Abstract
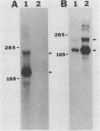
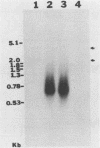
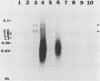
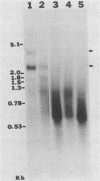
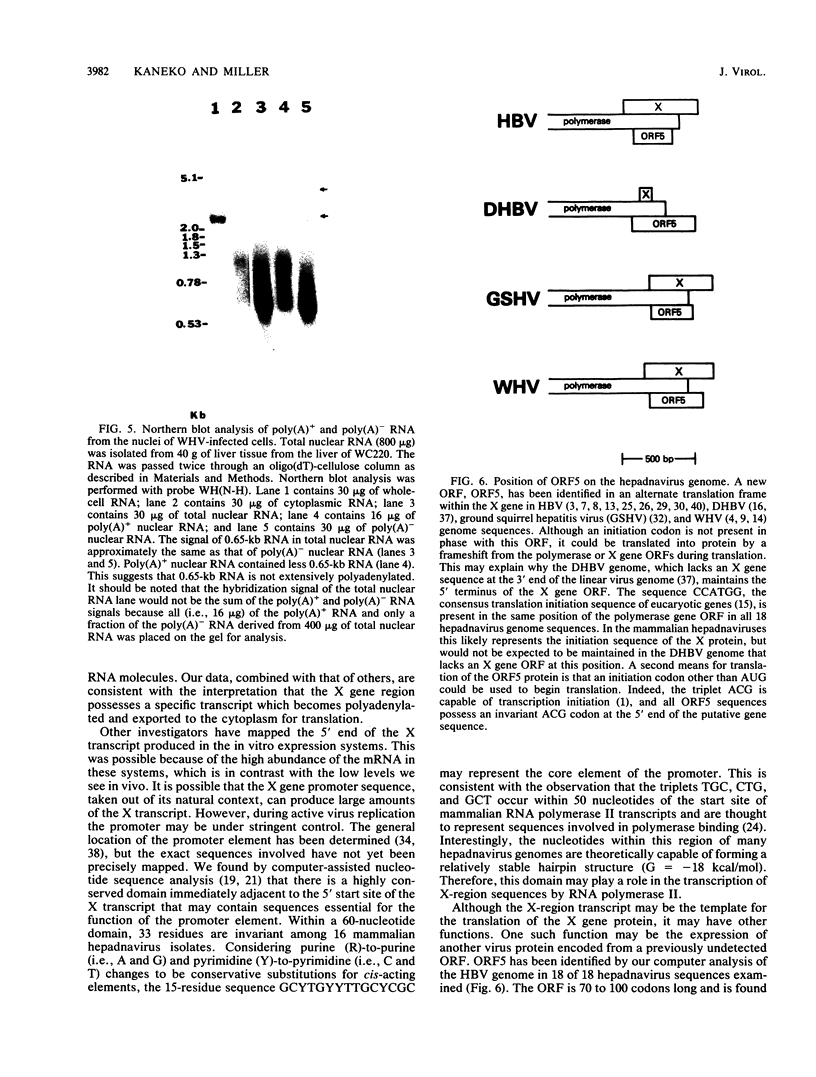
In vitro gene expression systems for hepatitis B virus have demonstrated that the virus genome is capable of producing an X-region-specific transcript of approximately 0.7 kilobases (kb). However, this transcript has not been detected in virus-infected cells. We now report the presence of a heterogeneous X-region-specific transcript of approximately 0.65 kb that is found primarily in the nucleus of liver cells infected with the woodchuck hepatitis virus. Interestingly, the majority of the transcripts are not polyadenylated. The transcript, which represents less than 1% of total virus-specific RNA, is found in animals with both acute and chronic woodchuck hepatitis virus infections. While it is probable that the 0.65-kb transcript is involved in the expression of the X gene protein, it may also direct the translation of a protein encoded by a newly identified open reading frame, ORF5, that is present in all hepadnavirus genomes analyzed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C. W., Buzash-Pollert E. Can ACG serve as an initiation codon for protein synthesis in eucaryotic cells? Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3621–3624. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asselbergs F. A., Will H., Wingfield P., Hirschi M. A recombinant Chinese hamster ovary cell line containing a 300-fold amplified tetramer of the hepatitis B genome together with a double selection marker expresses high levels of viral protein. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jun 5;189(3):401–411. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90312-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bichko V., Pushko P., Dreilina D., Pumpen P., Gren E. Subtype ayw variant of hepatitis B virus. DNA primary structure analysis. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jun 3;185(1):208–212. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80771-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. I., Miller R. H., Rosenblum B., Denniston K., Gerin J. L., Purcell R. H. Sequence comparison of woodchuck hepatitis virus replicative forms shows conservation of the genome. Virology. 1988 Jan;162(1):12–20. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90389-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elfassi E., Haseltine W. A., Dienstag J. L. Detection of hepatitis B virus X product using an open reading frame Escherichia coli expression vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2219–2222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feitelson M. A. Products of the "X" gene in hepatitis B and related viruses. Hepatology. 1986 Mar-Apr;6(2):191–198. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840060207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiyama A., Miyanohara A., Nozaki C., Yoneyama T., Ohtomo N., Matsubara K. Cloning and structural analyses of hepatitis B virus DNAs, subtype adr. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jul 11;11(13):4601–4610. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.13.4601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galibert F., Chen T. N., Mandart E. Nucleotide sequence of a cloned woodchuck hepatitis virus genome: comparison with the hepatitis B virus sequence. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):51–65. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.51-65.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galibert F., Mandart E., Fitoussi F., Tiollais P., Charnay P. Nucleotide sequence of the hepatitis B virus genome (subtype ayw) cloned in E. coli. Nature. 1979 Oct 25;281(5733):646–650. doi: 10.1038/281646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gan R. B., Chu M. J., Shen L. P., Qian S. W., Li Z. P. The complete nucleotide sequence of the cloned DNA of hepatitis B virus subtype adr in pADR-1. Sci Sin B. 1987 May;30(5):507–521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough N. M. Core and E antigen synthesis in rodent cells transformed with hepatitis B virus DNA is associated with greater than genome length viral messenger RNAs. J Mol Biol. 1983 Apr 25;165(4):683–699. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80274-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imazeki F., Yaginuma K., Omata M., Okuda K., Kobayashi M., Koike K. RNA transcripts of hepatitis B virus in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 1987 Jul-Aug;7(4):753–757. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840070423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay A., Mandart E., Trepo C., Galibert F. The HBV HBX gene expressed in E. coli is recognised by sera from hepatitis patients. EMBO J. 1985 May;4(5):1287–1292. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03774.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi M., Koike K. Complete nucleotide sequence of hepatitis B virus DNA of subtype adr and its conserved gene organization. Gene. 1984 Oct;30(1-3):227–232. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90124-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodama K., Ogasawara N., Yoshikawa H., Murakami S. Nucleotide sequence of a cloned woodchuck hepatitis virus genome: evolutional relationship between hepadnaviruses. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):978–986. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.978-986.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Regulation of protein synthesis in virus-infected animal cells. Adv Virus Res. 1986;31:229–292. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3527(08)60265-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandart E., Kay A., Galibert F. Nucleotide sequence of a cloned duck hepatitis B virus genome: comparison with woodchuck and human hepatitis B virus sequences. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):782–792. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.782-792.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers M. L., Trepo L. V., Nath N., Sninsky J. J. Hepatitis B virus polypeptide X: expression in Escherichia coli and identification of specific antibodies in sera from hepatitis B virus-infected humans. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):101–109. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.101-109.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. H. Human immunodeficiency virus may encode a novel protein on the genomic DNA plus strand. Science. 1988 Mar 18;239(4846):1420–1422. doi: 10.1126/science.3347840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. H., Robinson W. S. Common evolutionary origin of hepatitis B virus and retroviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2531–2535. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. H., Robinson W. S. Hepatitis B virus DNA forms in nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions of infected human liver. Virology. 1984 Sep;137(2):390–399. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90231-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriarty A. M., Alexander H., Lerner R. A., Thornton G. B. Antibodies to peptides detect new hepatitis B antigen: serological correlation with hepatocellular carcinoma. Science. 1985 Jan 25;227(4685):429–433. doi: 10.1126/science.2981434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möröy T., Etiemble J., Trépo C., Tiollais P., Buendia M. A. Transcription of woodchuck hepatitis virus in the chronically infected liver. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1507–1514. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03810.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussinov R., Owens J., Maizel J. V., Jr Sequence signals in eukaryotic upstream regions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Mar 26;866(2-3):109–119. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(86)90107-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Imai M., Shimozaki M., Hoshi Y., Iizuka H., Gotanda T., Tsuda F., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. Nucleotide sequence of a cloned hepatitis B virus genome, subtype ayr: comparison with genomes of the other three subtypes. J Gen Virol. 1986 Nov;67(Pt 11):2305–2314. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-11-2305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y., Onda H., Sasada R., Igarashi K., Sugino Y., Nishioka K. The complete nucleotide sequences of the cloned hepatitis B virus DNA; subtype adr and adw. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1747–1757. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaff E., Salfeld J., Gmelin K., Schaller H., Theilmann L. Synthesis of the X-protein of hepatitis B virus in vitro and detection of anti-X antibodies in human sera. Virology. 1987 Jun;158(2):456–460. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90221-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popper H., Roth L., Purcell R. H., Tennant B. C., Gerin J. L. Hepatocarcinogenicity of the woodchuck hepatitis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):866–870. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh J. C., Weber C., Houston H., Murray K. Expression of the X gene of hepatitis B virus. J Med Virol. 1986 Nov;20(3):229–246. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890200305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito I., Oya Y., Shimojo H. Novel RNA family structure of hepatitis B virus expressed in human cells, using a helper-free adenovirus vector. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):554–560. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.554-560.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeger C., Ganem D., Varmus H. E. Nucleotide sequence of an infectious molecularly cloned genome of ground squirrel hepatitis virus. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):367–375. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.367-375.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui A., Jameel S., Mapoles J. Expression of the hepatitis B virus X gene in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2513–2517. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui A., Jameel S., Mapoles J. Transcriptional control elements of hepatitis B surface antigen gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):566–570. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonsen C. C., Levinson A. D. Analysis of processing and polyadenylation signals of the hepatitis B virus surface antigen gene by using simian virus 40-hepatitis B virus chimeric plasmids. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;3(12):2250–2258. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.12.2250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spandau D. F., Lee C. H. trans-activation of viral enhancers by the hepatitis B virus X protein. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):427–434. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.427-434.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprengel R., Kuhn C., Will H., Schaller H. Comparative sequence analysis of duck and human hepatitis B virus genomes. J Med Virol. 1985 Apr;15(4):323–333. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890150402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treinin M., Laub O. Identification of a promoter element located upstream from the hepatitis B virus X gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):545–548. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twu J. S., Schloemer R. H. Transcriptional trans-activating function of hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3448–3453. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3448-3453.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Will H., Kuhn C., Cattaneo R., Schaller H. Structure and function of the hepatitis B virus genome. Princess Takamatsu Symp. 1982;12:237–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Y. Z., Butel J. S., Li P. J., Finegold M. J., Melnick J. L. Integrated state of subgenomic fragments of hepatitis B virus DNA in hepatocellular carcinoma from mainland China. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1987 Aug;79(2):223–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]