai G. Evidence that a second tumor antigen coded by adenovirus early gene region E1a is required for efficient cell transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):163–167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imperiale M. J., Hart R. P., Nevins J. R. An enhancer-like element in the adenovirus E2 promoter contains sequences essential for uninduced and E1A-induced transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):381–385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N., Shenk T. An adenovirus type 5 early gene function regulates expression of other early viral genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3665–3669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston R. E., Baldwin A. S., Sharp P. A. Transcription control by oncogenes. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):3–5. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90049-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston R. E., Kaufman R. J., Sharp P. A. Regulation of transcription of the adenovirus EII promoter by EIa gene products: absence of sequence specificity. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):1970–1977. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korman A. J., Frantz J. D., Strominger J. L., Mulligan R. C. Expression of human class II major histocompatibility complex antigens using retrovirus vectors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2150–2154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krippl B., Ferguson B., Jones N., Rosenberg M., Westphal H. Mapping of functional domains in adenovirus E1A proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7480–7484. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie J. W., Green M., Green M. R. An adenovirus E1a protein region required for transformation and transcriptional repression. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1043–1051. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90704-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie J. W., Loewenstein P. M., Green M. R., Green M. Functional domains of adenovirus type 5 E1a proteins. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1091–1100. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90175-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann R., Mulligan R. C., Baltimore D. Construction of a retrovirus packaging mutant and its use to produce helper-free defective retrovirus. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90344-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montell C., Courtois G., Eng C., Berk A. Complete transformation by adenovirus 2 requires both E1A proteins. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):951–961. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90045-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran E., Mathews M. B. Multiple functional domains in the adenovirus E1A gene. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):177–178. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90418-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran E., Zerler B., Harrison T. M., Mathews M. B. Identification of separate domains in the adenovirus E1A gene for immortalization activity and the activation of virus early genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3470–3480. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Induction of the synthesis of a 70,000 dalton mammalian heat shock protein by the adenovirus E1A gene product. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):913–919. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90453-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perricaudet M., Akusjärvi G., Virtanen A., Pettersson U. Structure of two spliced mRNAs from the transforming region of human subgroup C adenoviruses. Nature. 1979 Oct 25;281(5733):694–696. doi: 10.1038/281694a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricciardi R. P., Jones R. L., Cepko C. L., Sharp P. A., Roberts B. E. Expression of early adenovirus genes requires a viral encoded acidic polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6121–6125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts B. E., Miller J. S., Kimelman D., Cepko C. L., Lemischka I. R., Mulligan R. C. Individual adenovirus type 5 early region 1A gene products elicit distinct alterations of cellular morphology and gene expression. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):404–413. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.404-413.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruley H. E. Adenovirus early region 1A enables viral and cellular transforming genes to transform primary cells in culture. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):602–606. doi: 10.1038/304602a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodroski J., Rosen C., Goh W. C., Haseltine W. A transcriptional activator protein encoded by the x-lor region of the human T-cell leukemia virus. Science. 1985 Jun 21;228(4706):1430–1434. doi: 10.1126/science.2990028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein R. W., Ziff E. B. Repression of insulin gene expression by adenovirus type 5 E1a proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1164–1170. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein R., Ziff E. B. HeLa cell beta-tubulin gene transcription is stimulated by adenovirus 5 in parallel with viral early genes by an E1a-dependent mechanism. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2792–2801. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velcich A., Ziff E. Adenovirus E1a proteins repress transcription from the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90219-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. M., Levine A. J. Identification and mapping of Epstein-Barr virus early antigens and demonstration of a viral gene activator that functions in trans. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):149–156. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.149-156.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu S. F., von Rüden T., Kantoff P. W., Garber C., Seiberg M., Rüther U., Anderson W. F., Wagner E. F., Gilboa E. Self-inactivating retroviral vectors designed for transfer of whole genes into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3194–3198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerler B., Roberts R. J., Mathews M. B., Moran E. Different functional domains of the adenovirus E1A gene are involved in regulation of host cell cycle products. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):821–829. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]