Abstract
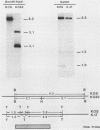
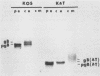
To study the effects of missense, nonsense, and deletion mutations of the gB glycoprotein gene of herpes simplex virus type 1, a gB-transformed cell line was isolated that, after virus infection, would express sufficient quantities of gB from the cellular chromosome to complement temperature-sensitive gB mutants. The transformed cell line was then used as a permissive cell to transfer two gB mutations from plasmid to viral DNA. One of the mutants, K082, harbored an HpaI linker insertion that introduced one new amino acid and a chain terminator codon within amino acid residue 43. The other mutant contained a 969-base-pair deletion in a part of the gene that includes the membrane-spanning region; a correspondingly shorter gB polypeptide was detected by sodium dodecyl sulfate-gel electrophoresis after immunoprecipitation of infected-cell extracts with four pooled monoclonal antibodies. No polypeptide was observed from K082-infected cells. The shortened gB polypeptide was efficiently processed and secreted into the growth medium. Each of the four monoclonal antibodies precipitated full-length gB, and three of the four precipitated the shortened polypeptide. Enveloped virus particles could be purified after infection of nonpermissive cells with either mutant virus. Virus particles appeared to possess normal polypeptide and glycopeptide profiles except for the absence of gB. Therefore, the presence of gB is not essential for viral assembly, including envelopment. Recombinants in virus stocks grown on the gB-transformed cells occurred at frequencies on the order of 10(-7) to 10(-5), compared with a frequency of approximately 10(-2) in mixed infections with the two mutants.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arsenakis M., Tomasi L. F., Speziali V., Roizman B., Campadelli-Fiume G. Expression and regulation of glycoprotein C gene of herpes simplex virus 1 resident in a clonal L-cell line. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):367–376. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.367-376.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin T. L. Host range mutants of polyoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):394–399. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckmaster E. A., Gompels U., Minson A. Characterisation and physical mapping of an HSV-1 glycoprotein of approximately 115 X 10(3) molecular weight. Virology. 1984 Dec;139(2):408–413. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90387-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bzik D. J., Fox B. A., DeLuca N. A., Person S. Nucleotide sequence of a region of the herpes simplex virus type 1 gB glycoprotein gene: mutations affecting rate of virus entry and cell fusion. Virology. 1984 Aug;137(1):185–190. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90022-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bzik D. J., Fox B. A., DeLuca N. A., Person S. Nucleotide sequence specifying the glycoprotein gene, gB, of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1984 Mar;133(2):301–314. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90397-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cepko C. L., Roberts B. E., Mulligan R. C. Construction and applications of a highly transmissible murine retrovirus shuttle vector. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1053–1062. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90440-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson I., Stow N. D. Expression of an immediate early polypeptide and activation of a viral origin of DNA replication in cells containing a fragment of herpes simplex virus DNA. Virology. 1985 Feb;141(1):77–88. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90184-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca N. A., McCarthy A. M., Schaffer P. A. Isolation and characterization of deletion mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1 in the gene encoding immediate-early regulatory protein ICP4. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):558–570. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.558-570.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca N., Bzik D. J., Bond V. C., Person S., Snipes W. Nucleotide sequences of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) affecting virus entry, cell fusion, and production of glycoprotein gb (VP7). Virology. 1982 Oct 30;122(2):411–423. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90240-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca N., Person S., Bzik D. J., Snipes W. Genome locations of temperature-sensitive mutants in glycoprotein gB of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1984 Sep;137(2):382–389. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90230-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldin A. L., Sandri-Goldin R. M., Levine M., Glorioso J. C. Cloning of herpes simplex virus type 1 sequences representing the whole genome. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):50–58. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.50-58.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S., Anderson R. G., Russell D. W., Schneider W. J. Receptor-mediated endocytosis: concepts emerging from the LDL receptor system. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:1–39. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Smiley J., Russell W. C., Nairn R. Characteristics of a human cell line transformed by DNA from human adenovirus type 5. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jul;36(1):59–74. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heine J. W., Honess R. W., Cassai E., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. XII. The virion polypeptides of type 1 strains. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):640–651. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.640-651.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland T. C., Marlin S. D., Levine M., Glorioso J. Antigenic variants of herpes simplex virus selected with glycoprotein-specific monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):672–682. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.672-682.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kousoulas K. G., Pellett P. E., Pereira L., Roizman B. Mutations affecting conformation or sequence of neutralizing epitopes identified by reactivity of viable plaques segregate from syn and ts domains of HSV-1(F) gB gene. Virology. 1984 Jun;135(2):379–394. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90194-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little S. P., Jofre J. T., Courtney R. J., Schaffer P. A. A virion-associated glycoprotein essential for infectivity of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1981 Nov;115(1):149–160. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90097-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longnecker R., Roizman B. Generation of an inverting herpes simplex virus 1 mutant lacking the L-S junction a sequences, an origin of DNA synthesis, and several genes including those specifying glycoprotein E and the alpha 47 gene. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):583–591. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.583-591.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manservigi R., Spear P. G., Buchan A. Cell fusion induced by herpes simplex virus is promoted and suppressed by different viral glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3913–3917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marlin S. D., Highlander S. L., Holland T. C., Levine M., Glorioso J. C. Antigenic variation (mar mutations) in herpes simplex virus glycoprotein B can induce temperature-dependent alterations in gB processing and virus production. J Virol. 1986 Jul;59(1):142–153. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.1.142-153.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dolan A., Donald S., Rixon F. J. Sequence determination and genetic content of the short unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jan 5;181(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90320-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minson A. C., Wildy P., Buchan A., Darby G. Introduction of the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene into mouse cells using virus DNA or transformed cell DNA. Cell. 1978 Mar;13(3):581–587. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90331-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellett P. E., Kousoulas K. G., Pereira L., Roizman B. Anatomy of the herpes simplex virus 1 strain F glycoprotein B gene: primary sequence and predicted protein structure of the wild type and of monoclonal antibody-resistant mutants. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):243–253. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.243-253.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira L., Dondero D., Roizman B. Herpes simplex virus glycoprotein gA/B: evidence that the infected Vero cell products comap and arise by proteolysis. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):88–97. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.88-97.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Person S., Knowles R. W., Read G. S., Warner S. C., Bond V. C. Kinetics of cell fusion induced by a syncytia-producing mutant of herpes simplex virus type I. J Virol. 1975 Jan;17(1):183–190. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.1.183-190.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman D. D., Buckmaster A., Bell S., Hodgman C., Minson A. C. Identification of a new glycoprotein of herpes simplex virus type 1 and genetic mapping of the gene that codes for it. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):647–655. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.647-655.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roizman B., Norrild B., Chan C., Pereira L. Identification and preliminary mapping with monoclonal antibodies of a herpes simplex virus 2 glycoprotein lacking a known type 1 counterpart. Virology. 1984 Feb;133(1):242–247. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90447-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandri-Goldin R. M., Goldin A. L., Holland L. E., Glorioso J. C., Levine M. Expression of herpes simplex virus beta and gamma genes integrated in mammalian cells and their induction by an alpha gene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;3(11):2028–2044. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.11.2028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarmiento M., Haffey M., Spear P. G. Membrane proteins specified by herpes simplex viruses. III. Role of glycoprotein VP7(B2) in virion infectivity. J Virol. 1979 Mar;29(3):1149–1158. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.3.1149-1158.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffer P. A., Aron G. M., Biswal N., Benyesh-Melnick M. Temperature-sensitive mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1: isolation, complementation and partial characterization. Virology. 1973 Mar;52(1):57–71. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90398-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffer P. A., Carter V. C., Timbury M. C. Collaborative complementation study of temperature-sensitive mutants of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. J Virol. 1978 Sep;27(3):490–504. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.3.490-504.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., McMonagle E. C., Davison A. J. Fragments from both termini of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome contain signals required for the encapsidation of viral DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Dec 10;11(23):8205–8220. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.23.8205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Translocation of proteins across the endoplasmic reticulum III. Signal recognition protein (SRP) causes signal sequence-dependent and site-specific arrest of chain elongation that is released by microsomal membranes. J Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;91(2 Pt 1):557–561. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.2.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Sweet R., Sim G. K., Wold B., Pellicer A., Lacy E., Maniatis T., Silverstein S., Axel R. Transformation of mammalian cells with genes from procaryotes and eucaryotes. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):777–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Bishop R. W., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Russell D. W. Deletion in cysteine-rich region of LDL receptor impedes transport to cell surface in WHHL rabbit. Science. 1986 Jun 6;232(4755):1230–1237. doi: 10.1126/science.3010466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]