Abstract
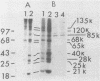
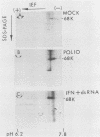
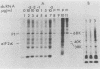
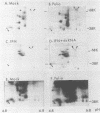
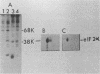
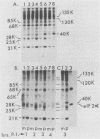
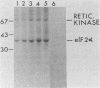
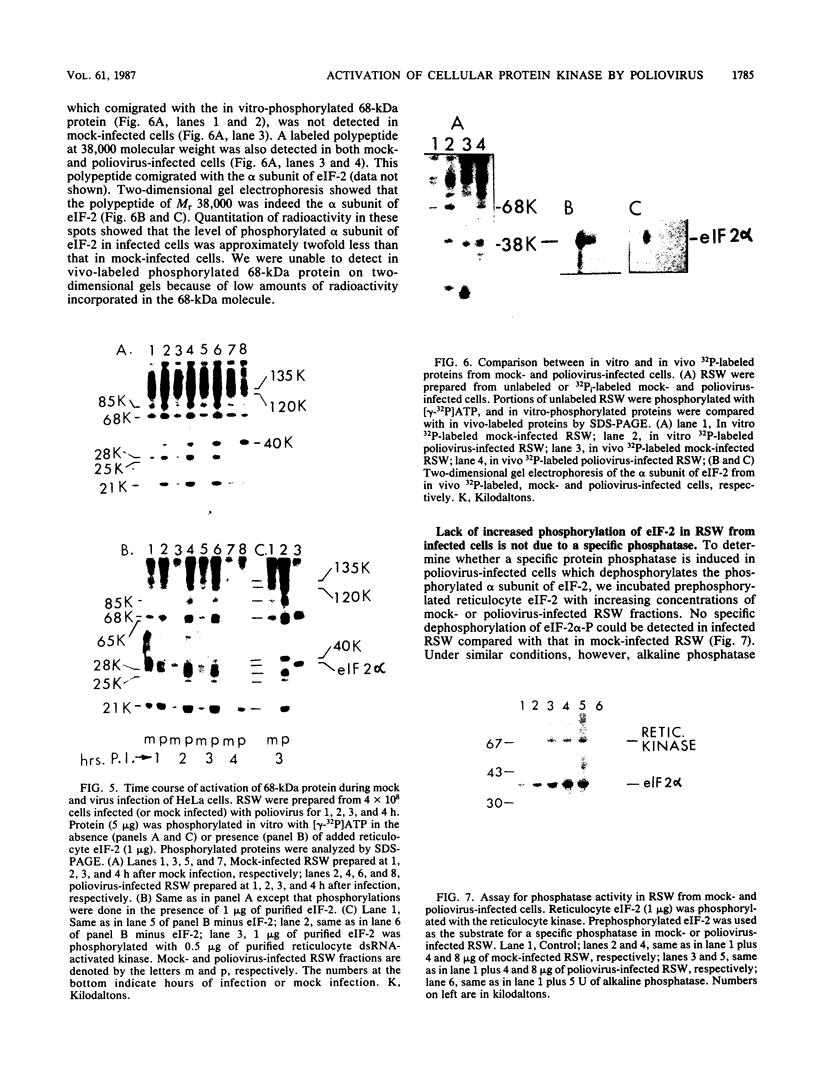
Protein kinase activity in general is stimulated at least 5- to 10-fold in ribosomal salt wash preparations from poliovirus-infected HeLa cells compared with those from mock-infected cells. The stimulation of kinase activity is manifested by increased phosphorylation of ribosome-associated polypeptides having approximate molecular weights of 135,000, 120,000, 85,000, 68,000, 65,000, 40,000, 28,000, 25,000, and 21,000. The Mr 68,000 phosphoprotein is structurally identical to the interferon-induced, double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase (P1) which phosphorylates the alpha subunit of eucaryotic initiation factor-2 (eIF-2). A similar protein of Mr 68,000 is more phosphorylated in poliovirus-infected cells than in mock-infected cells. Increased phosphorylation of P1 protein in poliovirus-infected cells, however, does not result in an increased phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of endogenous or exogenously added eIF-2, both in vitro and in vivo. These results suggest that a mechanism must exist in poliovirus-infected HeLa cells which prevents further phosphorylation of eIF-2 by the activated kinase.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baglioni C. Interferon-induced enzymatic activities and their role in the antriviral state. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):255–264. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90151-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta A., Baron M. H., Baltimore D. Poliovirus replicase: a soluble enzyme able to initiate copying of poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2679–2683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta A. Purification of host factor required for in vitro transcription of poliovirus RNA. Virology. 1983 Jul 15;128(1):245–251. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90335-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta A., Zabel P., Baltimore D. Dependence of the activity of the poliovirus replicase on the host cell protein. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):423–429. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90516-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Benedetti A., Baglioni C. Inhibition of mRNA binding to ribosomes by localized activation of dsRNA-dependent protein kinase. Nature. 1984 Sep 6;311(5981):79–81. doi: 10.1038/311079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKLIN R. M., BALTIMORE D. Patterns of macromolecular synthesis in normal and virus-infected mammalian cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1962;27:175–198. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1962.027.001.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. J., Balkow K., Hunt T., Jackson R. J., Trachsel H. Phosphorylation of initiation factor elF-2 and the control of reticulocyte protein synthesis. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):187–200. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90330-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S. L., Holmes S. L., Mehra L. L. Interferon action against reovirus: activation of interferon-induced protein kinase in mouse L929 cells upon reovirus infection. Virology. 1982 Jul 30;120(2):495–499. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90051-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katze M. G., Detjen B. M., Safer B., Krug R. M. Translational control by influenza virus: suppression of the kinase that phosphorylates the alpha subunit of initiation factor eIF-2 and selective translation of influenza viral mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1741–1750. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimchi A., Zilberstein A., Schmidt A., Shulman L., Revel M. The interferon-induced protein kinase PK-i from mouse L cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9846–9853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent A. G., Krust B., Galabru J., Svab J., Hovanessian A. G. Monoclonal antibodies to an interferon-induced Mr 68,000 protein and their use for the detection of double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase in human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4341–4345. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick W., Penman S. Inhibition of RNA synthesis in HeLa and L cells by Mengovirus. Virology. 1967 Jan;31(1):135–141. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow C. D., Gibbons G. F., Dasgupta A. The host protein required for in vitro replication of poliovirus is a protein kinase that phosphorylates eukaryotic initiation factor-2. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):913–921. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90351-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsen T. W., Maroney P. A., Baglioni C. Inhibition of protein synthesis in reovirus-infected HeLa cells with elevated levels of interferon-induced protein kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14593–14596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichel P. A., Merrick W. C., Siekierka J., Mathews M. B. Regulation of a protein synthesis initiation factor by adenovirus virus-associated RNA. Nature. 1985 Jan 17;313(5999):196–200. doi: 10.1038/313196a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice A. P., Duncan R., Hershey J. W., Kerr I. M. Double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase and 2-5A system are both activated in interferon-treated, encephalomyocarditis virus-infected HeLa cells. J Virol. 1985 Jun;54(3):894–898. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.3.894-898.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice A. P., Kerr I. M. Interferon-mediated, double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase is inhibited in extracts from vaccinia virus-infected cells. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):229–236. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.229-236.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel C. E., Duncan R., Knutson G. S., Hershey J. W. Mechanism of interferon action. Increased phosphorylation of protein synthesis initiation factor eIF-2 alpha in interferon-treated, reovirus-infected mouse L929 fibroblasts in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13451–13457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R. J., Safer B., Munemitsu S. M., Samuel C. E., Shenk T. Adenovirus VAI RNA prevents phosphorylation of the eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha subunit subsequent to infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4321–4325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R. J., Weinberger C., Shenk T. Adenovirus VAI RNA facilitates the initiation of translation in virus-infected cells. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):291–298. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90325-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen G. C., Taira H., Lengyel P. Interferon, double-stranded RNA, and protein phosphorylation. Characteristics of a double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase system partially purified from interferon treated Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 10;253(17):5915–5921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siekierka J., Mariano T. M., Reichel P. A., Mathews M. B. Translational control by adenovirus: lack of virus-associated RNAI during adenovirus infection results in phosphorylation of initiation factor eIF-2 and inhibition of protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):1959–1963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tershak D. R. Protein kinase activity of polysome-ribosome preparations from poliovirus infected cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Jan 13;80(1):283–289. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91134-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker-Dowling P., Youngner J. S. Characterization of a specific kinase inhibitory factor produced by vaccinia virus which inhibits the interferon-induced protein kinase. Virology. 1984 Aug;137(1):171–181. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilberstein A., Kimchi A., Schmidt A., Revel M. Isolation of two interferon-induced translational inhibitors: a protein kinase and an oligo-isoadenylate synthetase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4734–4738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]