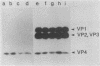
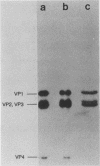
Abstract
The attachment of rhinoviruses to cellular receptors was studied by displacing bound virus particles with an anti-receptor monoclonal antibody. The two serotypes studied differed significantly with respect to the temperature dependence of displacement and the nature of the particles displaced. Binding was shown to be a two-step process, the first of which is reversible and is seen when viruses are bound either to isolated cell membranes or to cells at lower than physiological temperatures. Second-stage binding was seen with serotype 14 when bound to intact cells. Viral particles released from such cells by incubation at 37 degrees C or by anti-receptor antibody exhibited altered physical changes in the capsid and a loss of infectivity. In contrast, serotype 67 bound efficiently to cells at 37 degrees C and did not elute spontaneously but could be displaced by anti-receptor antibody to produce complete, infectious particles. Rhinoviruses labeled with [3H]myristic acid or with [35S]methionine were displaced similarly from cells or membranes by anti-receptor antibody, indicating that the majority of VP4 of rhinoviruses does not enter or remain attached to cells during either the first or second stage of virus binding. These data support the conclusion that the myristic acid moiety of VP4 is not involved in the initial viral interaction with cellular receptors.
Full text
PDF

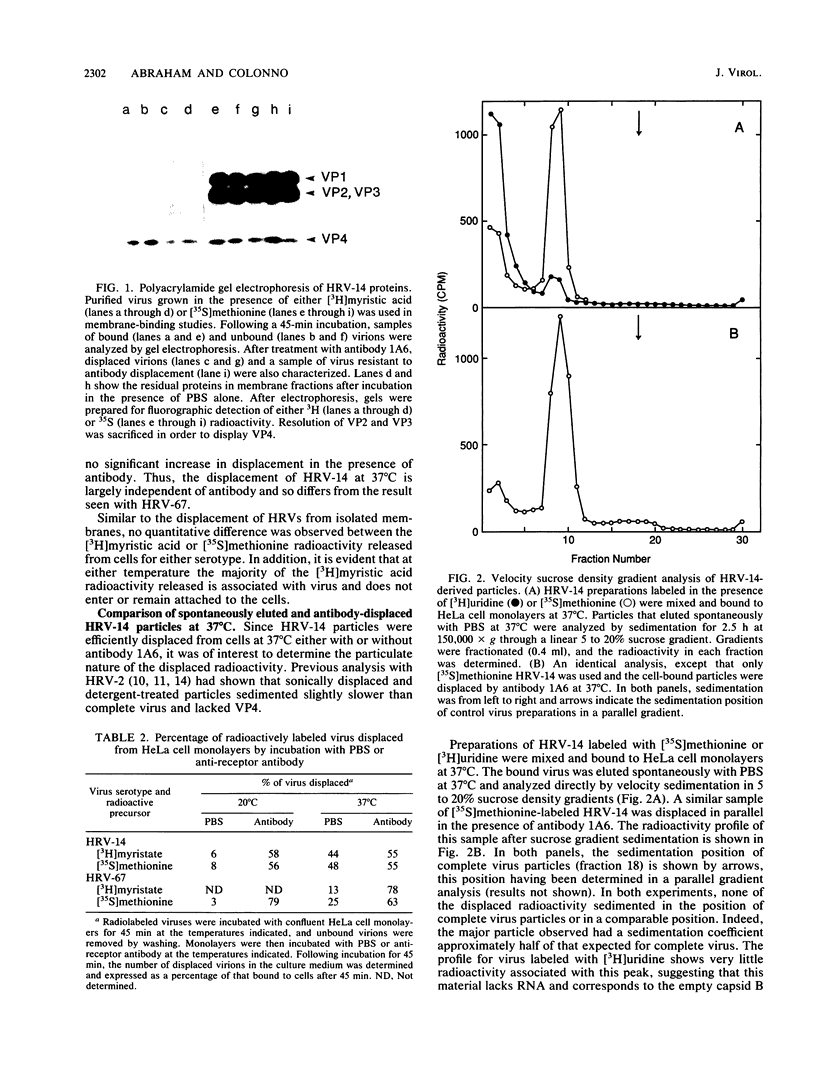
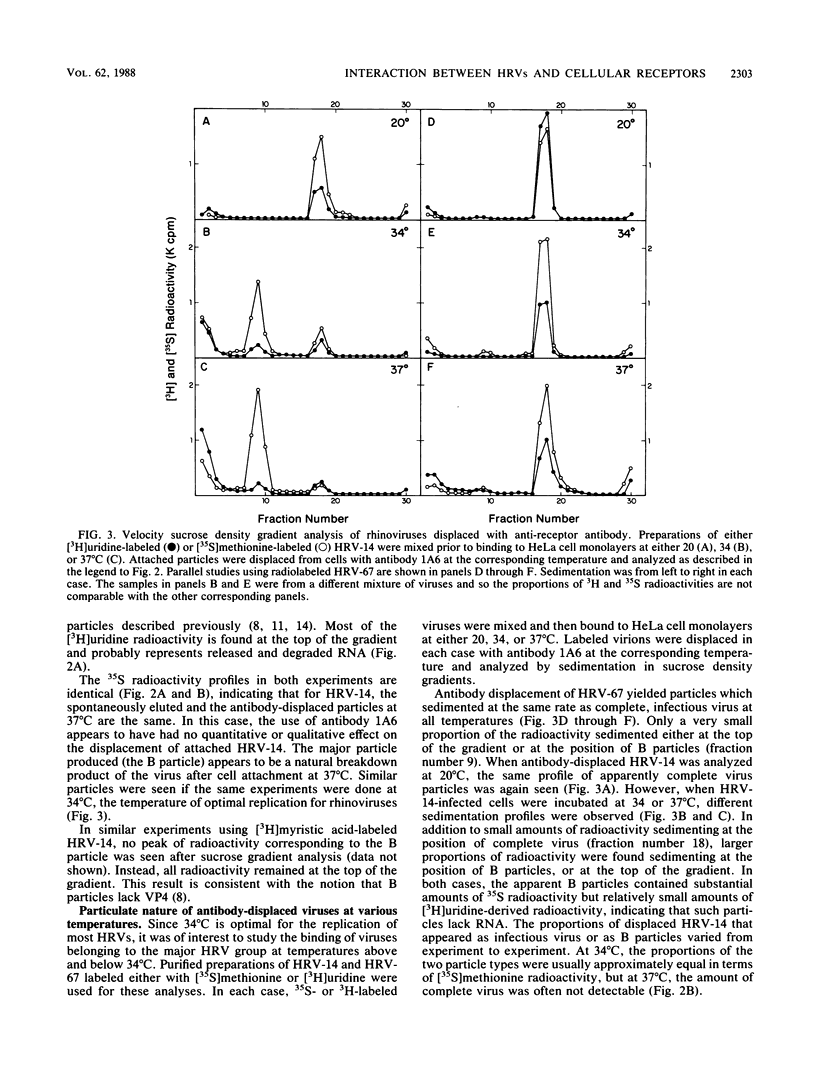



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham G., Colonno R. J. Many rhinovirus serotypes share the same cellular receptor. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):340–345. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.340-345.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callahan P. L., Mizutani S., Colonno R. J. Molecular cloning and complete sequence determination of RNA genome of human rhinovirus type 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):732–736. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow M., Newman J. F., Filman D., Hogle J. M., Rowlands D. J., Brown F. Myristylation of picornavirus capsid protein VP4 and its structural significance. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):482–486. doi: 10.1038/327482a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colonno R. J., Callahan P. L., Long W. J. Isolation of a monoclonal antibody that blocks attachment of the major group of human rhinoviruses. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):7–12. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.7-12.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauntt C. J. Fragmentation of RNA in virus particles of rhinovirus type 14. J Virol. 1974 Mar;13(3):762–764. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.3.762-764.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauntt C. J., Griffith M. M., Sauck J. R., Upson R. H., Carlson E. C. Properties and origins of infectious rhinovirus type 14 particles of different buoyant densities. J Virol. 1975 Nov;16(5):1265–1272. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.5.1265-1272.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korant B. D., Lonberg-Holm K., Noble J., Stasny J. T. Naturally occurring and artificially produced components of three rhinoviruses. Virology. 1972 Apr;48(1):71–86. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90115-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonberg-Holm K., Crowell R. L., Philipson L. Unrelated animal viruses share receptors. Nature. 1976 Feb 26;259(5545):679–681. doi: 10.1038/259679a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonberg-Holm K., Korant B. D. Early interaction of rhinoviruses with host cells. J Virol. 1972 Jan;9(1):29–40. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.1.29-40.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonberg-Holm K., Noble-Harvey J. Comparison of in vitro and cell-mediated alteration of a human Rhinovirus and its inhibition by sodium dodecyl sulfate. J Virol. 1973 Oct;12(4):819–826. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.4.819-826.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonberg-Holm K., Whiteley N. M. Physical and metabolic requirements for early interaction of poliovirus and human rhinovirus with HeLa cells. J Virol. 1976 Sep;19(3):857–870. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.3.857-870.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonberg-Holm K., Yin F. H. Antigenic determinants of infective and inactivated human rhinovirus type 2. J Virol. 1973 Jul;12(1):114–123. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.1.114-123.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble-Harvey J., Lonberg-Holm K. Sequential steps in attachment of human rhinovirus type 2 to HeLa cells. J Gen Virol. 1974 Oct;25(1):83–91. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-25-1-83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble J., Lonberg-Holm K. Interactions of components of human rhinovirus type 2 with Hela cells. Virology. 1973 Feb;51(2):270–278. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90427-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul A. V., Schultz A., Pincus S. E., Oroszlan S., Wimmer E. Capsid protein VP4 of poliovirus is N-myristoylated. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7827–7831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossmann M. G., Arnold E., Erickson J. W., Frankenberger E. A., Griffith J. P., Hecht H. J., Johnson J. E., Kamer G., Luo M., Mosser A. G. Structure of a human common cold virus and functional relationship to other picornaviruses. Nature. 1985 Sep 12;317(6033):145–153. doi: 10.1038/317145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanway G., Hughes P. J., Mountford R. C., Minor P. D., Almond J. W. The complete nucleotide sequence of a common cold virus: human rhinovirus 14. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 25;12(20):7859–7875. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.20.7859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomassini J. E., Colonno R. J. Isolation of a receptor protein involved in attachment of human rhinoviruses. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):290–295. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.290-295.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]