Abstract
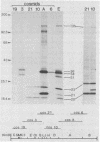
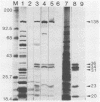
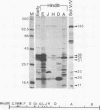
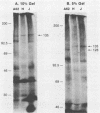
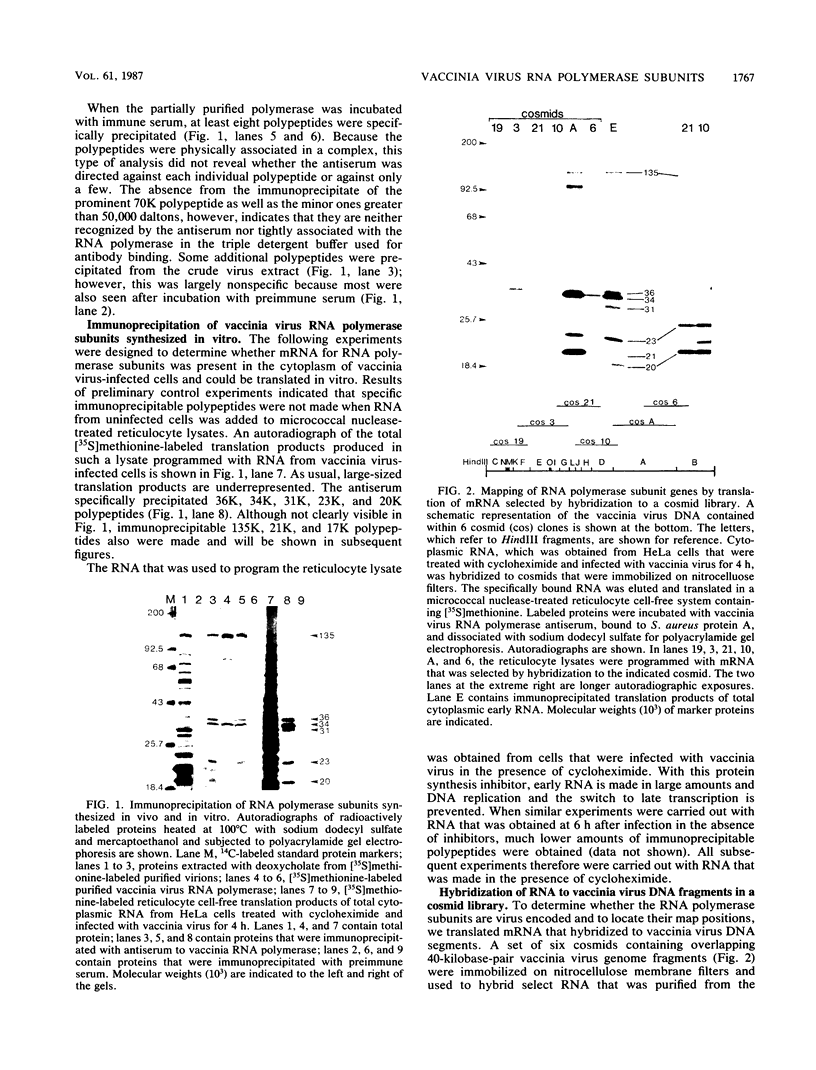
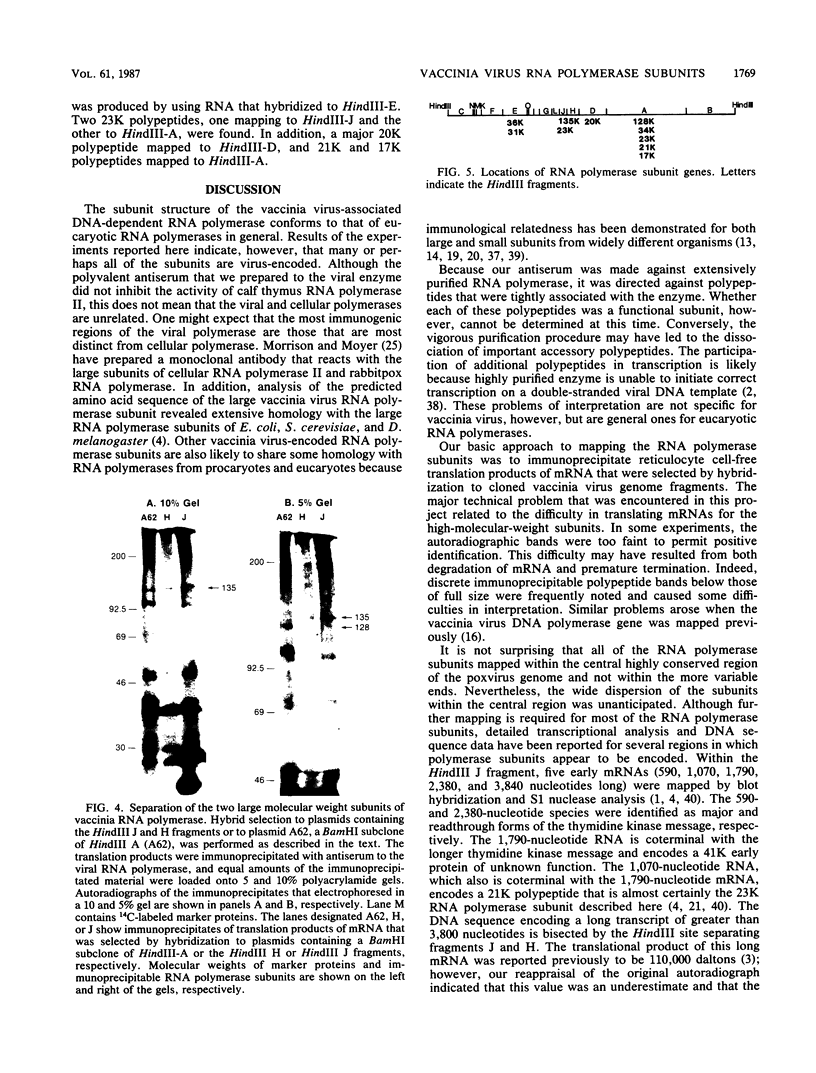
Antiserum to a multisubunit DNA-dependent RNA polymerase from vaccinia virions was prepared to carry out genetic studies. This antiserum selectively inhibited the activity of the viral polymerase but had no effect on calf thymus RNA polymerase II. The specificity of the antiserum was further demonstrated by immunoprecipitation of RNA polymerase subunits from dissociated virus particles. The presence in vaccinia virus-infected cells of mRNA that encodes the polymerase subunits was determined by in vitro translation. Immunoprecipitable polypeptides with Mrs of about 135,000, 128,000, 36,000, 34,000, 31,000, 23,000, 21,000, 20,000, and 17,000 were made when early mRNA was added to reticulocyte extracts. The subunits were encoded within the vaccinia virus genome, as demonstrated by translation of early mRNA that hybridized to vaccinia virus DNA. The locations of the subunit genes were determined initially by hybridization of RNA to a series of overlapping 40-kilobase-pair DNA fragments that were cloned in a cosmid vector. Further mapping was achieved with cloned HindIII restriction fragments. Results of these studies indicated that RNA polymerase subunit genes are transcribed early in infection and are distributed within the highly conserved central portion of the poxvirus genome in HindIII fragments E, J, H, D, and A.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bajszár G., Wittek R., Weir J. P., Moss B. Vaccinia virus thymidine kinase and neighboring genes: mRNAs and polypeptides of wild-type virus and putative nonsense mutants. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):62–72. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.62-72.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baroudy B. M., Moss B. Purification and characterization of a DNA-dependent RNA polymerase from vaccinia virions. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):4372–4380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broyles S. S., Moss B. Homology between RNA polymerases of poxviruses, prokaryotes, and eukaryotes: nucleotide sequence and transcriptional analysis of vaccinia virus genes encoding 147-kDa and 22-kDa subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3141–3145. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess R. R., Travers A. A., Dunn J. J., Bautz E. K. Factor stimulating transcription by RNA polymerase. Nature. 1969 Jan 4;221(5175):43–46. doi: 10.1038/221043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambon P. Eukaryotic nuclear RNA polymerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:613–638. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.003145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Moss B. In vitro translation of immediate early, early, and late classes of RNA from vaccinia virus-infected cells. Virology. 1979 Jul 30;96(2):368–380. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Moss B. Transcription of vaccinia virus mRNA coupled to translation in vitro. Virology. 1978 Jul 1;88(1):149–165. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90118-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dezélée S., Sentenac A. Role of DNA-RNA hybrids in eukaryotes. Purification and properties of yeast RNA polymerase B. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Apr 2;34(1):41–52. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02726.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foglesong P. D. In vitro transcription of a cloned vaccinia virus gene by a soluble extract prepared from vaccinia virus-infected HeLa cells. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):822–826. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.822-826.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golini F., Kates J. R. A soluble transcription system derived from purified vaccinia virions. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):205–213. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.205-213.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenleaf A. L., Bautz E. K. RNA polymerase B from Drosophila melanogaster larvae. Purification and partial characterization. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Dec 1;60(1):169–179. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb20989.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet J., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. Spot-immunodetection of conserved determinants in eukaryotic RNA polymerases. Study with antibodies to yeast RNA polymerases subunits. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2613–2618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingles C. J. Antigenic homology of eukaryotic RNA polymerases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Nov 16;55(2):364–371. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91096-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isle H. B., Venkatesan S., Moss B. Cell-free translation of early and late mRNAs selected by hybridization to cloned DNA fragments derived from the left 14 million to 72 million daltons of the vaccinia virus genome. Virology. 1981 Jul 15;112(1):306–317. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90636-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jendrisak J., Guilfoyle T. J. Eukaryotic RNA polymerase: comparative subunit structures, immunological properties, and alpha-amanitin sensitivities of the class II enzymes from higher plants. Biochemistry. 1978 Apr 4;17(7):1322–1327. doi: 10.1021/bi00600a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. V., Moss B. Mapping of the vaccinia virus DNA polymerase gene by marker rescue and cell-free translation of selected RNA. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):72–77. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.72-77.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kates J. R., McAuslan B. R. Poxvirus DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jul;58(1):134–141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.1.134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedinger C., Chambon P. Animal DNA-dependent RNA polymerases. 3. Purification of calf-thymus BI and BII enzymes. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jul 13;28(2):283–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01912.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedinger C., Gissinger F., Chambon P. Animal DNA-dependent RNA polymerases. Molecular structures and immunological properties of calf-thymus enzyme AI and of calf-thymus and rat-liver enzymes B. Eur J Biochem. 1974 May 15;44(2):421–436. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03500.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer A., Bautz E. K. Immunological relatedness of subunits of RNA polymerase II from insects and mammals. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jul;117(3):449–455. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06359.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahr A., Roberts B. E. Organization of six early transcripts synthesized from a vaccinia virus EcoRI DNA fragment. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):497–509. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.497-509.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel J. L., Chambon P. Purification of RNA polymerase B activity from rat liver. FEBS Lett. 1971 Jun 24;15(3):175–180. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80306-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. K., Carter J. K., Moyer R. W. Isolation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies directed against two subunits of rabbit poxvirus-associated, DNA-directed RNA polymerase. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):670–680. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.670-680.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. K., Moyer R. W. Detection of a subunit of cellular Pol II within highly purified preparations of RNA polymerase isolated from rabbit poxvirus virions. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):587–596. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90268-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B. Inhibition of HeLa cell protein synthesis by the vaccinia virion. J Virol. 1968 Oct;2(10):1028–1037. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.10.1028-1037.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munyon W., Paoletti E., Grace J. T., Jr RNA polymerase activity in purified infectious vaccinia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Dec;58(6):2280–2287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.6.2280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R., Joklik W. K. Isolation and properties of the vaccinia virus DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 10;252(19):6930–6938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niles E. G., Condit R. C., Caro P., Davidson K., Matusick L., Seto J. Nucleotide sequence and genetic map of the 16-kb vaccinia virus HindIII D fragment. Virology. 1986 Aug;153(1):96–112. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90011-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puckett C., Moss B. Selective transcription of vaccinia virus genes in template dependent soluble extracts of infected cells. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):441–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90177-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricciardi R. P., Miller J. S., Roberts B. E. Purification and mapping of specific mRNAs by hybridization-selection and cell-free translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4927–4931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder R. G. Multiple forms of deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase in Xenopus laevis. Isolation and partial characterization. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 10;249(1):241–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrmann G., Moss B. Transcription of vaccinia virus early genes by a template-dependent soluble extract of purified virions. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):349–355. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.349-355.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. B., Roeder R. G. Purification and subunit structure of deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase II from the mouse plasmacytoma, MOPC 315. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 10;250(9):3221–3228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sklar V. E., Schwartz L. B., Roeder R. G. Distinct molecular structures of nuclear class I, II, and III DNA-dependent RNA polymerases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):348–352. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer E., Shuman S., Hurwitz J. Purification and properties of vaccinia virus DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 10;255(11):5388–5395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks J. R., Coulter D. E., Greenleaf A. L. Immunological studies of RNA polymerase II using antibodies to subunits of Drosophila and wheat germ enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5884–5892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir J. P., Bajszár G., Moss B. Mapping of the vaccinia virus thymidine kinase gene by marker rescue and by cell-free translation of selected mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1210–1214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]