Abstract
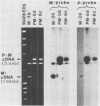
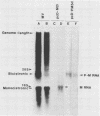
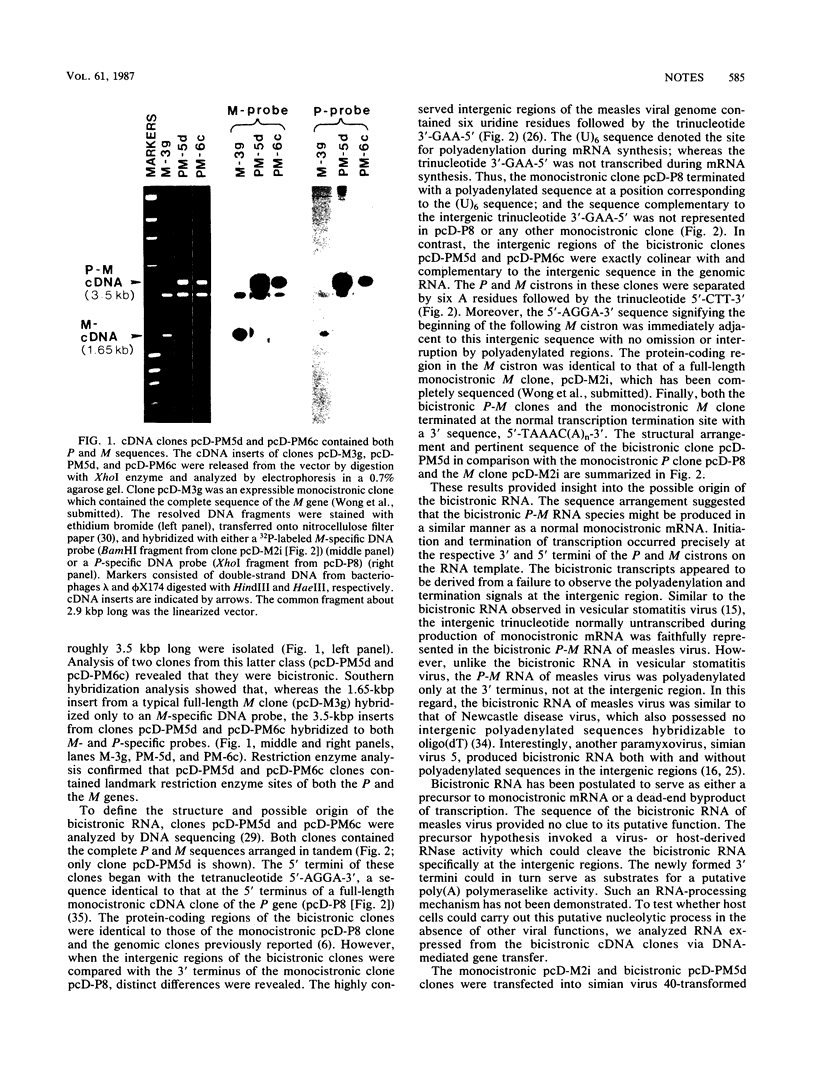
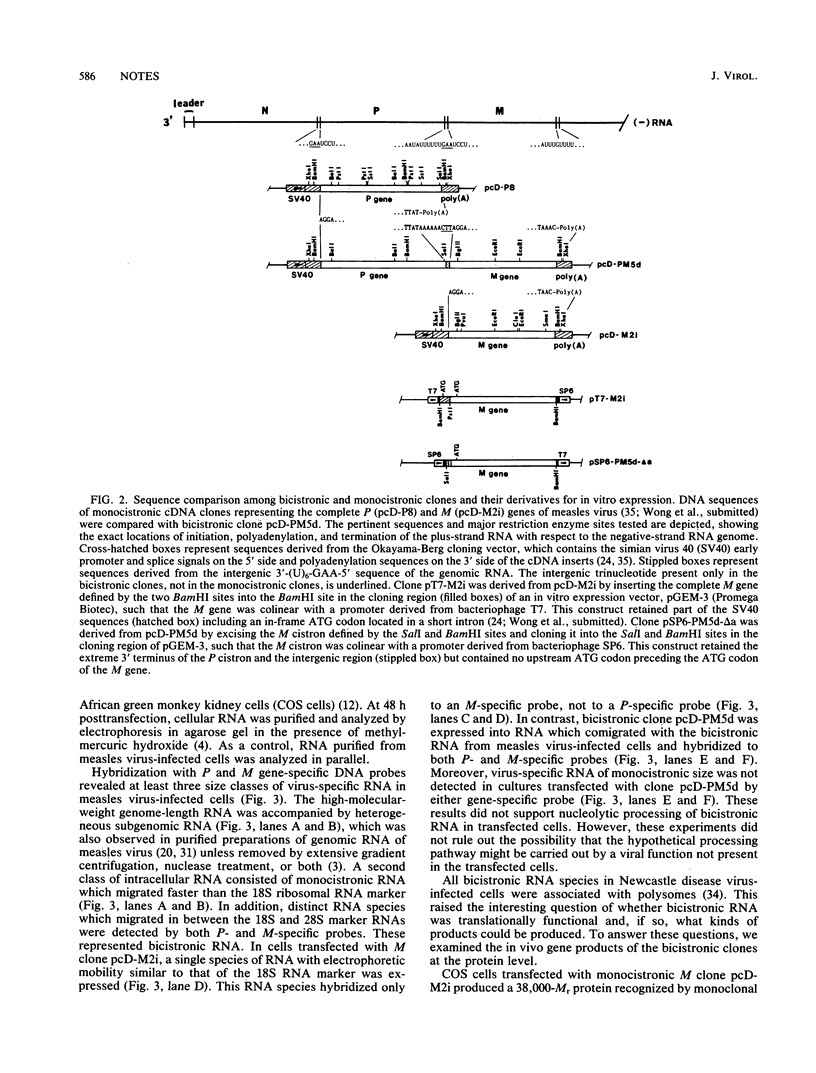
Two independent full-length replicas of a bicistronic RNA species containing the complete P and M genes of measles virus arranged in tandem were isolated from an expressible cDNA library. Sequences at the 5' and 3' termini suggested that the bicistronic RNA was initiated and terminated at precisely the same locations as the monocistronic mRNAs of the P and M genes, respectively. The P and M cistrons were fused together via an intergenic region which was exactly colinear with and complementary to the intergenic region of the genomic RNA. This RNA species was polyadenylated at the normal polyadenylation site at the 3' terminus of the M cistron, but not in the intergenic region. By DNA-mediated gene transfer, these cDNA clones were expressed into bicistronic RNA containing both P and M sequences in primate cells. RNA thus generated did not undergo nucleolytic processing but was translated into high levels of a 70,000-Mr protein immunoprecipitated by monoclonal antiserum against the measles virus P protein. M protein was not produced in the same cells even though the M cistron could direct M protein synthesis in vitro once excised from the upstream P cistron. These results suggested that bicistronic RNA could direct protein synthesis from the first but not the second cistron and might contribute at least in part to expression of viral genes in vivo.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham G., Banerjee A. K. Sequential transcription of the genes of vesicular stomatitis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1504–1508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alkhatib G., Briedis D. J. The predicted primary structure of the measles virus hemagglutinin. Virology. 1986 Apr 30;150(2):479–490. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90312-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baczko K., Billeter M., ter Meulen V. Purification and molecular weight determination of measles virus genomic RNA. J Gen Virol. 1983 Jun;64(Pt 6):1409–1413. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-6-1409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey J. M., Davidson N. Methylmercury as a reversible denaturing agent for agarose gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellini W. J., Englund G., Richardson C. D., Rozenblatt S., Lazzarini R. A. Matrix genes of measles virus and canine distemper virus: cloning, nucleotide sequences, and deduced amino acid sequences. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):408–416. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.408-416.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellini W. J., Englund G., Rozenblatt S., Arnheiter H., Richardson C. D. Measles virus P gene codes for two proteins. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):908–919. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.908-919.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billeter M. A., Baczko K., Schmid A., Ter Meulen V. Cloning of DNA corresponding to four different measles virus genomic regions. Virology. 1984 Jan 15;132(1):147–159. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90099-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohn W., Rutter G., Mannweiler K. Production of monoclonal antibodies to measles virus proteins by immunization of mice with heated and detergent-treated antigens. Virology. 1982 Jan 15;116(1):368–371. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90430-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins P. L., Wertz G. W. cDNA cloning and transcriptional mapping of nine polyadenylylated RNAs encoded by the genome of human respiratory syncytial virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3208–3212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall W. W., Kiessling W., ter Meulen V. Membrane proteins of subacute sclerosing panencephalitis and measles viruses. Nature. 1978 Mar 30;272(5652):460–462. doi: 10.1038/272460a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman R. C., Adler S., Lazzarini R. A., Colonno R. J., Banerjee A. K., Westphal H. Intervening polyadenylate sequences in RNA transcripts of vesicular stomatitis virus. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):587–596. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90027-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman R. C., Schubert M., Keene J. D., Lazzarini R. A. Polycistronic vesicular stomatitis virus RNA transcripts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4662–4665. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiebert S. W., Paterson R. G., Lamb R. A. Hemagglutinin-neuraminidase protein of the paramyxovirus simian virus 5: nucleotide sequence of the mRNA predicts an N-terminal membrane anchor. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):1–6. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.1-6.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Melton D. A. Functional messenger RNAs are produced by SP6 in vitro transcription of cloned cDNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7057–7070. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund G. A., Tyrrell D. L., Bradley R. D., Scraba D. G. The molecular length of measles virus RNA and the structural organization of measles nucleocapsids. J Gen Virol. 1984 Sep;65(Pt 9):1535–1542. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-9-1535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby E., Chen S. N., Togashi T., Shesberadaran H., Johnson K. P. Five measles virus antigens demonstrated by use of mouse hybridoma antibodies in productively infected tissue culture cells. Arch Virol. 1982;71(1):1–11. doi: 10.1007/BF01315171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. A cDNA cloning vector that permits expression of cDNA inserts in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):280–289. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson R. G., Harris T. J., Lamb R. A. Fusion protein of the paramyxovirus simian virus 5: nucleotide sequence of mRNA predicts a highly hydrophobic glycoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6706–6710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson C. D., Berkovich A., Rozenblatt S., Bellini W. J. Use of antibodies directed against synthetic peptides for identifying cDNA clones, establishing reading frames, and deducing the gene order of measles virus. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):186–193. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.186-193.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozenblatt S., Eizenberg O., Ben-Levy R., Lavie V., Bellini W. J. Sequence homology within the morbilliviruses. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):684–690. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.684-690.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozenblatt S., Gesang C., Lavie V., Neumann F. S. Cloning and characterization of DNA complementary to the measles virus mRNA encoding hemagglutinin and matrix protein. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):790–797. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.790-797.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson J. R., ter Meulen V. A comparative analysis of measles virus RNA by oligonucleotide fingerprinting. Arch Virol. 1982;71(4):279–290. doi: 10.1007/BF01315058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R., Urlaub G., Chasin L. DNA-mediated transfer of the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase locus into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1373–1376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilde A., Morrison T. Structural and functional characterization of Newcastle disease virus polycistronic RNA species. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):71–76. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.71-76.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong T. C., Hirano A. Functional cDNA library for efficient expression of measles virus-specific gene products in primate cells. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):343–348. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.343-348.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]