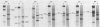Abstract
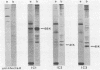
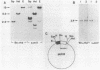
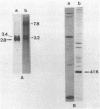
We report that nondividing neuroretina cells from chicken embryos can be induced to proliferate following infection with Rous-associated virus type 1 (RAV-1), an avian lymphomatosis retrovirus lacking transforming genes. Multiplication of RAV-1-infected neuroretina cells is observed after a long latency period and takes place initially in a small number of cells. We also show that serial virus passaging onto fresh neuroretina cultures leads to the generation of novel mitogenic viruses containing the mil oncogene. DNA analysis indicated that RAV-1 is the only provirus detected in cells infected at virus passage 1, whereas neuroretina cells infected at subsequent virus passages harbor mil-containing proviruses. Three viruses, designated IC1, IC2, and IC3, were molecularly cloned. Restriction mapping indicated that in each virus, truncated c-mil sequences were inserted within different portions of the RAV-1 genome. In addition, IC1 and IC2 viruses have transduced novel sequences that belong to the 3' noncoding portion of the c-mil locus. All three viruses induce neuroretina cell multiplication and direct the synthesis of mil-specific proteins. Proliferation of neuroretina cells infected at passage 1 of RAV-1 was not associated with any detectable rearrangement of c-mil, when a v-mil probe was used. However, these cells expressed high levels of an aberrant 2.8-kilobase mRNA hybridizing to mil but not to a long terminal repeat probe. Therefore, transcriptional activation of a portion of c-mil could represent the initial events induced by RAV-1 infection and lead to retroviral transduction of activated c-mil sequences.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bechade C., Calothy G., Pessac B., Martin P., Coll J., Denhez F., Saule S., Ghysdael J., Stéhelin D. Induction of proliferation or transformation of neuroretina cells by the mil and myc viral oncogenes. Nature. 1985 Aug 8;316(6028):559–562. doi: 10.1038/316559a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calothy G., Pessac B. Growth stimulation of chicl embryo neuroretinal cells infected with Rous sarcoma virus: relationship to viral replication and morphological transformation. Virology. 1976 May;71(1):336–345. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90117-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calothy G., Poirier F., Dambrine G., Mignatti P., Combes P., Pessac B. Expression of viral oncogenes in differentiating chick embryo neuroretinal cells infected with avian tumor viruses. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 2):983–990. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coll J., Righi M., Taisne C., Dissous C., Gegonne A., Stehelin D. Molecular cloning of the avian acute transforming retrovirus MH2 reveals a novel cell-derived sequence (v-mil) in addition to the myc oncogene. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2189–2194. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01722.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Combes P. C., Privat A., Pessac B., Calothy G. Differentiation of chick embryo neuroretina cells in monolayer cultures. An ultrastructural study. I. Seven-day retina. Cell Tissue Res. 1977 Dec 13;185(2):159–173. doi: 10.1007/BF00220661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLorbe W. J., Luciw P. A., Goodman H. M., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Molecular cloning and characterization of avian sarcoma virus circular DNA molecules. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):50–61. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.50-61.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhez F., Heimann B., d'Auriol L., Graf T., Coquillaud M., Coll J., Galibert F., Moelling K., Stehelin D., Ghysdael J. Replacement of lys 622 in the ATP binding domain of P100gag-mil abolishes the in vitro autophosphorylation of the protein and the biological properties of the v-mil oncogene of MH2 virus. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):541–546. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02843.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dozier C., Denhez F., Coll J., Amouyel P., Quatannens B., Begue A., Stehelin D., Saule S. Induction of proliferation of neuroretina cells by long terminal repeat activation of the carboxy-terminal part of c-mil. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1995–1998. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H., Poustka A., Murray N. Lambda replacement vectors carrying polylinker sequences. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):827–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung Y. K., Lewis W. G., Crittenden L. B., Kung H. J. Activation of the cellular oncogene c-erbB by LTR insertion: molecular basis for induction of erythroblastosis by avian leukosis virus. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):357–368. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90417-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galibert F., Dupont de Dinechin S., Righi M., Stehelin D. The second oncogene mil of avian retrovirus MH2 is related to the src gene family. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1333–1338. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01972.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross-Bellard M., Oudet P., Chambon P. Isolation of high-molecular-weight DNA from mammalian cells. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 2;36(1):32–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02881.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagino-Yamagishi K., Ikawa S., Kawai S., Hihara H., Yamamoto T., Toyoshima K. Characterization of two strains of avian sarcoma virus isolated from avian lymphatic leukosis virus-induced sarcomas. Virology. 1984 Sep;137(2):266–275. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90218-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward W. S., Neel B. G., Astrin S. M. Activation of a cellular onc gene by promoter insertion in ALV-induced lymphoid leukosis. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):475–480. doi: 10.1038/290475a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hihara H., Yamamoto H., Shimohira H., Arai K., Shimizu T. Avian erythroblastosis virus isolated from chick erythroblastosis induced by lymphatic leukemia virus subgroup A. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1983 May;70(5):891–897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikawa S., Hagino-Yamagishi K., Kawai S., Yamamoto T., Toyoshima K. Activation of the cellular src gene by transducing retrovirus. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2420–2428. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen H. W., Bister K. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the chicken gene c-mil, the progenitor of the retroviral oncogene v-mil. Virology. 1985 Jun;143(2):359–367. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90376-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen H. W., Trachmann C., Bister K. Structural relationship between the chicken protooncogene c-mil and the retroviral oncogene v-mil. Virology. 1984 Aug;137(1):217–224. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kan N. C., Flordellis C. S., Mark G. E., Duesberg P. H., Papas T. S. Nucleotide sequence of avian carcinoma virus MH2: two potential onc genes, one related to avian virus MC29 and the other related to murine sarcoma virus 3611. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3000–3004. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles B. D., Robinson H. L. High-frequency transduction of c-erbB in avian leukosis virus-induced erythroblastosis. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):295–303. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.295-303.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neel B. G., Wang L. H., Mathey-Prevot B., Hanafusa T., Hanafusa H., Hayward W. S. Isolation of 16L virus: a rapidly transforming sarcoma virus from an avian leukosis virus-induced sarcoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):5088–5092. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.5088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizawa M., Goto N., Kawai S. An avian transforming retrovirus isolated from a nephroblastoma that carries the fos gene as the oncogene. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3733–3740. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3733-3740.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patschinsky T., Schroeer B., Bister K. Protein product of proto-oncogene c-mil. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):739–744. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne G. S., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Multiple arrangements of viral DNA and an activated host oncogene in bursal lymphomas. Nature. 1982 Jan 21;295(5846):209–214. doi: 10.1038/295209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pessac B., Calothy G. Transformation of chick embryo neuroretinal cells by Rous sarcoma virus in vitro: induction of cell proliferation. Science. 1974 Aug;185(4152):709–710. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4152.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poirier F., Calothy G., Karess R. E., Erikson E., Hanafusa H. Role of p60src kinase activity in the induction of neuroretinal cell proliferation by rous sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):780–789. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.780-789.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F. Determination of nucleotide sequences in DNA. Science. 1981 Dec 11;214(4526):1205–1210. doi: 10.1126/science.7302589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. E., Tizard R., Gilbert W. Nucleotide sequence of Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):853–869. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90071-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stavnezer E., Gerhard D. S., Binari R. C., Balazs I. Generation of transforming viruses in cultures of chicken fibroblasts infected with an avian leukosis virus. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):920–934. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.920-934.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Hihara H., Nishida T., Kawai S., Toyoshima K. A new avian erythroblastosis virus, AEV-H, carries erbB gene responsible for the induction of both erythroblastosis and sarcomas. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):225–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90153-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]