Abstract
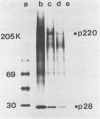
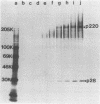
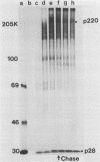
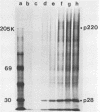
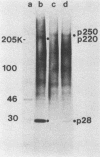
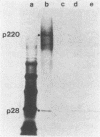
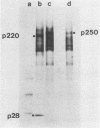
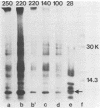
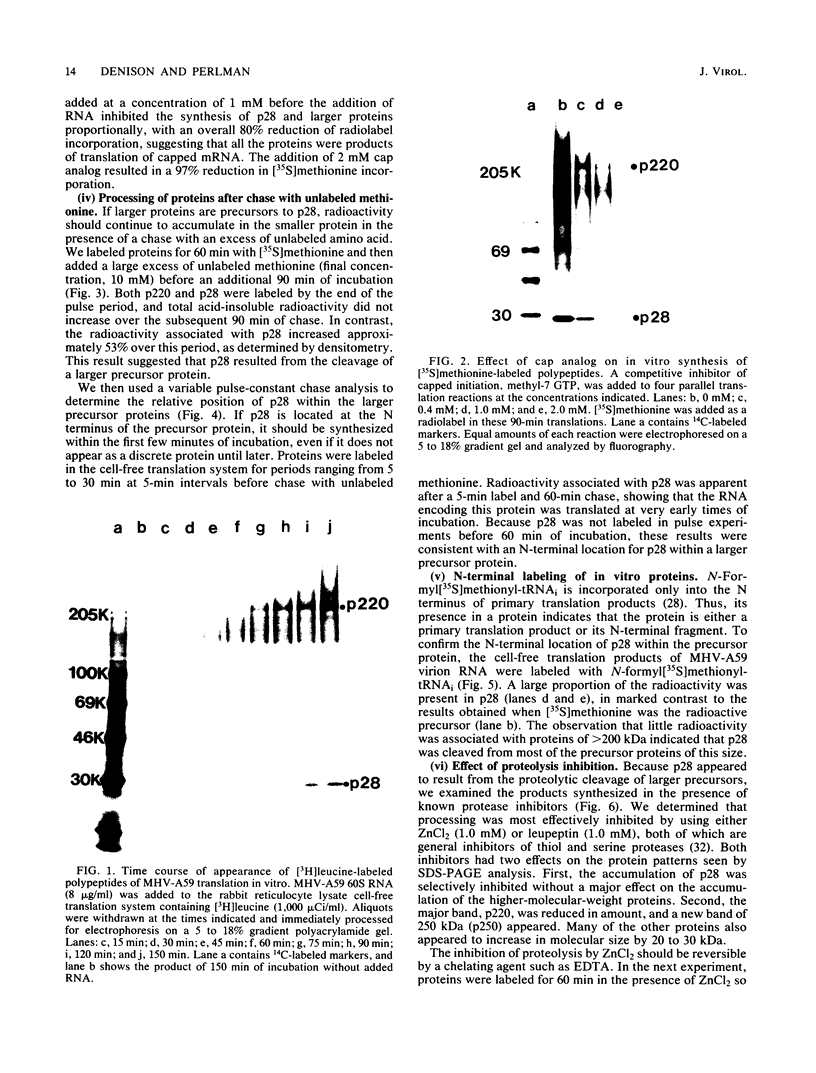
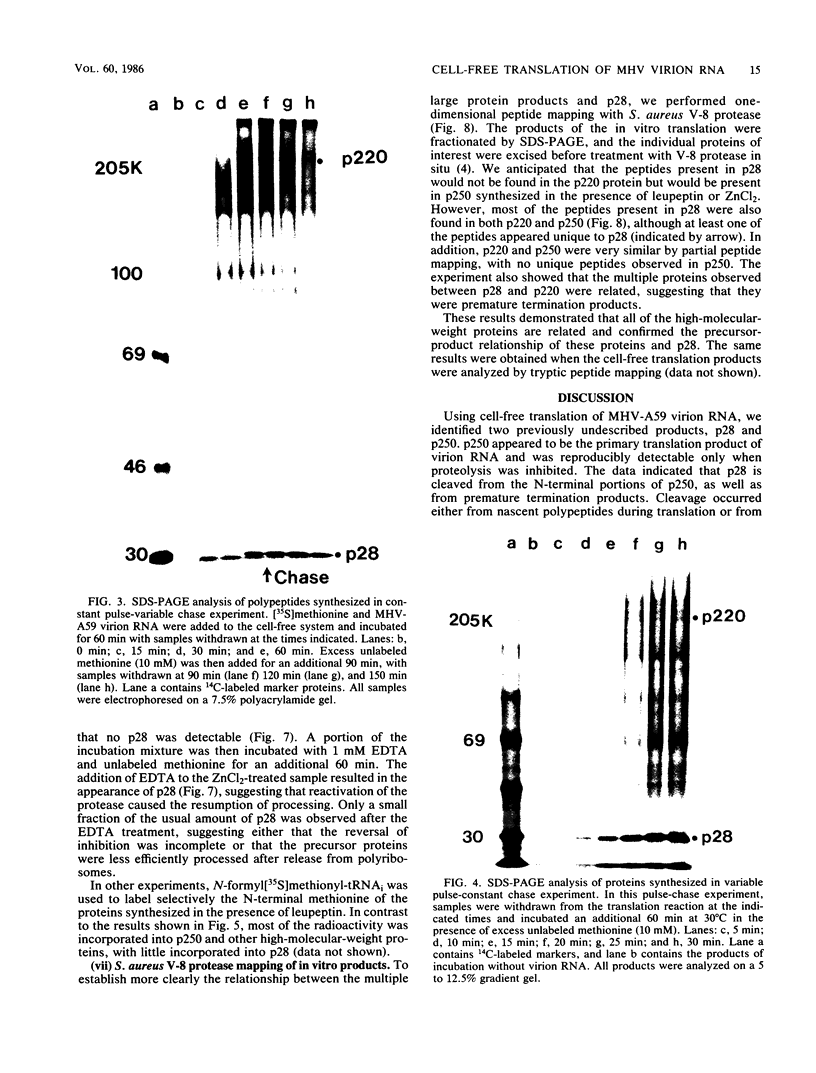
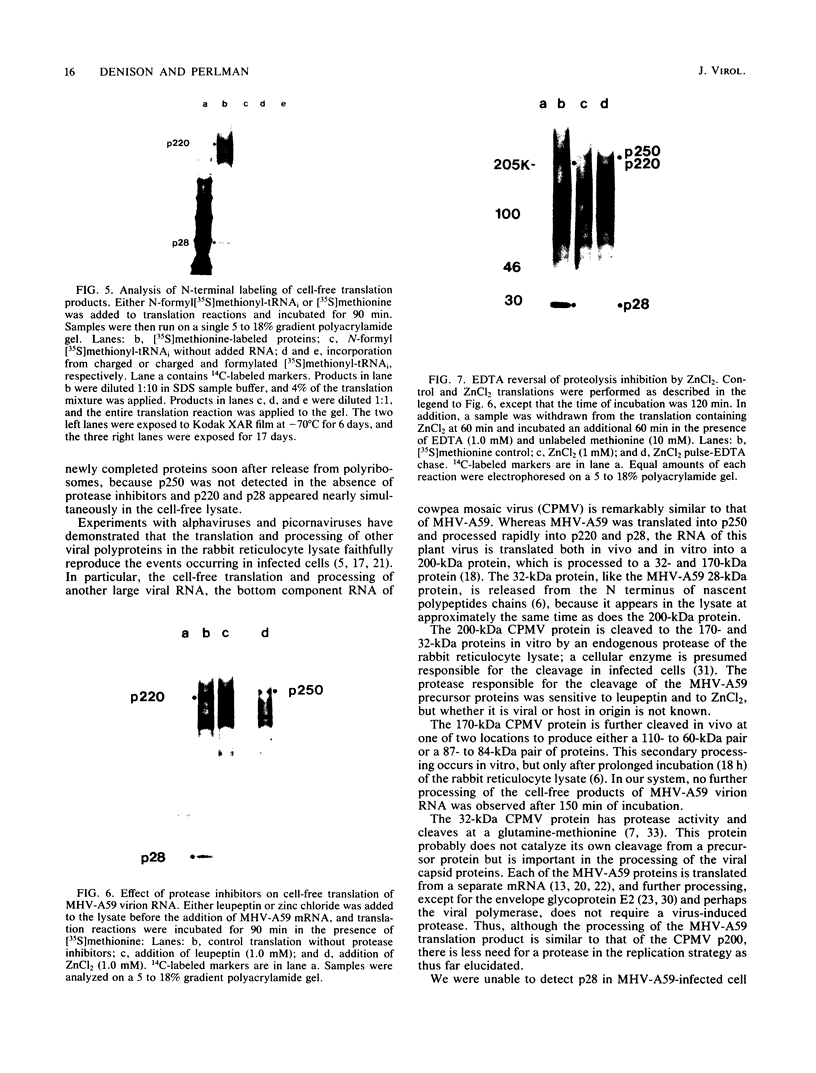
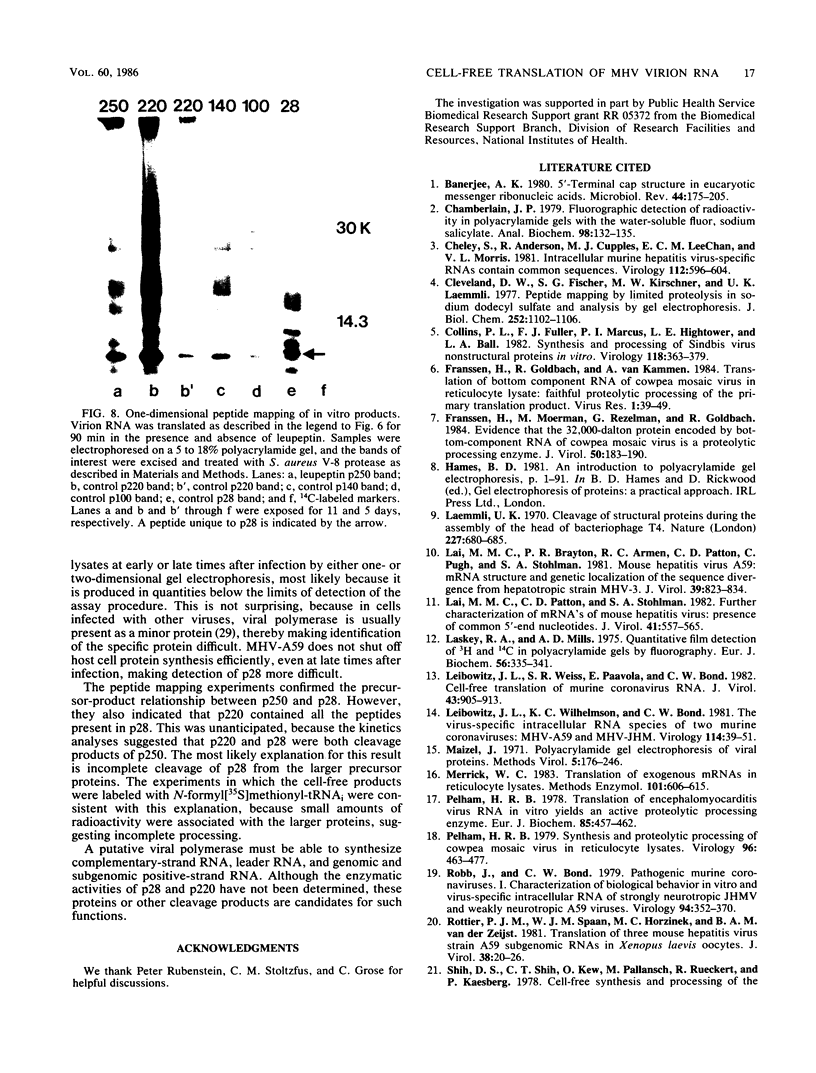
The first event after infection with mouse hepatitis virus strain A59 (MHV-A59) is presumed to be the synthesis of an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from the input genomic RNA. The synthesis and processing of this putative polymerase protein was studied in a cell-free translation system utilizing 60S RNA from MHV-A59 virions. The polypeptide products of this reaction included two major species of 220 and 28 kilodaltons. Kinetics experiments indicated that both p220 and p28 appeared after 60 min of incubation and that protein p28 was synthesized initially as the N-terminal portion of a larger precursor protein. When the cell-free translation products were labeled with N-formyl[35S]methionyl-tRNAi, p28 was the predominant radioactive product, confirming its N-terminal location within a precursor protein. Translation in the presence of the protease inhibitors leupeptin and ZnCl2 resulted in the disappearance of p28 and p220 and the appearance of a new protein, p250. This product, which approached the maximal size predicted for a protein synthesized from genomic RNA, was not routinely detected in the absence of inhibitors even under conditions which optimized the translation reaction for elongation of proteins. Subsequent chelation of ZnCl2 resulted in the partial cleavage of the precursor protein and the reappearance of p28. One-dimensional peptide mapping with Staphylococcus aureus V-8 protease confirmed the precursor-product relationship of p250 and p28. The results show that MHV virion RNA, like many other viral RNAs, is translated into a large polyprotein, which is cleaved soon after synthesis into smaller, presumably functional proteins. This is in marked contrast to the synthesis of other MHV proteins, in which minimal proteolytic processing occurs.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banerjee A. K. 5'-terminal cap structure in eucaryotic messenger ribonucleic acids. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Jun;44(2):175–205. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.2.175-205.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. P. Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with the water-soluble fluor, sodium salicylate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):132–135. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90716-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheley S., Anderson R., Cupples M. J., Chan E. C., Morris V. L. Intracellular murine hepatitis virus-specific RNAs contain common sequences. Virology. 1981 Jul 30;112(2):596–604. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90305-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins P. L., Fuller F. J., Marcus P. I., Hightower L. E., Ball L. A. Synthesis and processing of Sindbis virus nonstructural proteins in vitro. Virology. 1982 Apr 30;118(2):363–379. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90356-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franssen H., Moerman M., Rezelman G., Goldbach R. Evidence That the 32,000-Dalton Protein Encoded by Bottom-Component RNA of Cowpea Mosaic Virus is a Proteolytic Processing Enzyme. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):183–190. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.183-190.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M., Brayton P. R., Armen R. C., Patton C. D., Pugh C., Stohlman S. A. Mouse hepatitis virus A59: mRNA structure and genetic localization of the sequence divergence from hepatotropic strain MHV-3. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):823–834. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.823-834.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M., Patton C. D., Stohlman S. A. Further characterization of mRNA's of mouse hepatitis virus: presence of common 5'-end nucleotides. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):557–565. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.557-565.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibowitz J. L., Weiss S. R., Paavola E., Bond C. W. Cell-free translation of murine coronavirus RNA. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):905–913. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.905-913.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibowitz J. L., Wilhelmsen K. C., Bond C. W. The virus-specific intracellular RNA species of two murine coronaviruses: MHV-a59 and MHV-JHM. Virology. 1981 Oct 15;114(1):39–51. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90250-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrick W. C. Translation of exogenous mRNAs in reticulocyte lysates. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:606–615. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01041-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Synthesis and proteolytic processing of cowpea mosaic virus proteins in reticulocyte lysates. Virology. 1979 Jul 30;96(2):463–477. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90104-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Translation of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA in vitro yields an active proteolytic processing enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Apr 17;85(2):457–462. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12260.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb J. A., Bond C. W. Pathogenic murine coronaviruses. I. Characterization of biological behavior in vitro and virus-specific intracellular RNA of strongly neurotropic JHMV and weakly neurotropic A59V viruses. Virology. 1979 Apr 30;94(2):352–370. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90467-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottier P. J., Spaan W. J., Horzinek M. C., van der Zeijst B. A. Translation of three mouse hepatitis virus strain A59 subgenomic RNAs in Xenopus laevis oocytes. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):20–26. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.20-26.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih D. S., Shih C. T., Kew O., Pallansch M., Rueckert R., Kaesberg P. Cell-free synthesis and processing of the proteins of poliovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5807–5811. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddell S. Coronavirus JHM: coding assignments of subgenomic mRNAs. J Gen Virol. 1983 Jan;64(Pt 1):113–125. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-1-113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddell S., Wege H., Ter Meulen V. The biology of coronaviruses. J Gen Virol. 1983 Apr;64(Pt 4):761–776. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-4-761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner M. A., Ebner D., Siddell S. G. Coronavirus MHV-JHM mRNA 5 has a sequence arrangement which potentially allows translation of a second, downstream open reading frame. J Gen Virol. 1985 Mar;66(Pt 3):581–592. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-3-581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner M. A., Siddell S. G. Coding sequence of coronavirus MHV-JHM mRNA 4. J Gen Virol. 1985 Mar;66(Pt 3):593–596. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-3-593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaan W. J., Rottier P. J., Horzinek M. C., van der Zeijst B. A. Isolation and identification of virus-specific mRNAs in cells infected with mouse hepatitis virus (MHV-A59). Virology. 1981 Jan 30;108(2):424–434. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90449-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaan W. J., Rottier P. J., Horzinek M. C., van der Zeijst B. A. Sequence relationships between the genome and the intracellular RNA species 1, 3, 6, and 7 of mouse hepatitis virus strain A59. J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):432–439. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.432-439.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley W. M., Jr Specific aminoacylation of the methionine-specific tRNA's of eukaryotes. Methods Enzymol. 1974;29:530–547. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)29049-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss E. G., Strauss J. H. Replication strategies of the single stranded RNA viruses of eukaryotes. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1983;105:1–98. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-69159-1_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturman L. S., Holmes K. V. The molecular biology of coronaviruses. Adv Virus Res. 1983;28:35–112. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3527(08)60721-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian Y. C., Shih D. S. Cleavage of a viral polyprotein by a cellular proteolytic activity. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):547–551. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.547-551.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezawa H. Low-molecular-weight enzyme inhibitors of microbial origin. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1982;36:75–99. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.36.100182.000451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Wezenbeek P., Verver J., Harmsen J., Vos P., van Kammen A. Primary structure and gene organization of the middle-component RNA of cowpea mosaic virus. EMBO J. 1983;2(6):941–946. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01525.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]