Abstract
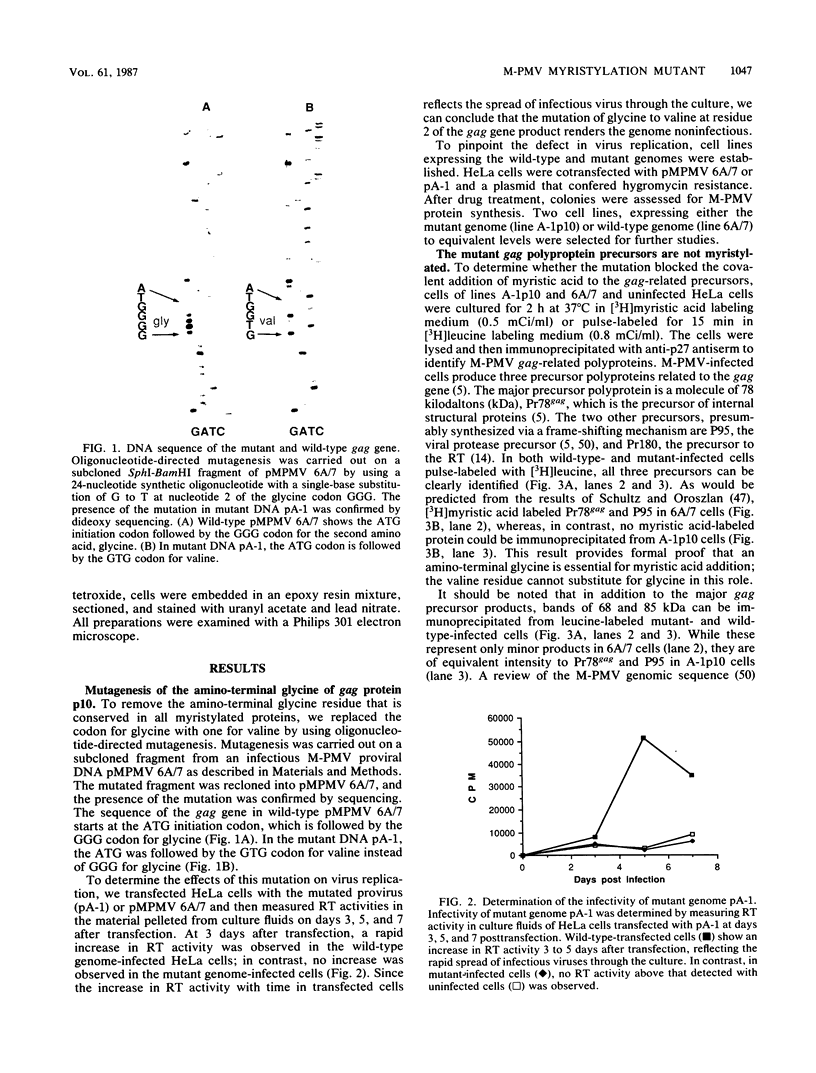
The role of myristylation, a fatty acid modification of nascent polypeptides, in the assembly and intracellular transport of D-type retroviral capsids was investigated through the use of oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Myristic acid is normally esterified through an amide linkage to a glycine residue at the amino terminus of the Mason-Pfizer monkey virus gag gene products. Mutant pA-1, which has a codon for valine substituted for that of the normally myristylated glycine, is completely noninfectious. While the mutant gag polyprotein precursors are synthesized at normal levels, they are not myristylated and are not cleaved to the mature virion proteins. No extracellular virus particles are released from mutant pA-1-infected cells, but intracytoplasmic A-type particles (capsids) accumulate in the cytoplasm. Since none of the intracellular capsids can be found associated with the plasma membrane, these results strongly suggest that myristylation is a critical signal for intracytoplasmic transport of completed viral capsids to their normal site of budding and release.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aitken A., Cohen P., Santikarn S., Williams D. H., Calder A. G., Smith A., Klee C. B. Identification of the NH2-terminal blocking group of calcineurin B as myristic acid. FEBS Lett. 1982 Dec 27;150(2):314–318. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80759-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker C. S., Wills J. W., Bradac J. A., Hunter E. Molecular cloning of the Mason-Pfizer monkey virus genome: characterization and cloning of subgenomic fragments. Virology. 1985 Apr 30;142(2):223–240. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90331-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Dobberstein B. Transfer of proteins across membranes. I. Presence of proteolytically processed and unprocessed nascent immunoglobulin light chains on membrane-bound ribosomes of murine myeloma. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):835–851. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G. Intracellular protein topogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1496–1500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradac J. A., Hunter E. Polypeptides of Mason-Pfizer monkey virus. III. Translational order of proteins on the gag and env gene specified precursor polypeptides. Virology. 1986 Apr 30;150(2):503–508. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90314-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradac J., Hunter E. Polypeptides of Mason-Pfizer monkey virus. I. Synthesis and processing of the gag-gene products. Virology. 1984 Oct 30;138(2):260–275. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90350-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradac J., Hunter E. Polypeptides of Mason-Pfizer monkey virus. II. Synthesis and processing of the env gene products. Virology. 1986 Apr 30;150(2):491–502. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90313-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J., Yonemoto W., Darrow D. Interaction between the Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein and two cellular phosphoproteins: analysis of the turnover and distribution of this complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jan;3(1):9–19. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buss J. E., Kamps M. P., Gould K., Sefton B. M. The absence of myristic acid decreases membrane binding of p60src but does not affect tyrosine protein kinase activity. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):468–474. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.468-474.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buss J. E., Kamps M. P., Sefton B. M. Myristic acid is attached to the transforming protein of Rous sarcoma virus during or immediately after synthesis and is present in both soluble and membrane-bound forms of the protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2697–2704. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buss J. E., Sefton B. M. Myristic acid, a rare fatty acid, is the lipid attached to the transforming protein of Rous sarcoma virus and its cellular homolog. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):7–12. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.7-12.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr S. A., Biemann K., Shoji S., Parmelee D. C., Titani K. n-Tetradecanoyl is the NH2-terminal blocking group of the catalytic subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase from bovine cardiac muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6128–6131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee S., Bradac J. A., Hunter E. Effect of monensin on Mason-Pfizer monkey virus glycoprotein synthesis. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):1003–1012. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.1003-1012.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee S., Bradac J., Hunter E. A rapid screening procedure for the isolation of nonconditional replication mutants of Mason-Pfizer monkey virus: identification of a mutant defective in pol. Virology. 1985 Feb;141(1):65–76. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90183-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee S., Hunter E. The characterization of Mason-Pfizer monkey virus-induced cell fusion. Virology. 1979 Jun;95(2):421–433. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90497-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee S., Hunter E., Whitley R. Effect of cloned human interferons on protein synthesis and morphogenesis of herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):419–425. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.419-425.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra H. C., Mason M. M. A new virus in a spontaneous mammary tumor of a rhesus monkey. Cancer Res. 1970 Aug;30(8):2081–2086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compans R. W., Holmes K. V., Dales S., Choppin P. W. An electron microscopic study of moderate and virulent virus-cell interactions of the parainfluenza virus SV5. Virology. 1966 Nov;30(3):411–426. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90119-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A., Bishop J. M. Transit of pp60v-src to the plasma membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7117–7121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford S., Goff S. P. A deletion mutation in the 5' part of the pol gene of Moloney murine leukemia virus blocks proteolytic processing of the gag and pol polyproteins. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):899–907. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.899-907.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R., Garber E. A., Pellman D., Hanafusa H. A short sequence in the p60src N terminus is required for p60src myristylation and membrane association and for cell transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1834–1842. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine D. L., Landon J. C., Pienta R. J., Kubicek M. T., Valerio M. G., Loeb W. F., Chopra H. C. Responses of infant rhesus monkeys to inoculation with Mason-Pfizer monkey virus materials. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Mar;54(3):651–658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber E. A., Cross F. R., Hanafusa H. Processing of p60v-src to its myristylated membrane-bound form. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2781–2788. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber E. A., Krueger J. G., Hanafusa H., Goldberg A. R. Only membrane-associated RSV src proteins have amino-terminally bound lipid. Nature. 1983 Mar 10;302(5904):161–163. doi: 10.1038/302161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hase T., Müller U., Riezman H., Schatz G. A 70-kd protein of the yeast mitochondrial outer membrane is targeted and anchored via its extreme amino terminus. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3157–3164. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02274.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson L. E., Krutzsch H. C., Oroszlan S. Myristyl amino-terminal acylation of murine retrovirus proteins: an unusual post-translational proteins modification. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):339–343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson L. E., Sowder R., Smythers G., Benveniste R. E., Oroszlan S. Purification and N-terminal amino acid sequence comparisons of structural proteins from retrovirus-D/Washington and Mason-Pfizer monkey virus. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):778–787. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.778-787.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. C., Smiley J. R. Intracellular transport of herpes simplex virus gD occurs more rapidly in uninfected cells than in infected cells. J Virol. 1985 Jun;54(3):682–689. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.3.682-689.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Richardson W. D., Markham A. F., Smith A. E. Sequence requirements for nuclear location of simian virus 40 large-T antigen. Nature. 1984 Sep 6;311(5981):33–38. doi: 10.1038/311033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Roberts B. L., Richardson W. D., Smith A. E. A short amino acid sequence able to specify nuclear location. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):499–509. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90457-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Buss J. E., Sefton B. M. Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein lacking myristic acid phosphorylates known polypeptide substrates without inducing transformation. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):105–112. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90542-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramarsky B., Sarkar N. H., Moore D. H. Ultrastructural comparison of a virus from a Rhesus-monkey mammary carcinoma with four oncogenic RNA viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jul;68(7):1603–1607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.7.1603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning J. S., Hackett A. J. Morphological and biophysical properties of the Mason-Pfizer monkey virus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 Feb;48(2):417–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozols J., Carr S. A., Strittmatter P. Identification of the NH2-terminal blocking group of NADH-cytochrome b5 reductase as myristic acid and the complete amino acid sequence of the membrane-binding domain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13349–13354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palade G. Intracellular aspects of the process of protein synthesis. Science. 1975 Aug 1;189(4200):347–358. doi: 10.1126/science.1096303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellman D., Garber E. A., Cross F. R., Hanafusa H. An N-terminal peptide from p60src can direct myristylation and plasma membrane localization when fused to heterologous proteins. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):374–377. doi: 10.1038/314374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellman D., Garber E. A., Cross F. R., Hanafusa H. Fine structural mapping of a critical NH2-terminal region of p60src. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1623–1627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabatini D. D., Kreibich G., Morimoto T., Adesnik M. Mechanisms for the incorporation of proteins in membranes and organelles. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;92(1):1–22. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks T. L., Devare S. G., Blennerhassett G. T., Stephenson J. R. Nonconditional replication mutants of type C and type D retroviruses defective in gag gene-coded polyprotein post-translational processing. Virology. 1978 Dec;91(2):352–363. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90383-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. F., Bracha M., Schlesinger M. J. Evidence for covalent attachment of fatty acids to Sindbis virus glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1687–1691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. F., Schlesinger M. J. Fatty acid binding to vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein: a new type of post-translational modification of the viral glycoprotein. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):813–819. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90321-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier P. H., Seftor E. A., Schell J., Bohnert H. J. The use of nuclear-encoded sequences to direct the light-regulated synthesis and transport of a foreign protein into plant chloroplasts. EMBO J. 1985 Jan;4(1):25–32. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02312.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz A. M., Henderson L. E., Oroszlan S., Garber E. A., Hanafusa H. Amino terminal myristylation of the protein kinase p60src, a retroviral transforming protein. Science. 1985 Jan 25;227(4685):427–429. doi: 10.1126/science.3917576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz A. M., Oroszlan S. In vivo modification of retroviral gag gene-encoded polyproteins by myristic acid. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):355–361. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.355-361.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz A., Oroszlan S. Myristylation of gag-onc fusion proteins in mammalian transforming retroviruses. Virology. 1984 Mar;133(2):431–437. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90409-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. H. Evidence for a precursor-product relationship between intracytoplasmic A particles and mouse mammary tumour virus cores. J Gen Virol. 1978 Oct;41(1):193–200. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-41-1-193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonigo P., Barker C., Hunter E., Wain-Hobson S. Nucleotide sequence of Mason-Pfizer monkey virus: an immunosuppressive D-type retrovirus. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):375–385. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90323-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., Wilkie N. M. An improved technique for obtaining enhanced infectivity with herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA. J Gen Virol. 1976 Dec;33(3):447–458. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-33-3-447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeya T., Hanafusa H. DNA sequence of the viral and cellular src gene of chickens. II. Comparison of the src genes of two strains of avian sarcoma virus and of the cellular homolog. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):12–18. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.12-18.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Doren K., Hanahan D., Gluzman Y. Infection of eucaryotic cells by helper-independent recombinant adenoviruses: early region 1 is not obligatory for integration of viral DNA. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):606–614. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.606-614.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt V. M., Bruckenstein D. A., Bell A. P. Avian sarcoma virus gag precursor polypeptide is not processed in mammalian cells. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):725–730. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.725-730.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voronova A. F., Buss J. E., Patschinsky T., Hunter T., Sefton B. M. Characterization of the protein apparently responsible for the elevated tyrosine protein kinase activity in LSTRA cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2705–2713. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis: a simple method using two oligonucleotide primers and a single-stranded DNA template. DNA. 1984 Dec;3(6):479–488. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1984.3.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]








