Abstract
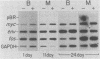
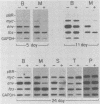
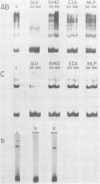
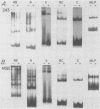
Bursal lymphomas induced by avian leukosis virus (ALV) are characterized by integration of long terminal repeat (LTR) enhancer sequences next to the myc proto-oncogene and by subsequent myc hyperexpression. Nuclear runoff transcription analyses have shown that protein synthesis inhibition specifically decreases transcription of LTR-enhanced genes in bursal lymphoma cell lines (M. Linial, N. Gunderson, and M. Groudine, Science 230:1126-1132, 1985). Here, we show that LTR-enhanced transcription is also labile in nontransformed bursa, bone marrow, and spleen but not in other ALV-infected tissues from lymphoma-susceptible chickens. The bursal cells demonstrated this lability of LTR-enhanced transcription only at an early stage of development, when chickens are susceptible to ALV-induced lymphomagenesis. Mature bursal cells show stable LTR transcription enhancement (unaffected by inhibition of protein synthesis) and are not susceptible to lymphomagenesis. In lymphoma-resistant chicken strains, LTR-enhanced transcription was stable in all tissues during development. These data suggest that lability of LTR transcription enhancement in hematopoietic cells is involved in susceptibility to lymphomagenesis, and we propose a model for the action of these labile enhancing factors. Gel shift analysis of nuclear proteins from lymphoma cells indicated that four or more binding proteins specifically interact with the three LTR enhancer regions. These proteins can be separated by their differential sensitivity to heat treatment or protein synthesis inhibition. The lability of a subset of these binding proteins correlates with lability of LTR-enhanced transcription in certain lymphoid cell types, suggesting that these proteins are essential for LTR transcription enhancement.
Full text
PDF


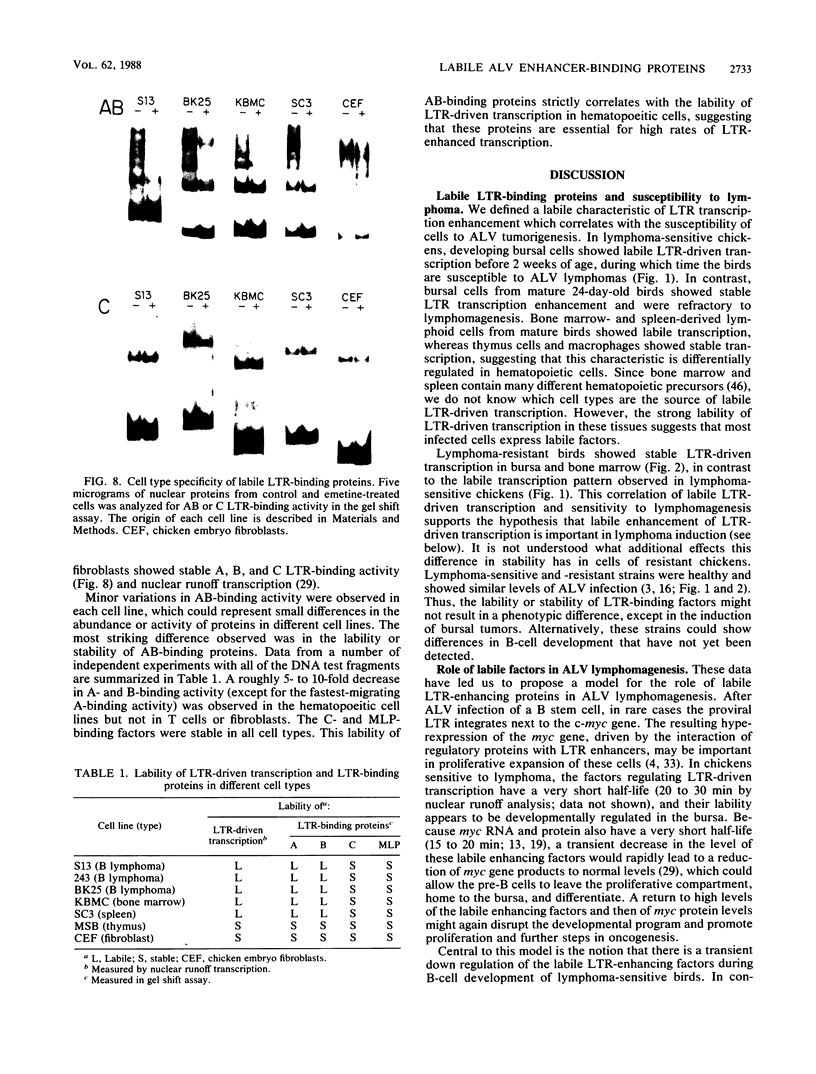


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyama Y., Kato S. Two cell lines from lymphomas of Marek's disease. Biken J. 1974 Sep;17(3):105–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baba T. W., Humphries E. H. Differential response to avian leukosis virus infection exhibited by two chicken lines. Virology. 1984 May;135(1):181–188. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90128-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bister K., Jansen H. W. Oncogenes in retroviruses and cells: biochemistry and molecular genetics. Adv Cancer Res. 1986;47:99–188. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60199-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bizub D., Katz R. A., Skalka A. M. Nucleotide sequence of noncoding regions in Rous-associated virus-2: comparisons delineate conserved regions important in replication and oncogenesis. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):557–565. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.557-565.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carthew R. W., Chodosh L. A., Sharp P. A. An RNA polymerase II transcription factor binds to an upstream element in the adenovirus major late promoter. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. C., Courtneidge S. A., Bishop J. M. Immunological phenotype of lymphomas induced by avian leukosis viruses. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):1077–1085. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.1077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppola J. A., Cole M. D. Constitutive c-myc oncogene expression blocks mouse erythroleukaemia cell differentiation but not commitment. Nature. 1986 Apr 24;320(6064):760–763. doi: 10.1038/320760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crittenden L. B. The epidemiology of avian lymphoid leukosis. Cancer Res. 1976 Feb;36(2 Pt 2):570–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Raymond K., Ju G. Functional analysis of the transcription control region located within the avian retroviral long terminal repeat. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):438–447. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson B. M., Nickol J. M., Jackson P. D., Felsenfeld G. Analysis of the tissue-specific enhancer at the 3' end of the chicken adult beta-globin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4786–4790. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung Y. K., Fadly A. M., Crittenden L. B., Kung H. J. Avian lymphoid leukosis virus infection and DNA integration in the preleukotic bursal tissues: a comparative study of susceptible and resistant lines. Virology. 1982 Jun;119(2):411–421. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90100-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann S. R., Eisenman R. N. Proteins encoded by the human c-myc oncogene: differential expression in neoplastic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2486–2497. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward W. S., Neel B. G., Astrin S. M. Activation of a cellular onc gene by promoter insertion in ALV-induced lymphoid leukosis. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):475–480. doi: 10.1038/290475a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearing P., Shenk T. The adenovirus type 5 E1A transcriptional control region contains a duplicated enhancer element. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):695–703. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hihara H., Shimizu T., Yamamoto H. Establishment of tumor cell lines cultured from chickens with avian lymphoid leukosis. Natl Inst Anim Health Q (Tokyo) 1974 Winter;14(4):163–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., Landschulz W. H., Graves B. J., McKnight S. L. Identification of a rat liver nuclear protein that binds to the enhancer core element of three animal viruses. Genes Dev. 1987 Apr;1(2):133–146. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.2.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Tsichlis P., Khoury G. Multiple enhancer domains in the 3' terminus of the Prague strain of Rous sarcoma virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 24;12(16):6427–6442. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.16.6427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langdon W. Y., Harris A. W., Cory S., Adams J. M. The c-myc oncogene perturbs B lymphocyte development in E-mu-myc transgenic mice. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):11–18. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90361-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. B., McClure J., Rup B., Niesel D. W., Garry R. F., Hoelzer J. D., Nazerian K., Bose H. R., Jr Avian reticuloendotheliosis virus: identification of the hematopoietic target cell for transformation. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):421–431. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90060-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linial M., Groudine M. Transcription of three c-myc exons is enhanced in chicken bursal lymphoma cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):53–57. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linial M., Gunderson N., Groudine M. Enhanced transcription of c-myc in bursal lymphoma cells requires continuous protein synthesis. Science. 1985 Dec 6;230(4730):1126–1132. doi: 10.1126/science.2999973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linial M. Two retroviruses with similar transforming genes exhibit differences in transforming potential. Virology. 1982 Jun;119(2):382–391. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90097-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montminy M. R., Bilezikjian L. M. Binding of a nuclear protein to the cyclic-AMP response element of the somatostatin gene. Nature. 1987 Jul 9;328(6126):175–178. doi: 10.1038/328175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton P. A., Coffin J. M. Characterization of Rous sarcoma virus sequences essential for viral gene expression. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1171–1179. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1171-1179.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pachl C., Schubach W., Eisenman R., Linial M. Expression of c-myc RNA in bursal lymphoma cell lines: identification of c-myc-encoded proteins by hybrid-selected translation. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90415-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne G. S., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Multiple arrangements of viral DNA and an activated host oncogene in bursal lymphomas. Nature. 1982 Jan 21;295(5846):209–214. doi: 10.1038/295209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piette J., Kryszke M. H., Yaniv M. Specific interaction of cellular factors with the B enhancer of polyoma virus. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2675–2685. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03987.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purchase H. G., Gilmour D. G., Romero C. H., Okazaki W. Post-infection genetic resistance to avian lymphoid leukosis resides in B target cell. Nature. 1977 Nov 3;270(5632):61–62. doi: 10.1038/270061a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R., Gander I., Müller U., Mertz R., Winnacker E. L. A sensitive and rapid gel retention assay for nuclear factor I and other DNA-binding proteins in crude nuclear extracts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 11;14(3):1303–1317. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.3.1303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubach W., Groudine M. Alteration of c-myc chromatin structure by avian leukosis virus integration. Nature. 1984 Feb 23;307(5953):702–708. doi: 10.1038/307702a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealey L., Chalkley R. At least two nuclear proteins bind specifically to the Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):787–798. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen-Ong G. L., Keath E. J., Piccoli S. P., Cole M. D. Novel myc oncogene RNA from abortive immunoglobulin-gene recombination in mouse plasmacytomas. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):443–452. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90137-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Hennighausen L., Battey J., Leder P. Chromatin structure and protein binding in the putative regulatory region of the c-myc gene in Burkitt lymphoma. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):381–391. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90368-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taub R., Kirsch I., Morton C., Lenoir G., Swan D., Tronick S., Aaronson S., Leder P. Translocation of the c-myc gene into the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus in human Burkitt lymphoma and murine plasmacytoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7837–7841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt M., Lesley J., Bogenberger J., Volkman S., Haas M. Coinfection with viruses carrying the v-Ha-ras and v-myc oncogenes leads to growth factor independence by an indirect mechanism. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3545–3549. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurm F. M., Gwinn K. A., Kingston R. E. Inducible overproduction of the mouse c-myc protein in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5414–5418. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]