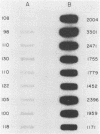
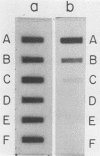
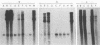
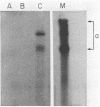
Abstract
We investigated the helper-independent replication of adeno-associated virus (AAV) in cells synchronized by pretreatment with hydroxyurea, reversal of polyamine depletion, or physical mitotic detachment. In Chinese hamster cells (OD4 line) treated with hydroxyurea prior to infection. AAV underwent a complete cycle of replication. Transfection of such cells with plasmid-cloned AAV DNAs also gave rise to infectious viral progeny. Synchronization of OD4 cells by reversal of polyamine depletion or mitotic detachment led to independent AAV DNA synthesis (and infectious viral progeny in the case of the former procedure), but these procedures were not as effective as hydroxyurea pretreatment. Independent AAV DNA synthesis was also detected in some other cell lines of Chinese hamster, human, and monkey origin treated with hydroxyurea prior to infection. The results demonstrate that, in contrast to previous notions, the AAV infectious process is not absolutely dependent upon the addition of a coinfecting helper virus.
Full text
PDF



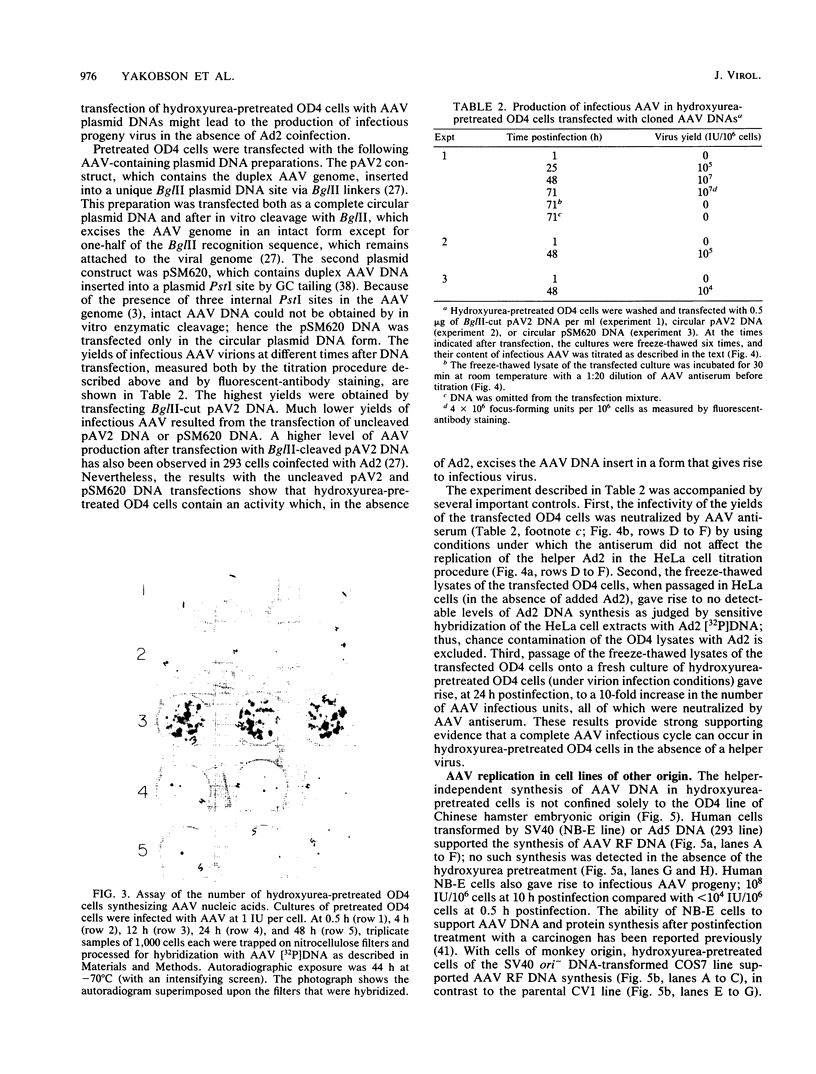
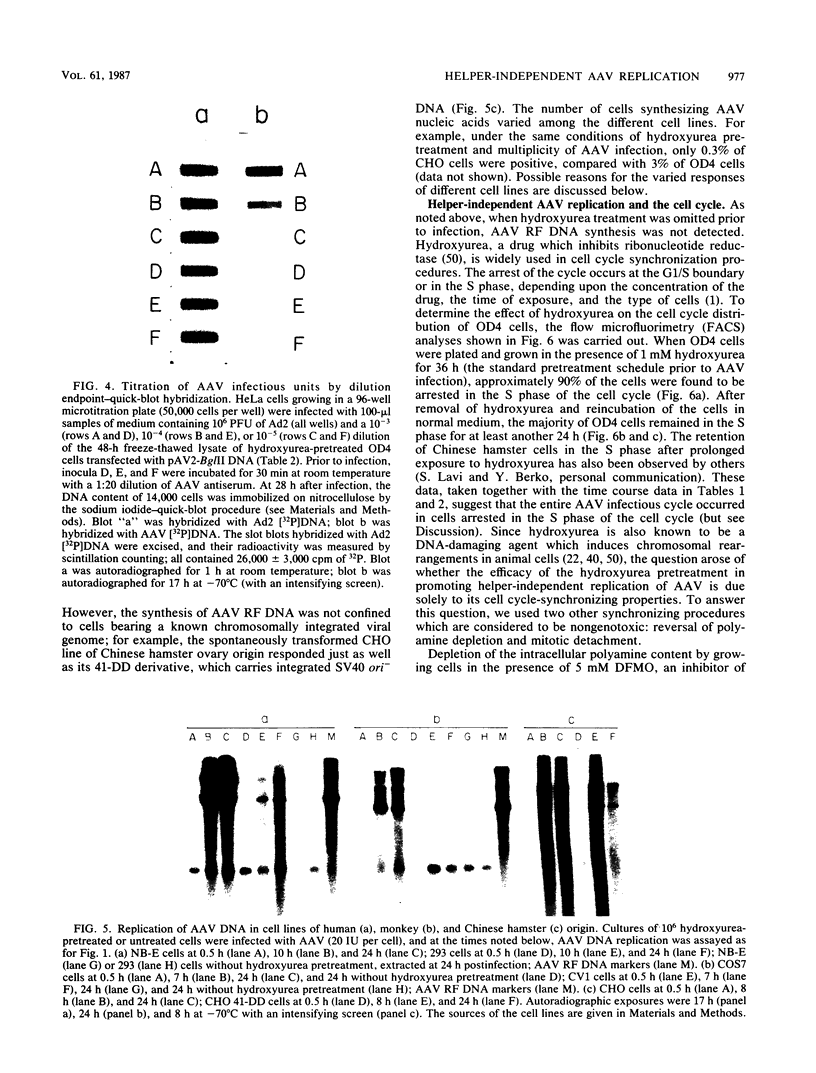
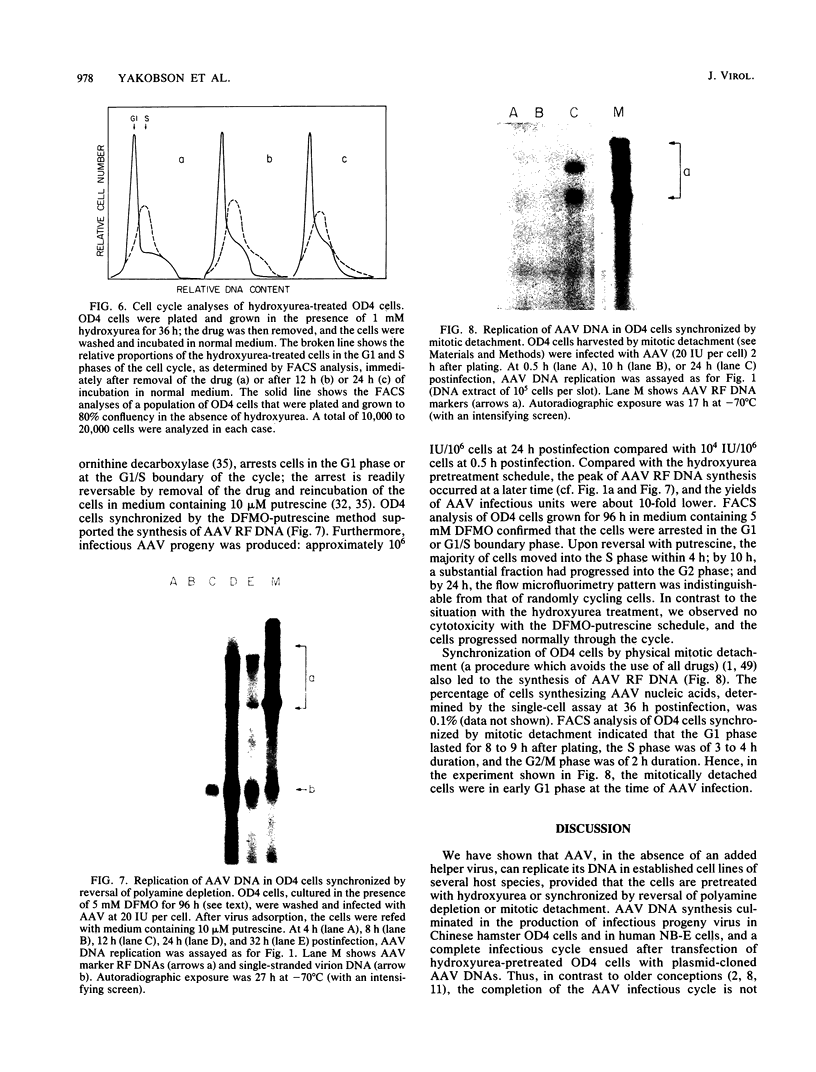



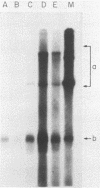
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashihara T., Baserga R. Cell synchronization. Methods Enzymol. 1979;58:248–262. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)58141-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berns K. I., Kort J., Fife K. H., Grogan E. W., Spear I. Study of the fine structure of adeno-associated virus DNA with bacterial restriction endonucleases. J Virol. 1975 Sep;16(3):712–719. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.3.712-719.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berns K. I., Rose J. A. Evidence for a single-stranded adenovirus-associated virus genome: isolation and separation of complementary single strands. J Virol. 1970 Jun;5(6):693–699. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.6.693-699.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bethell D. R., Pegg A. E. Polyamines are needed for the differentiation of 3T3-L1 fibroblasts into adipose cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Sep 16;102(1):272–278. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91517-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresser J., Doering J., Gillespie D. Quick-blot: selective mRNA or DNA immobilization from whole cells. DNA. 1983;2(3):243–254. doi: 10.1089/dna.1983.2.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter B. J., Laughlin C. A., de la Maza L. M., Myers M. Adeno-associated virus autointerference. Virology. 1979 Jan 30;92(2):449–462. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90149-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challberg S. S., Ketner G. Deletion mutants of adenovirus 2: isolation and initial characterization of virus carrying mutations near the right end of the viral genome. Virology. 1981 Oct 15;114(1):196–209. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90265-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorsett D. L., Keshet I., Winocour E. Quantitation of a simian virus 40 nonhomologous recombination pathway. J Virol. 1983 Oct;48(1):218–228. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.1.218-228.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Smiley J., Russell W. C., Nairn R. Characteristics of a human cell line transformed by DNA from human adenovirus type 5. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jul;36(1):59–74. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman Z., Berns K. I., Winocour E. Structure of simian virus 40-adeno-associated virus recombinant genomes. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):457–465. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.457-465.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman Z., Winocour E., Berns K. I. Recombination between simian virus 40 and adeno-associated virus: virion coinfection compared to DNA cotransfection. Virology. 1984 Apr 15;134(1):125–137. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilbronn R., Schlehofer J. R., Yalkinoglu A. O., Zur Hausen H. Selective DNA-amplification induced by carcinogens (initiators): evidence for a role of proteases and DNA polymerase alpha. Int J Cancer. 1985 Jul 15;36(1):85–91. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910360114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilbronn R., Schlehofer J. R., zur Hausen H. Selective killing of carcinogen-treated SV40-transformed Chinese hamster cells by a defective parvovirus. Virology. 1984 Jul 30;136(2):439–441. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90180-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill A. B., Schimke R. T. Increased gene amplification in L5178Y mouse lymphoma cells with hydroxyurea-induced chromosomal aberrations. Cancer Res. 1985 Oct;45(10):5050–5057. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman J. A. New views of the biochemistry of eucaryotic DNA replication revealed by aphidicolin, an unusual inhibitor of DNA polymerase alpha. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):647–648. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90426-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao F. T., Puck T. T. Genetics of somatic mammalian cells, VII. Induction and isolation of nutritional mutants in Chinese hamster cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Aug;60(4):1275–1281. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.4.1275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughlin C. A., Tratschin J. D., Coon H., Carter B. J. Cloning of infectious adeno-associated virus genomes in bacterial plasmids. Gene. 1983 Jul;23(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90217-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavi S. Carcinogen-mediated amplification of viral DNA sequences in simian virus 40-transformed Chinese hamster embryo cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6144–6148. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledinko N., Hopkins S., Toolan H. Relationship between potentiation of H-1 growth by human adenovirus 12 and inhibition of the 'helper' adenovirus by H-1. J Gen Virol. 1969 Jul;5(1):19–31. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-5-1-19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu H. T., Baserga R., Mercer W. E. Adenovirus type 2 activates cell cycle-dependent genes that are a subset of those activated by serum. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):2936–2942. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.2936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mamont P. S., Duchesne M. C., Grove J., Bey P. Anti-proliferative properties of DL-alpha-difluoromethyl ornithine in cultured cells. A consequence of the irreversible inhibition of ornithine decarboxylase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Mar 15;81(1):58–66. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91630-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan J. H., Pagano J. S. Enchancement of the infectivity of simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid with diethylaminoethyl-dextran. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1968 Aug;41(2):351–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Beard P., Engers H. D., Hirt B. Characterization of an immunosuppressive parvovirus related to the minute virus of mice. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):317–326. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.317-326.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pegg A. E., McCann P. P. Polyamine metabolism and function. Am J Physiol. 1982 Nov;243(5):C212–C221. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1982.243.5.C212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson A. T., Stout E. R., Bates R. C. Aphidicolin inhibition of the production of replicative-form DNA during bovine parvovirus infection. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):652–657. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.652-657.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samulski R. J., Berns K. I., Tan M., Muzyczka N. Cloning of adeno-associated virus into pBR322: rescue of intact virus from the recombinant plasmid in human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):2077–2081. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.2077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samulski R. J., Srivastava A., Berns K. I., Muzyczka N. Rescue of adeno-associated virus from recombinant plasmids: gene correction within the terminal repeats of AAV. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):135–143. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90342-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimke R. T., Sherwood S. W., Hill A. B., Johnston R. N. Overreplication and recombination of DNA in higher eukaryotes: potential consequences and biological implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2157–2161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlehofer J. R., Ehrbar M., zur Hausen H. Vaccinia virus, herpes simplex virus, and carcinogens induce DNA amplification in a human cell line and support replication of a helpervirus dependent parvovirus. Virology. 1986 Jul 15;152(1):110–117. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90376-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlehofer J. R., Heilbronn R., Georg-Fries B., zur Hausen H. Inhibition of initiator-induced SV40 gene amplification in SV40-transformed Chinese hamster cells by infection with a defective parvovirus. Int J Cancer. 1983 Nov 15;32(5):591–595. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910320512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. R., Westphal K. H., Rigby P. W. Activation of mouse genes in transformed cells. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):557–567. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90388-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senapathy P., Tratschin J. D., Carter B. J. Replication of adeno-associated virus DNA. Complementation of naturally occurring rep- mutants by a wild-type genome or an ori- mutant and correction of terminal palindrome deletions. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 15;179(1):1–20. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90303-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegl G., Bates R. C., Berns K. I., Carter B. J., Kelly D. C., Kurstak E., Tattersall P. Characteristics and taxonomy of Parvoviridae. Intervirology. 1985;23(2):61–73. doi: 10.1159/000149587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegl G., Gautschi M. The multiplication of parvovirus Lu3 in a synchronized culture system. I. Optimum conditions for virus replication. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1973;40(1):105–118. doi: 10.1007/BF01242642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERASIMA T., TOLMACH L. J. Growth and nucleic acid synthesis in synchronously dividing populations of HeLa cells. Exp Cell Res. 1963 Apr;30:344–362. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(63)90306-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timson J. Hydroxyurea. Mutat Res. 1975;32(2):115–132. doi: 10.1016/0165-1110(75)90002-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. F. Enhancement of adenovirus plaque formation on HeLa cells by magnesium chloride. J Gen Virol. 1970 Dec;9(3):251–255. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-9-3-251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winocour E., Keshet I. Indiscriminate recombination in simian virus 40-infected monkey cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4861–4865. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]