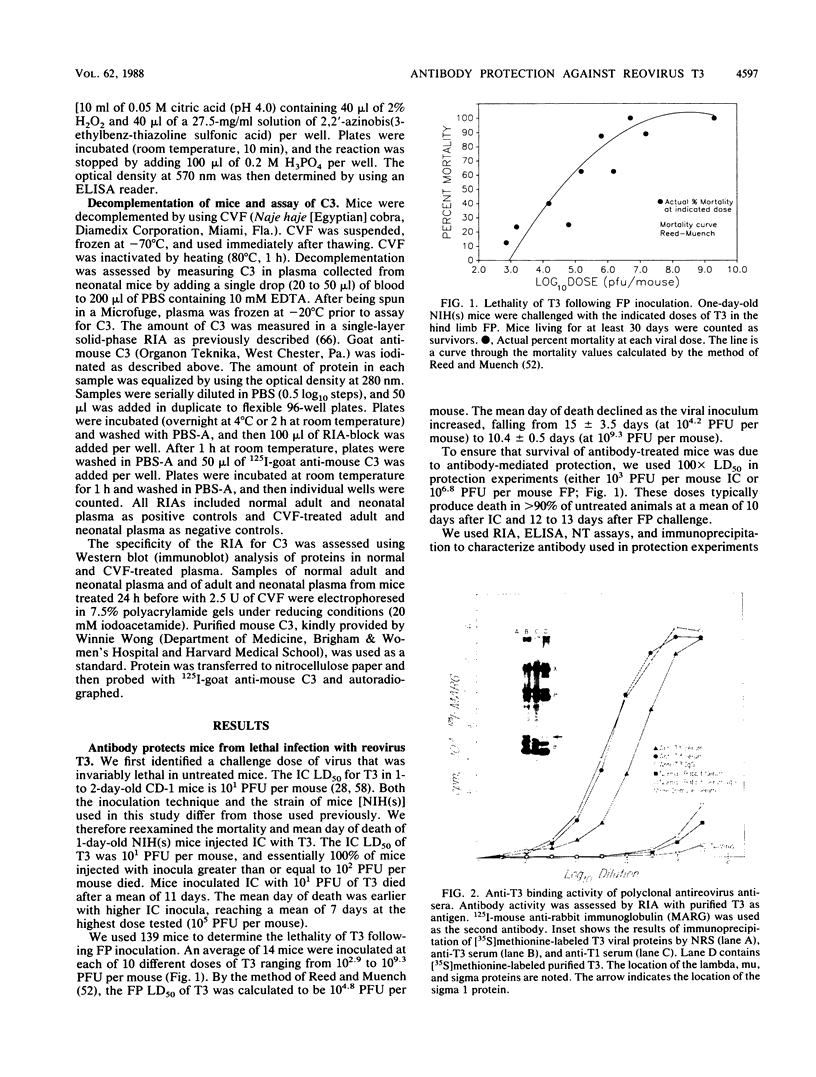
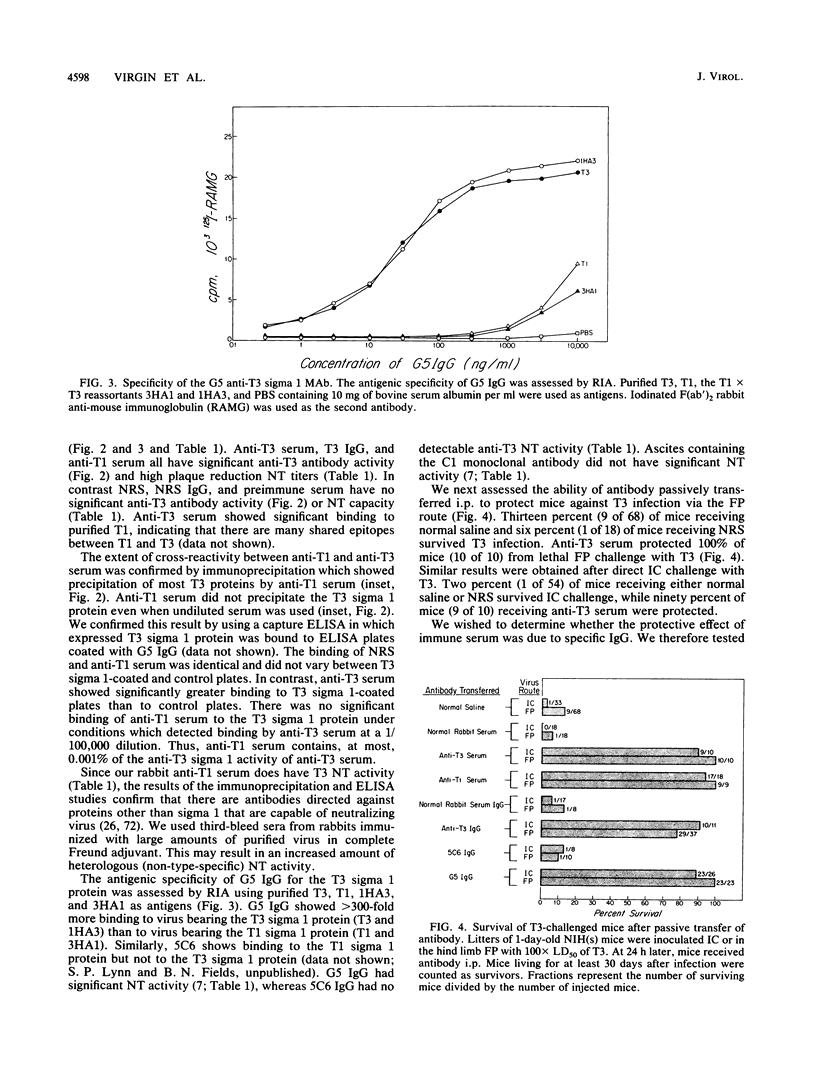
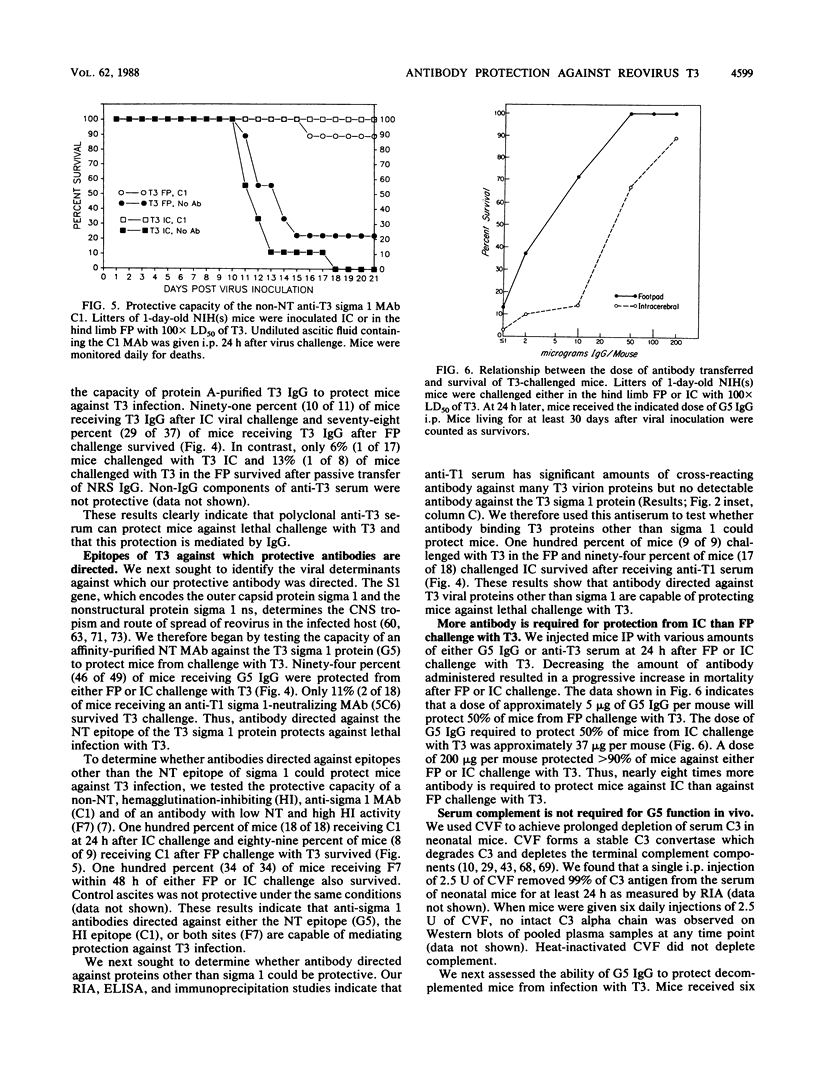
Abstract
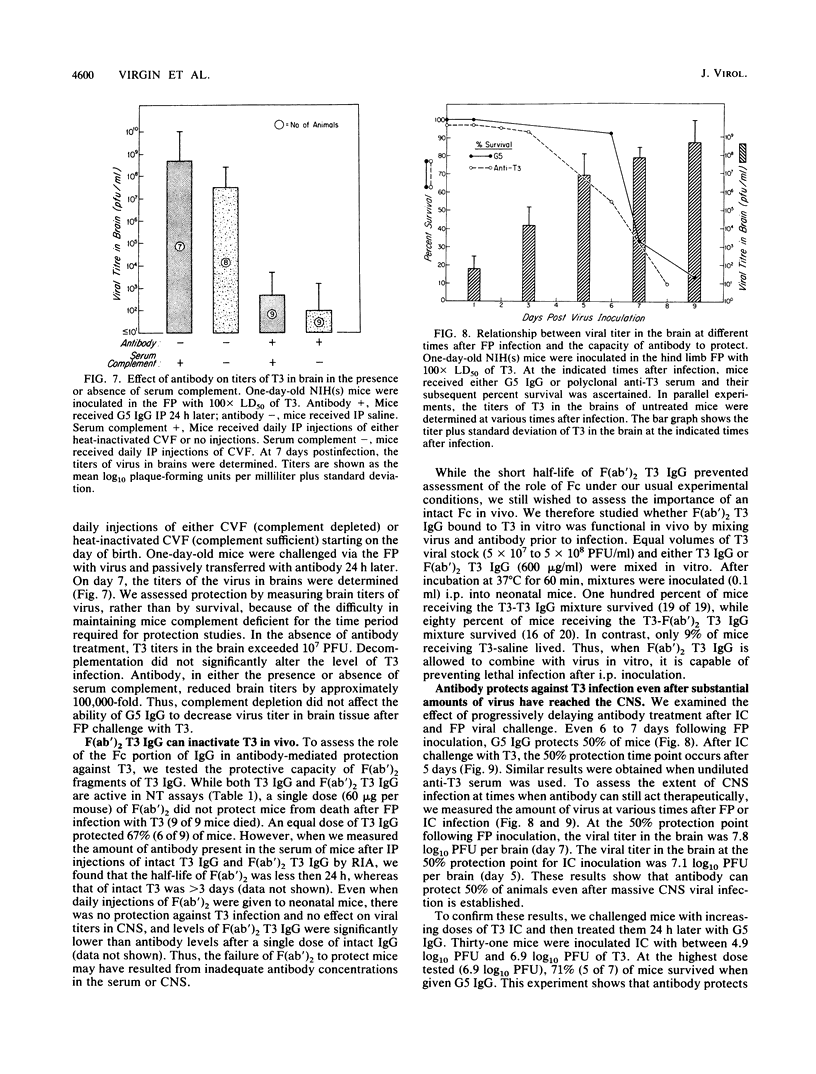
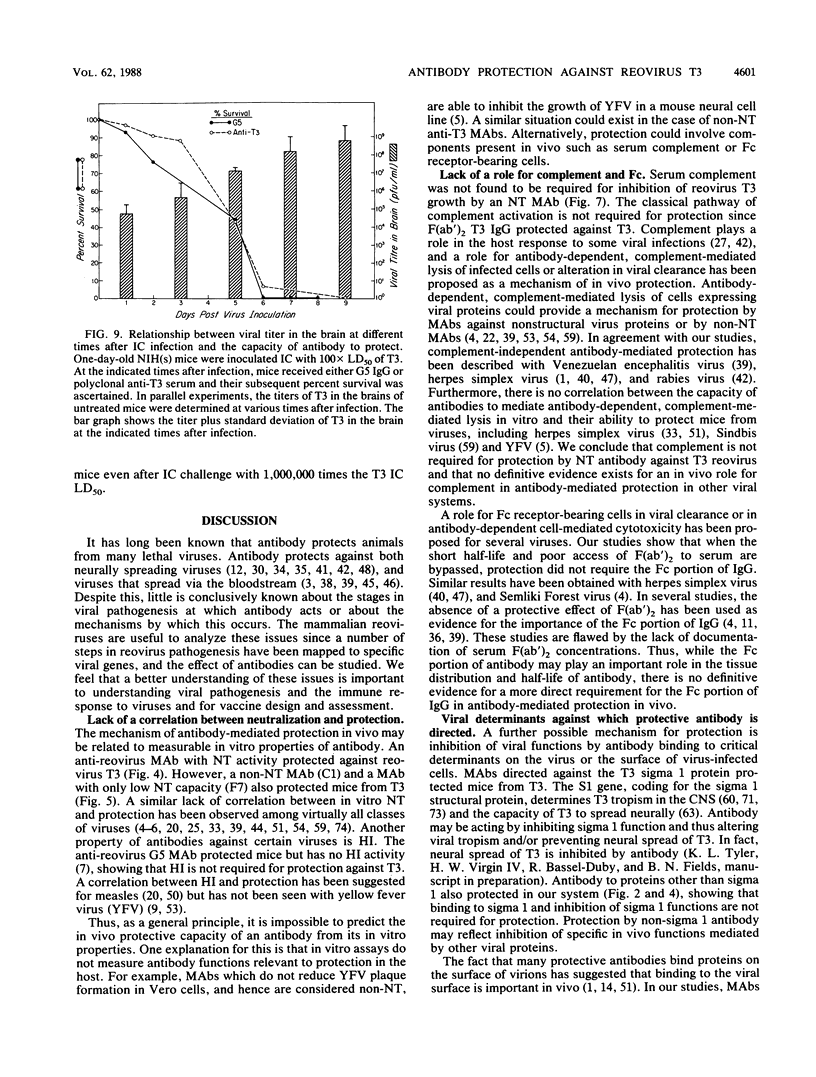
The mammalian reoviruses have provided a valuable model for studying the pathogenesis of viral infections of the central nervous system (CNS). We have used this model to study the effect of antibody on disease produced by the neurally spreading reovirus type 3 (Dearing) (T3). Polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies protect mice from fatal infection with T3 after either footpad or intracerebral virus challenge. Protection occurs with monoclonal antibodies directed against the viral cell attachment protein sigma 1, and with polyclonal antisera without T3 sigma 1 binding activity. In vivo protection occurs with both neutralizing and nonneutralizing monoclonal antibodies. Antibody-mediated protection does not require serum complement and, under specific circumstances, can occur via Fc-independent mechanisms. Antibody can protect mice when transferred up to 5 days after intracerebral challenge and up to 7 days after footpad challenge, times when high titers of virus are present in the CNS. Thus, antibody mediated protection against this neurally spreading virus does not require neutralizing antibody or serum complement and occurs even in the face of established CNS infection.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BODIAN D. Experimental studies on passive immunization against poliomyelitis. II. The prophylactic effect of human gamma globulin on paralytic poliomyelitis in cynomolgus monkeys after virus feeding. Am J Hyg. 1952 Jul;56(1):78–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BODIAN D., NATHANSON N. Inhibitory effects of passive antibody on virulent poliovirus excretion and on immune response in chimpanzees. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1960 Sep;107:143–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balachandran N., Bacchetti S., Rawls W. E. Protection against lethal challenge of BALB/c mice by passive transfer of monoclonal antibodies to five glycoproteins of herpes simplex virus type 2. Infect Immun. 1982 Sep;37(3):1132–1137. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.3.1132-1137.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boere W. A., Benaissa-Trouw B. J., Harmsen T., Erich T., Kraaijeveld C. A., Snippe H. Mechanisms of monoclonal antibody-mediated protection against virulent Semliki Forest virus. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):546–551. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.546-551.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandriss M. W., Schlesinger J. J., Walsh E. E., Briselli M. Lethal 17D yellow fever encephalitis in mice. I. Passive protection by monoclonal antibodies to the envelope proteins of 17D yellow fever and dengue 2 viruses. J Gen Virol. 1986 Feb;67(Pt 2):229–234. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-2-229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmeier M. J., Lewicki H. A., Talbot P. J., Knobler R. L. Murine hepatitis virus-4 (strain JHM)-induced neurologic disease is modulated in vivo by monoclonal antibody. Virology. 1984 Jan 30;132(2):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90033-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstin S. J., Spriggs D. R., Fields B. N. Evidence for functional domains on the reovirus type 3 hemagglutinin. Virology. 1982 Feb;117(1):146–155. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90514-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camenga D. L., Nathanson N., Cole G. A. Cyclophosphamide-potentiated West Nile viral encephalitis: relative influence of cellular and humoral factors. J Infect Dis. 1974 Dec;130(6):634–641. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.6.634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cammack N., Gould E. A. Topographical analysis of epitope relationships on the envelope glycoprotein of yellow fever 17D vaccine and the wild type Asibi parent virus. Virology. 1986 Apr 30;150(2):333–341. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90298-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane C. G., Müller-Eberhard H. J., Aikin B. S. Depletion of plasma complement in vivo by a protein of cobra venom: its effect on various immunologic reactions. J Immunol. 1970 Jul;105(1):55–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. J., Sackie D. M., Johnson G. R. Immunotherapy of murine leukemia. IX. The requirement for the Fc portion of antibody for successful passive serum therapy of Friend leukemia virus-induced disease. Virology. 1983 Apr 15;126(1):259–266. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90477-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis W. B., Taylor J. A., Oakes J. E. Ocular infection with herpes simplex virus type 1: prevention of acute herpetic encephalitis by systemic administration of virus-specific antibody. J Infect Dis. 1979 Oct;140(4):534–540. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.4.534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimmock N. J. Mechanisms of neutralization of animal viruses. J Gen Virol. 1984 Jun;65(Pt 6):1015–1022. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-6-1015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dix R. D., Pereira L., Baringer J. R. Use of monoclonal antibody directed against herpes simplex virus glycoproteins to protect mice against acute virus-induced neurological disease. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):192–199. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.192-199.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty P. C., Gerhard W. Breakdown of the blood--cerebrospinal fluid barrier to immunoglobulin in mice injected intracerebrally with a neurotropic influenza A virus. Post-exposure treatment with monoclonal antibody promotes recovery. J Neuroimmunol. 1981 Sep;1(3):227–237. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(81)90027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabian R. H., Petroff G. Intraneuronal IgG in the central nervous system: uptake by retrograde axonal transport. Neurology. 1987 Nov;37(11):1780–1784. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.11.1780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujinami R. S., Oldstone M. B. Alterations in expression of measles virus polypeptides by antibody: molecular events in antibody-induced antigenic modulation. J Immunol. 1980 Jul;125(1):78–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujinami R. S., Oldstone M. B. Antiviral antibody reacting on the plasma membrane alters measles virus expression inside the cell. Nature. 1979 Jun 7;279(5713):529–530. doi: 10.1038/279529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlong D. B., Nibert M. L., Fields B. N. Sigma 1 protein of mammalian reoviruses extends from the surfaces of viral particles. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):246–256. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.246-256.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giraudon P., Wild T. F. Correlation between epitopes on hemagglutinin of measles virus and biological activities: passive protection by monoclonal antibodies is related to their hemagglutination inhibiting activity. Virology. 1985 Jul 15;144(1):46–58. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90303-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gollins S. W., Porterfield J. S. A new mechanism for the neutralization of enveloped viruses by antiviral antibody. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):244–246. doi: 10.1038/321244a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonatas N. K., Margolis G., Kilham L. Reovirus type 3 encephalitis: observations of virus-cell interactions in neural tissues. II. Electron microscopic studies. Lab Invest. 1971 Feb;24(2):101–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould E. A., Buckley A., Barrett A. D., Cammack N. Neutralizing (54K) and non-neutralizing (54K and 48K) monoclonal antibodies against structural and non-structural yellow fever virus proteins confer immunity in mice. J Gen Virol. 1986 Mar;67(Pt 3):591–595. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-3-591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin D. E., Giffels J. Study of protein characteristics that influence entry into the cerebrospinal fluid of normal mice and mice with encephalitis. J Clin Invest. 1982 Aug;70(2):289–295. doi: 10.1172/JCI110616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin D. E., Johnson R. T. Role of the immune response in recovery from Sindbis virus encephalitis in mice. J Immunol. 1977 Mar;118(3):1070–1075. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes E. C., Lee P. W., Miller S. E., Joklik W. K. The interaction of a series of hybridoma IgGs with reovirus particles. Demonstration that the core protein lambda 2 is exposed on the particle surface. Virology. 1981 Jan 15;108(1):147–155. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90534-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch R. L., Griffin D. E., Winkelstein J. A. The effect of complement depletion on the course of Sindbis virus infection in mice. J Immunol. 1978 Oct;121(4):1276–1278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hrdy D. B., Rubin D. H., Fields B. N. Molecular basis of reovirus neurovirulence: role of the M2 gene in avirulence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1298–1302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunsicker L. G., Ruddy S., Austen K. F. Alternate complement pathway: factors involved in cobra venom factor (CoVF) activation of the third component of complement (C3). J Immunol. 1973 Jan;110(1):128–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapoor A. K., Nash A. A., Wildy P., Phelan J., McLean C. S., Field H. J. Pathogenesis of herpes simplex virus in congenitally athymic mice: the relative roles of cell-mediated and humoral immunity. J Gen Virol. 1982 Jun;60(Pt 2):225–233. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-60-2-225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy-Stoskopf S., Narayan O. Neutralizing antibodies to visna lentivirus: mechanism of action and possible role in virus persistence. J Virol. 1986 Jul;59(1):37–44. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.1.37-44.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kümel G., Kaerner H. C., Levine M., Schröder C. H., Glorioso J. C. Passive immune protection by herpes simplex virus-specific monoclonal antibodies and monoclonal antibody-resistant mutants altered in pathogenicity. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):930–937. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.930-937.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIU O. C., CARTER J. E., DESANCTIS A. N., GEATING J. A., HAMPIL B. A study of the effect of antiserum on poliovirus infection induced by the intraspinal inoculation of rhesus monkeys. J Immunol. 1958 Feb;80(2):106–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIU O. C., CARTER J. E., SANDERS B. E., SMITH E. C., HAMPIL B. A study on serotherapy of poliomyelitis in rhesus monkeys. Br J Exp Pathol. 1959 Apr;40(2):133–144. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löve A., Rydbeck R., Utter G., Orvell C., Kristensson K., Norrby E. Monoclonal antibodies against the fusion protein are protective in necrotizing mumps meningoencephalitis. J Virol. 1986 Apr;58(1):220–222. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.1.220-222.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews J. H., Roehrig J. T. Elucidation of the topography and determination of the protective epitopes on the E glycoprotein of Saint Louis encephalitis virus by passive transfer with monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1984 Mar;132(3):1533–1537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews J. H., Roehrig J. T., Trent D. W. Role of complement and the Fc portion of immunoglobulin G in immunity to Venezuelan equine encephalomyelitis virus infection with glycoprotein-specific monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):594–600. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.594-600.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKendall R. R. IgG-mediated viral clearance in experimental infection with herpes simplex virus type 1: role for neutralization and Fc-dependent functions but not C' cytolysis and C5 chemotaxis. J Infect Dis. 1985 Mar;151(3):464–470. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.3.464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKendall R. R., Klassen T., Baringer J. R. Host defenses in herpes simplex infections of the nervous system: effect of antibody on disease and viral spread. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):305–311. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.305-311.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A., Morse H. C., 3rd, Winkelstein J., Nathanson N. The role of antibody in recovery from experimental rabies. I. Effect of depletion of B and T cells. J Immunol. 1978 Jul;121(1):321–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J., Fjellström K. E. Isolation of the anticomplementary protein from cobra venom and its mode of action on C3. J Immunol. 1971 Dec;107(6):1666–1672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NATHANSON N., BODIAN D. Experimental poliomyelitis following intramuscular virus injection. II. Viremia and the effect of antibody. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1961 May;108:320–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NATHANSON N., BODIAN D. Experimental poliomyelitis following intramuscular virus injection. III. The effect of passive antibody on paralysis and viremia. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1962 Oct;111:198–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanaga K., Yamanouchi K., Fujiwara K. Protective effect of monoclonal antibodies on lethal mouse hepatitis virus infection in mice. J Virol. 1986 Jul;59(1):168–171. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.1.168-171.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakes J. E., Lausch R. N. Role of Fc fragments in antibody-mediated recovery from ocular and subcutaneous herpes simplex virus infections. Infect Immun. 1981 Jul;33(1):109–114. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.1.109-114.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakes J. E., Rosemond-Hornbeak H. Antibody-mediated recovery from subcutaneous herpes simplex virus type 2 infection. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):489–495. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.489-495.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J., Nicholson R., Bassel-Duby R., Fields B. N., Sonenberg N. Expression of reovirus type 3 (Dearing) sigma 1 and sigma s polypeptides in Escherichia coli. J Gen Virol. 1987 Jan;68(Pt 1):135–145. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-1-135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rammohan K. W., McFarland H. F., McFarlin D. E. Induction of subacute murine measles encephalitis by monoclonal antibody to virus haemagglutinin. Nature. 1981 Apr 16;290(5807):588–589. doi: 10.1038/290588a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rector J. T., Lausch R. N., Oakes J. E. Use of monoclonal antibodies for analysis of antibody-dependent immunity to ocular herpes simplex virus type 1 infection. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):168–174. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.168-174.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger J. J., Brandriss M. W., Walsh E. E. Protection against 17D yellow fever encephalitis in mice by passive transfer of monoclonal antibodies to the nonstructural glycoprotein gp48 and by active immunization with gp48. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2805–2809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmaljohn A. L., Johnson E. D., Dalrymple J. M., Cole G. A. Non-neutralizing monoclonal antibodies can prevent lethal alphavirus encephalitis. Nature. 1982 May 6;297(5861):70–72. doi: 10.1038/297070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmaljohn A. L., Kokubun K. M., Cole G. A. Protective monoclonal antibodies define maturational and pH-dependent antigenic changes in Sindbis virus E1 glycoprotein. Virology. 1983 Oct 15;130(1):144–154. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90124-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe A. H., Fields B. N. Pathogenesis of viral infections. Basic concepts derived from the reovirus model. N Engl J Med. 1985 Feb 21;312(8):486–497. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198502213120806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. E., Zweerink H. J., Joklik W. K. Polypeptide components of virions, top component and cores of reovirus type 3. Virology. 1969 Dec;39(4):791–810. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley J., Cooper S. J., Griffin D. E. Monoclonal antibody cure and prophylaxis of lethal Sindbis virus encephalitis in mice. J Virol. 1986 Apr;58(1):107–115. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.1.107-115.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler K. L., Bronson R. T., Byers K. B., Fields B. Molecular basis of viral neurotropism: experimental reovirus infection. Neurology. 1985 Jan;35(1):88–92. doi: 10.1212/wnl.35.1.88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler K. L., McPhee D. A., Fields B. N. Distinct pathways of viral spread in the host determined by reovirus S1 gene segment. Science. 1986 Aug 15;233(4765):770–774. doi: 10.1126/science.3016895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdin E. M., Lynn S. P., Fields B. N., Maratos-Flier E. Uptake of reovirus serotype 1 by the lungs from the bloodstream is mediated by the viral hemagglutinin. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):545–551. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.545-551.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virgin H. W., 4th, Unanue E. R. Suppression of the immune response to Listeria monocytogenes. I. Immune complexes inhibit resistance. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):104–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virgin H. W., 4th, Wittenberg G. F., Bancroft G. J., Unanue E. R. Suppression of immune response to Listeria monocytogenes: mechanism(s) of immune complex suppression. Infect Immun. 1985 Nov;50(2):343–353. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.2.343-353.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virgin H. W., 4th, Wittenberg G. F., Unanue E. R. Immune complex effects on murine macrophages. I. Immune complexes suppress interferon-gamma induction of Ia expression. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):3735–3743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel C. W., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The cobra venom factor-dependent C3 convertase of human complement. A kinetic and thermodynamic analysis of a protease acting on its natural high molecular weight substrate. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8292–8299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt W., Dieminger L., Lynen R., Schmidt G. Alternative pathway for the activation of complement in human serum. Formation and composition of the complex with cobra venom factor that cleaves the third component of complement. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1974 Feb;355(2):171–183. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1974.355.1.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALTERS M. N., JOSKE R. A., LEAK P. J., STANLEY N. F. MURINE INFECTION WITH REOVIRUS: I. PATHOLOGY OF THE ACUTE PHASE. Br J Exp Pathol. 1963 Aug;44:427–436. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner H. L., Drayna D., Averill D. R., Jr, Fields B. N. Molecular basis of reovirus virulence: role of the S1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5744–5748. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner H. L., Fields B. N. Neutralization of reovirus: the gene responsible for the neutralization antigen. J Exp Med. 1977 Nov 1;146(5):1305–1310. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.5.1305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner H. L., Powers M. L., Fields B. N. Absolute linkage of virulence and central nervous system cell tropism of reoviruses to viral hemagglutinin. J Infect Dis. 1980 May;141(5):609–616. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.5.609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolinsky J. S., Waxham M. N., Server A. C. Protective effects of glycoprotein-specific monoclonal antibodies on the course of experimental mumps virus meningoencephalitis. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):727–734. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.727-734.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Iwasaki Y., Konno H., Iizuka H., Zhao J. X. Retrograde transport and differential accumulation of serum proteins in motor neurons: implications for motor neuron diseases. Neurology. 1987 May;37(5):843–846. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.5.843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]